Similar presentations:
Assessment. Types of assessment
1.
Assessment:What is assessment?
What for is assessment necessary?
What is the purpose of assessment?
Who are the stakeholders of assessment?
What are the types of assessment?
Assessment
What is criteria-based assessment?
What is criteria?
What is the role of criteria?
Necessity of
introduction
the
criteria-based
assessment
2.
B.G. Ananiev: “Lack of assessment ... is the worst kind of assessment,because this impact is not orienting, but disorienting, stimulating
negatively, affecting depressively to an object as well as forcing people
to develop their own self-esteem relying on highly subjective
interpretations of hints, semi-understandable situations, behavior of a
teacher and learners instead of relying on an objective assessment in
which their actual knowledge is reflected”.
B.G Ananiev (1907-1972) is the Soviet psychologist, founder of the concept of the Faculty of Psychology of Leningrad State University (St. Petersburg State University),
creator of the system model of humanobiology where the central role is given to psychology
3. What is assessment?
• The process of gatheringevidence
• Then use defined criteria to
judge performance based on the
evidence
• Arrive at conclusion on
performance
3
4.
Who is involved in, affected by or interested inassessment? Who are the stakeholders?
Learners
Parents
Schools
School administration
Employers
Governmental decision-makers
Society as a whole
The public’s view of education and learners
Any more ...?
4
5. Types of assessment
Formative• assessment of learners during teaching and
learning
Summative
• assessment of learning
Diagnostic
• measures skills and knowledge to identify strengths
and weaknesses
5
6.
Assessment: What for is assessment necessary?What is criteria-based assessment?
What is the purpose of criteria-based assessment?
What are the types of criteria-based assessment?
7.
The term “criteria-based assessment” was first used by Robert Eugene Glazer (1963)and characterized as the process that helps to determine the correspondence between
reached and planned academic achievements of learners.
Criteria-based assessment excludes comparison and dependence on achievements of
other learners, and aims to inform about the level of competence of each learner.
Glaser, R. 1963. Instructional technology and the measurement of learning outcomes: some questions. The American psychologist. Issue: 8. Vol.18. pp. 519 - 521
8. Criteria-based Assessment
• Assessment, which is measured against general, specific criteria• General, all learners are assessed against the same standards
• Specific, assessment is carried out against established standards
8
9. The purpose of the criteria-based assessment is to obtain objective information on learning achievements of learners on the
basis of assessment criteria, as well as toprovide all stakeholders with this information for further improvement of the learning
process.
Objectives of the criteria-based assessment:
1. To expand provision and functions of assessment in the learning process;
2. To create conditions for constant self-improvement of learners by providing them
regular feedback;
3. To promote development of common standards, qualitative assessment
mechanisms and tools;
4. To provide objective, continuous and reliable information:
- to learners about the quality of their learning;
- to teachers about the learners’ progress;
- to parents about the degree of achievement of learning outcomes by learners;
- to management bodies on the quality of the educational services provided.
9
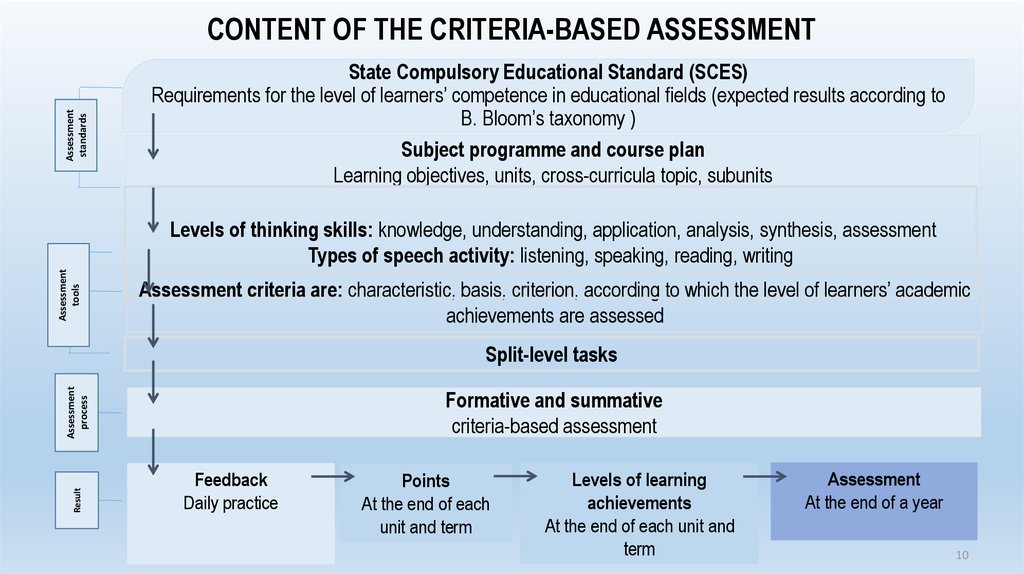
10. State Compulsory Educational Standard (SCES) Requirements for the level of learners’ competence in educational fields (expected
Assessmentstandards
CONTENT OF THE CRITERIA-BASED ASSESSMENT
State Compulsory Educational Standard (SCES)
Requirements for the level of learners’ competence in educational fields (expected results according to
B. Bloom’s taxonomy )
Subject programme and course plan
Learning objectives, units, cross-curricula topic, subunits
Assessment
tools
Levels of thinking skills: knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis, assessment
Types of speech activity: listening, speaking, reading, writing
Assessment criteria are: characteristic, basis, criterion, according to which the level of learners’ academic
achievements are assessed
Result
Assessment
process
Split-level tasks
Formative and summative
criteria-based assessment
Feedback
Daily practice
Points
At the end of each
unit and term
Levels of learning
achievements
At the end of each unit and
term
Assessment
At the end of a year
10
11. Instructive and methodological documents
1) State Compulsory Educational Standard (Primary, Secondary, High);2) Subject programme (by subject);
3) Course plan (by subject);
4) The Procedure of criteria-based assessment of learners’ academic
achievements in the educational organizations, implementing subject
programmes of Primary, Secondary, High School Education;
5) Criteria-based Assessment Primary, Secondary and High School
Level Handbook for Teachers
6) Collection of Tasks for Formative Assessment;
7) Methodical Recommendations for Summative Assessment
11
12. Principles of criteria-based assessment
• What is the relationship between learning andassessment?
• What is good assessment?
• What is the content of good assessment?
• What forms are inherent to criteria-based assessment?
• What affects the assessment success?
• How does criteria-based assessment affect the learning
process?
13. Assessment
• Assessment of learning achievements is the process of establishingthe level of accordance between the learners’ achieved results and
the planned learning objectives for adjusting and managing the
educational process through feedback.
• Criteria-based assessment is the process based on conformity of
learner’s learning achievements with clearly defined, collectively
developed criteria complying with the objectives and content of
education and that are clear to learners, parents and educators.
14. Principles of criteria-based assessment
• Interrelation of learning and assessment. Assessment is an integral part of learning, it isdirectly related to the objectives and expected outcomes of the subject programme.
• Objectivity, reliability and validity. Assessment provides accurate and reliable
information. It ensures the criteria and tools applied provide assessment of learning
objectives and expected outcomes.
• Transparency and accessibility. Assessment provides clear and comprehensible
information, as well as increases the interest of all participants of learning process.
• Continuity. Assessment is a continuous process that enables timely and systematically
monitor the progress of educational achievements of students.
• Focus on development. Assessment determines the direction of development for
educational system, schools, teachers and learners.
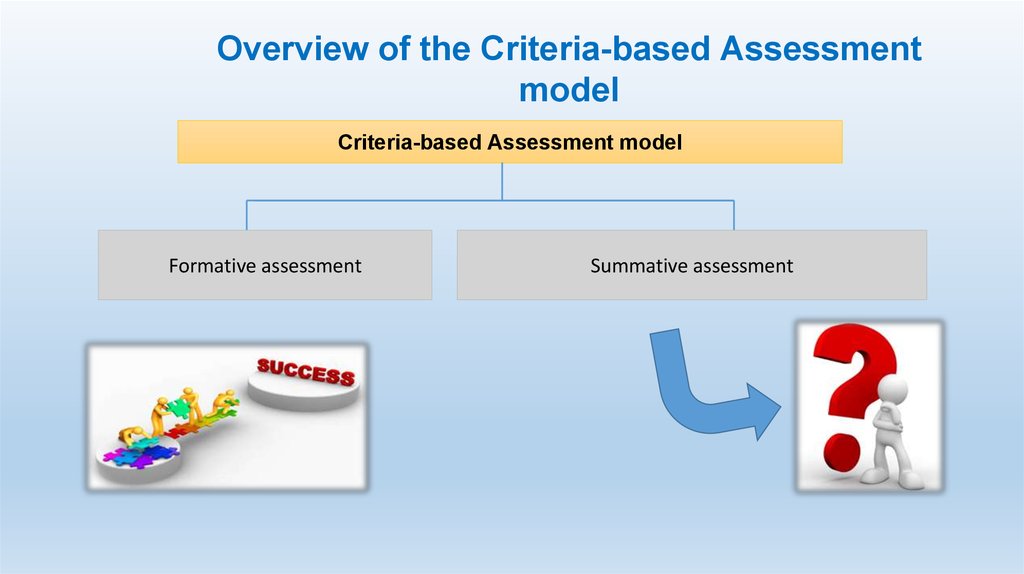
15.
Overview of the Criteria-based Assessmentmodel
Criteria-based Assessment model
Formative
assessment
Summative assessment
16. Formative Assessment
Task: Discuss questions in groups and write down your answerson the flipcharts.
1. What is formative assessment?
2. What are the purposes and principles?
3. When is it carried out?
4. Who is informed?
5. What is the role of a teacher?
6. What is the role of a learner?
7. What are the forms of assessment?
Presentation of groups
17.
Formative assessmentFormative Assessment (FA) - is a type of assessment that provides
feedback between learners and teachers and allows adapting timely the
learning process without scoring and allocating marks.
Principles of FA:
• part of teaching and learning (“assessment for learning”);
• covers all learning objectives (the learning objectives for all grades are
shown in the course plans for subjects);
• assessment is not indicated;
• achievement of learning objectives is determined in accordance with
assessment criteria;
• feedback is provided on the progress of each learner;
• FA results are used to improve the quality of education, subject
programme.
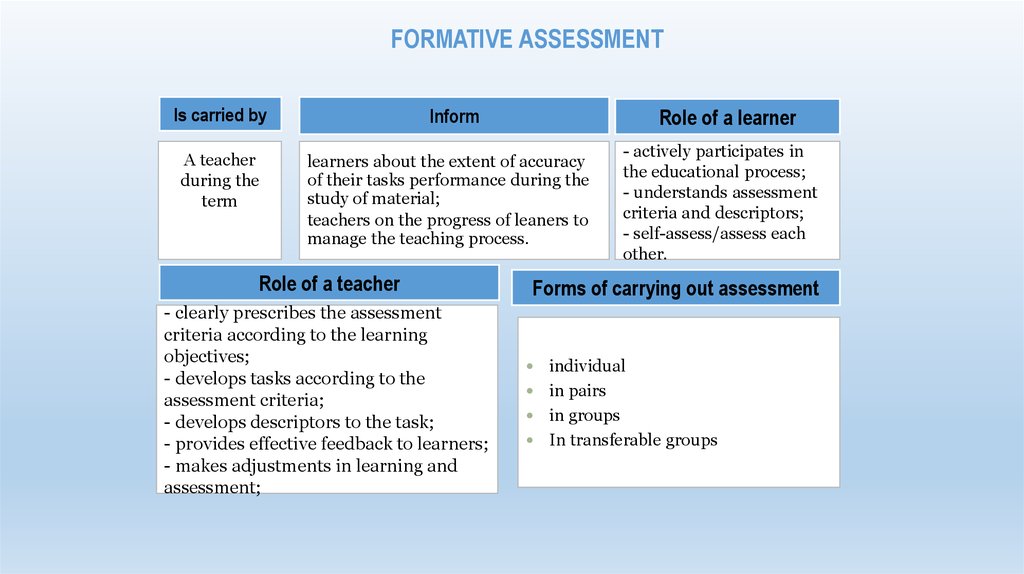
18. Formative assessment
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENTIs carried by
A teacher
during the
term
Role of a learner
Inform
learners about the extent of accuracy
of their tasks performance during the
study of material;
teachers on the progress of leaners to
manage the teaching process.
Role of a teacher
- clearly prescribes the assessment
criteria according to the learning
objectives;
- develops tasks according to the
assessment criteria;
- develops descriptors to the task;
- provides effective feedback to learners;
- makes adjustments in learning and
assessment;
- actively participates in
the educational process;
- understands assessment
criteria and descriptors;
- self-assess/assess each
other.
.
Forms of carrying out assessment
individual
in pairs
in groups
In transferable groups
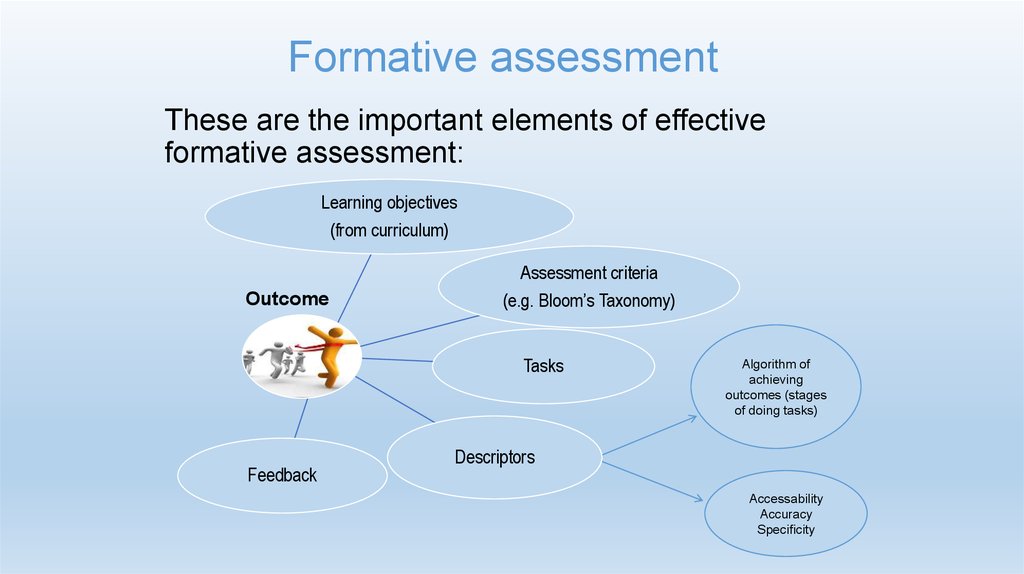
19. Formative assessment
These are the important elements of effectiveformative assessment:
Learning objectives
(from curriculum)
Outcome
Assessment criteria
(e.g. Bloom’s Taxonomy)
Tasks
Feedback
Algorithm of
achieving
outcomes (stages
of doing tasks)
Descriptors
Accessability
Accuracy
Specificity
20. THE FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT PROCESS
State Compulsory Educational StandardExpected results in subject fields
Units/cross-curricula topics – subunits –
learning objectives
Subject programmes
Functions
Levels of thinking skills: KNOWLEDGE, UNDERSTANDING, APPLICATION, ANALYSIS, SYNTHESIS, ASSESSMENT
Types of speech activity: LISTENING, SPEAKING, READING, WRITING
Formative –
lies in establishment, formation and
practice of the system of values
Methods
Objectives
To form self-assessment skills of learners
“Traffic light”
To give time for a learner to think over
instead of answering the question instantly
Portfolio, journals and columns
Quiz/questionnaire
Concept maps
Assessment criteria
Levels of learning achievements
Formative assessment practice
Stimulating
– lies in creation of favorable conditions for
effective promotion of a learner for achieving
desired result
To provide regular
To motivate a
feedback for learners
learner for further
object-oriented
learning
Hand signals
Card index for communication
One-minute essay
Speech samples
Examination of inaccuracy in understanding
Three-minute pause
Daily practice of a teacher
Motivating
– lies in motivation of learners to learn and
achieve results
To provide information:
- To learners about the quality of their education;
- To teachers about the learners’ progress;
- To parents about the degree of achievement of
learning outcomes by learners;
Temperature measurements
Mini-test
Summary in one sentence
Self-assessment
Two stars and a wish
Verbal score and many other things
21. Formative assessment: Daily practice of a teacher
Planning and organizing formative assessment;Selecting formative assessment methods;
Analyzing formative assessment results;
Providing feedback on the results of formative
assessment.
21
22. Formative assessment
Task:It is necessary to carry out a formative assessment depending on the
following learning objectives from the subject programme for English
(Grade 5):
5.S7 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a
limited range of general topics.
5.C4 Evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from other.
5.C7 Develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing.
1) Identify the levels of thinking skills
2) Define assessment criteria
3) Preparation of tasks
4) Define assessment criteria and prepare a task according to them, draw up
descriptors.
22
Resource: pictures
23. Formative assessment
Learning objectiveLevel of thinking skills
Assessment criteria
Task
5.S7 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics.
5.C4 Evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from other.
5.C7 Develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing.
Application
Higher order thinking skills
Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences;
Analyze given feedback and give constructive answers to feedback;
Make an argument and reason it.
Work in pairs. Look at the pictures. Learner A: Choose a picture. Present your ideas to the class. Evaluate the
feedback and respond to it. Learner B: Give feedback to your classmate on presenting his/her thoughts. Asks
questions to clarify the ideas. Swap the roles.
Assessment criteria
Apply topic related vocabulary in A learner
speech appropriately arranging - works in a pair;
words and phrases into well- talks on the topic;
formed sentences;
- uses topical vocabulary;
Analyze given feedback and give - evaluates partner’s answer;
constructive answers to
- asks questions for clarification;
feedback;
- gives constructive answers to feedback.
Make an argument and reason it.
Descriptors
24. Formative assessment (example)
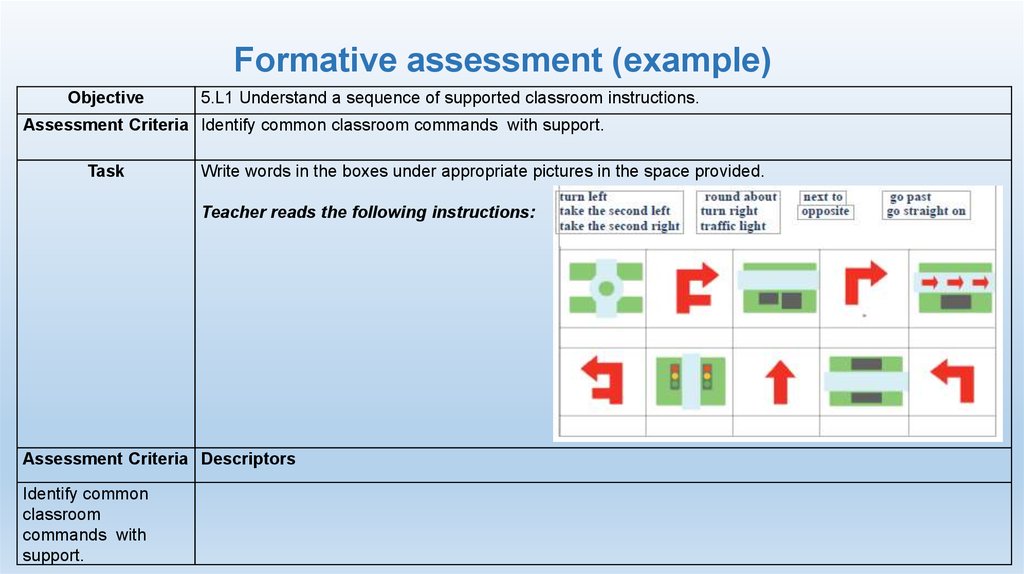
Objective5.L1 Understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions.
Assessment Criteria Identify common classroom commands with support.
Task
Write words in the boxes under appropriate pictures in the space provided.
Teacher reads the following instructions:
Assessment Criteria Descriptors
Identify common
classroom
commands with
support.
25. Formative assessment in English (example)
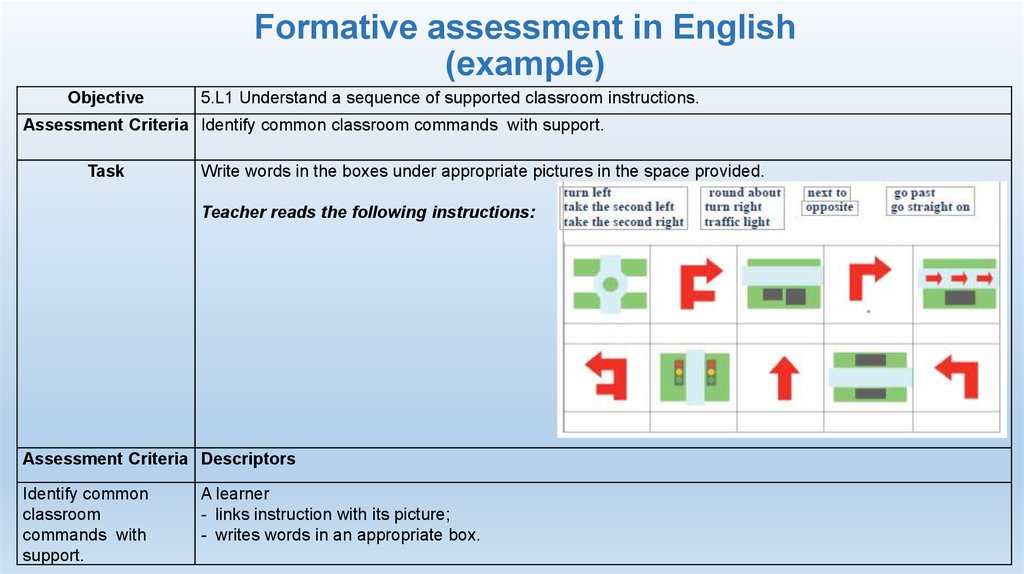
Objective5.L1 Understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions.
Assessment Criteria Identify common classroom commands with support.
Task
Write words in the boxes under appropriate pictures in the space provided.
Teacher reads the following instructions:
Assessment Criteria Descriptors
Identify common
classroom
commands with
support.
A learner
- links instruction with its picture;
- writes words in an appropriate box.
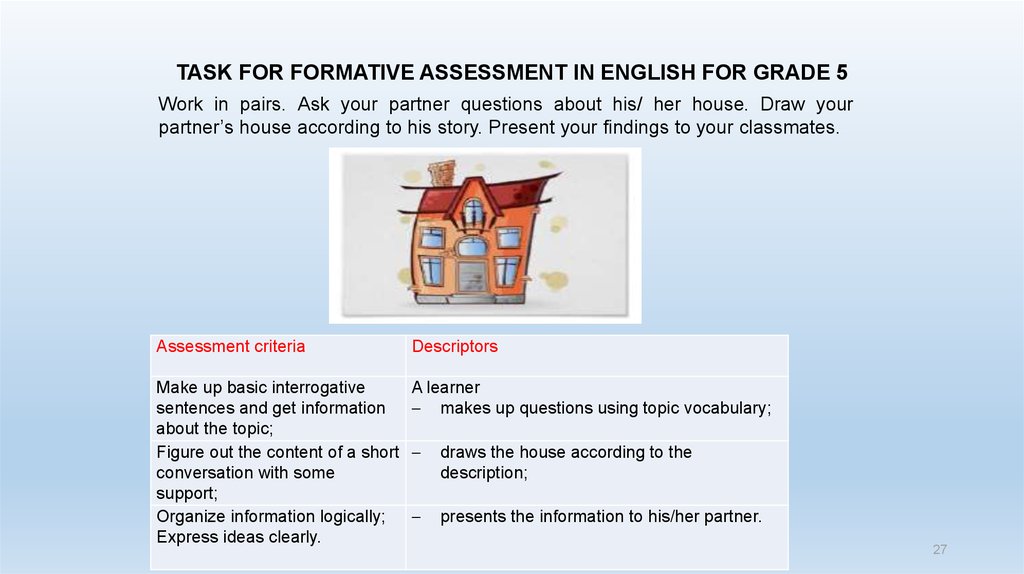
26. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5
Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions about his/ her house. Draw yourpartner’s house according to his story. Present your findings to your classmates.
Assessment criteria
Make up basic interrogative
sentences and get information
about the topic;
Figure out the content of a short
conversation with some
support;
Organize information logically;
Express ideas clearly.
Descriptors
26
27. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5
Work in pairs. Ask your partner questions about his/ her house. Draw yourpartner’s house according to his story. Present your findings to your classmates.
Assessment criteria
Descriptors
Make up basic interrogative
sentences and get information
about the topic;
Figure out the content of a short
conversation with some
support;
Organize information logically;
Express ideas clearly.
A learner
makes up questions using topic vocabulary;
draws the house according to the
description;
presents the information to his/her partner.
27
28. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5
Read the text.Once a deer, a crow, a mouse and a turtle were great friends.
One day the deer went out to graze. He was caught in a hunter net. In the evening the deer did not return to his friends.
The mouse said to the crow, ‘Will you fly over the trees and find the deer? Then fly back to us and tell us where he is.’
The crow flew away. He came back after half an hour. He said, ‘Our friend, the deer is in the hunter’s net.’
‘What shall we do’? said the mouse and the turtle.
‘I will take mouse on my back,’ said the crow. ‘He will bite through the net and set the deer free.’
‘Yes,’ said the mouse. I will do that.’ ‘And I will walk to the deer,’ said the turtle. The crow took the mouse on his back and flew
with him to the deer.
The mouse bit through the net. The deer was free. The turtle got friends were all very happy together.
Tasks to the text
The following statements are wrong. Correct them according to the information in the text.
1. A crow and a mouse were not friends.
2. The deer was caught in a hunter net but he came back to his friends.
3. The crow flew away with the deer.
4. The crow takes the tortoise to his back.
5. At the end only the tortoise was happy.
Assessment criteria
Descriptors
Answer the questions.
What does the story teach us?
28
29. TASK FOR FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT IN ENGLISH FOR GRADE 5
Read the text.Once a deer, a crow, a mouse and a turtle were great friends.
One day the deer went out to graze. He was caught in a hunter net. In the evening the deer did not return to his friends.
The mouse said to the crow, ‘Will you fly over the trees and find the deer? Then fly back to us and tell us where he is.’
The crow flew away. He came back after half an hour. He said, ‘Our friend, the deer is in the hunter’s net.’
‘What shall we do’? said the mouse and the turtle.
‘I will take mouse on my back,’ said the crow. ‘He will bite through the net and set the deer free.’
‘Yes,’ said the mouse. I will do that.’ ‘And I will walk to the deer,’ said the turtle. The crow took the mouse on his back and flew
with him to the deer.
The mouse bit through the net. The deer was free. The turtle got friends were all very happy together.
Tasks to the text
The following statements are wrong. Correct them according to the information in the text.
1. A crow and a mouse were not friends.
2. The deer was caught in a hunter net but he came back to his friends.
3. The crow flew away with the deer.
4. The crow takes the tortoise to his back.
Assessment criteria
Descriptors
5. At the end only the tortoise was happy.
Answer the questions.
What does the story teach us?
Identify the attitude and
opinion of the author.
A learner
- reads the text;
- interprets the information and corrects
sentences;
- recognizes the author’s attitude and
answers the question.
29
30. State Compulsory Educational Standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Requirements for the level of a leaner's performanceBiology
A learner after graduation of a secondary school:
State
Compulsory
Educational
Standard
1) knows the structure, composition and functions of proteins, fats, carbohydrates,
nucleic acids ...;
2) understands the processes occurring during the dark and light phase of
photosynthesis ....;
3) applies schemes and methods for solving the problems of molecular biology and
genetics. ..;
4) analyzes the features of the photosynthesis and chemosynthesis processes...;
5) synthesizes the scheme of gametogenesis in humans; schemes of food chains in
ecosystems;
6) assesses the effect of various factors on the activity of enzymes ....
30
31.
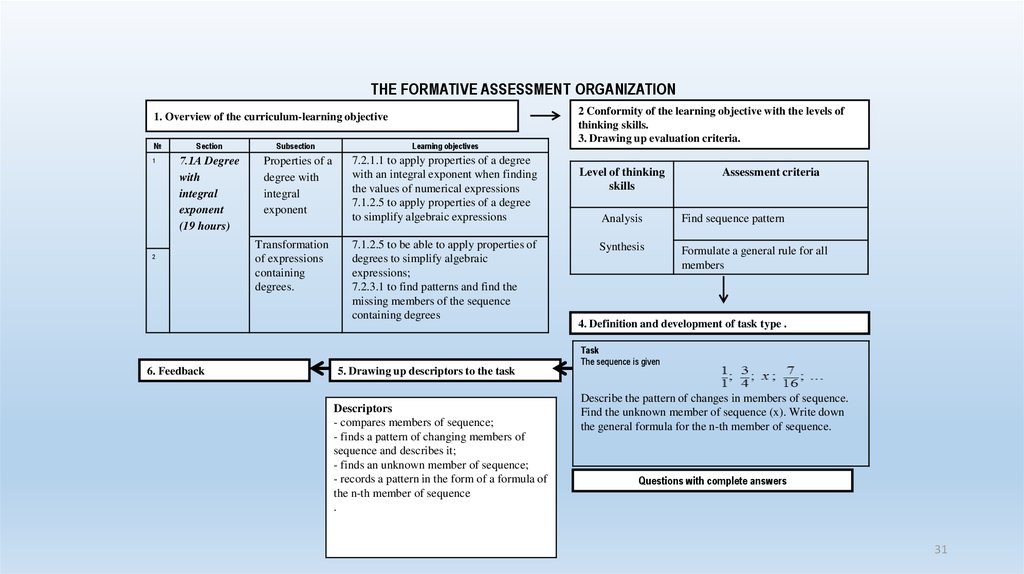
THE FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT ORGANIZATION1. Overview of the curriculum-learning objective
№
1
Section
Subsection
Learning objectives
7.1А Degree
with
integral
exponent
(19 hours)
Properties of a
degree with
integral
exponent
7.2.1.1 to apply properties of a degree
with an integral exponent when finding
the values of numerical expressions
7.1.2.5 to apply properties of a degree
to simplify algebraic expressions
2
6. Feedback
Transformation
of expressions
containing
degrees.
7.1.2.5 to be able to apply properties of
degrees to simplify algebraic
expressions;
7.2.3.1 to find patterns and find the
missing members of the sequence
containing degrees
5. Drawing up descriptors to the task
Descriptors
- compares members of sequence;
- finds a pattern of changing members of
sequence and describes it;
- finds an unknown member of sequence;
- records a pattern in the form of a formula of
the n-th member of sequence
.
2 Conformity of the learning objective with the levels of
thinking skills.
3. Drawing up evaluation criteria.
Level of thinking
skills
Assessment criteria
Analysis
Find sequence pattern
Synthesis
Formulate a general rule for all
members
4. Definition and development of task type .
Task
The sequence is given
Describe the pattern of changes in members of sequence.
Find the unknown member of sequence (x). Write down
the general formula for the n-th member of sequence.
Questions with complete answers
31
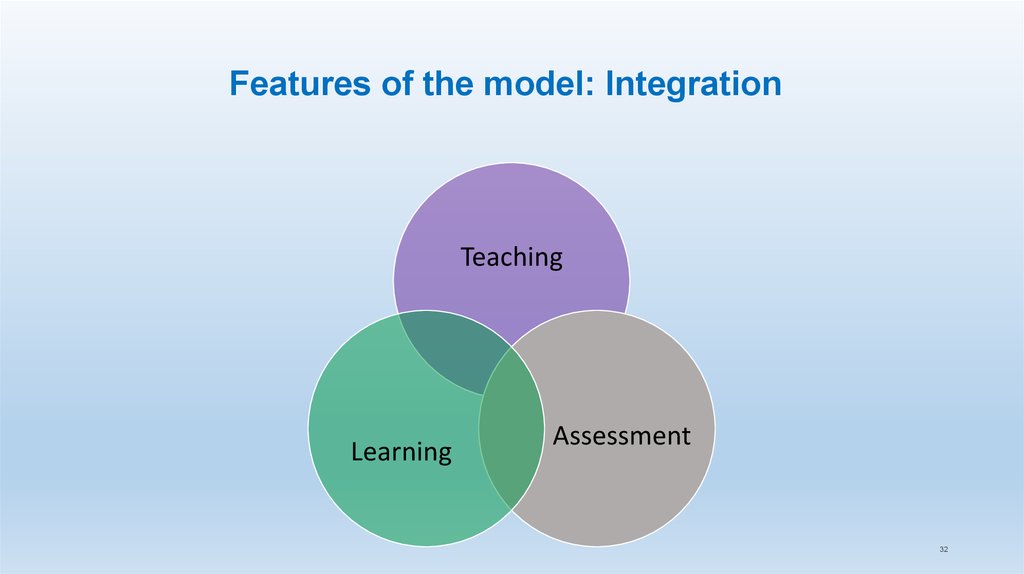
32. Features of the model: Integration
TeachingLearning
Assessment
32
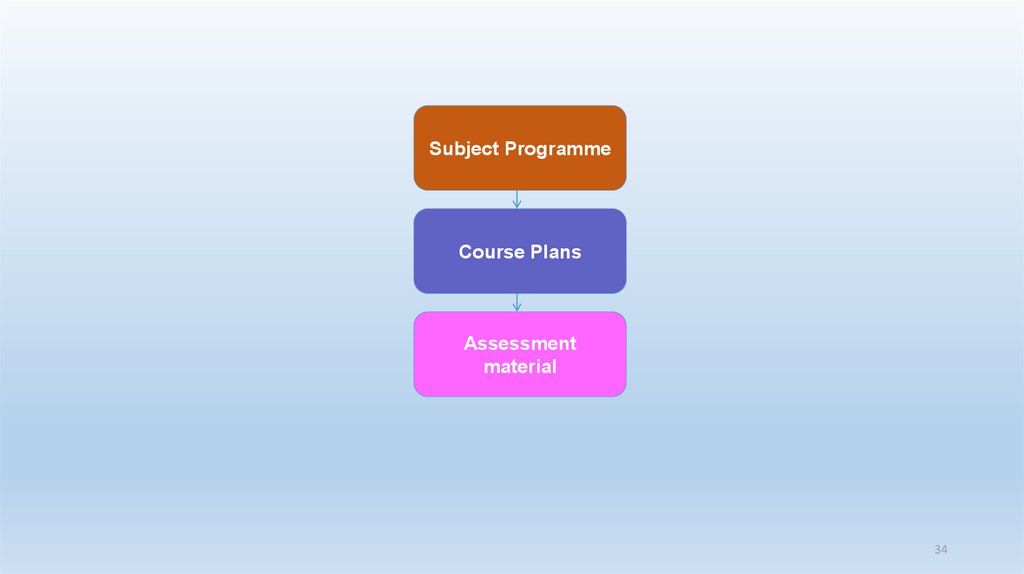
33. The main documents: Subject programme + Course plans + Assessment materials
34.
Subject ProgrammeCourse Plans
33
35.
Subject ProgrammeCourse Plans
Assessment
material
34
36.
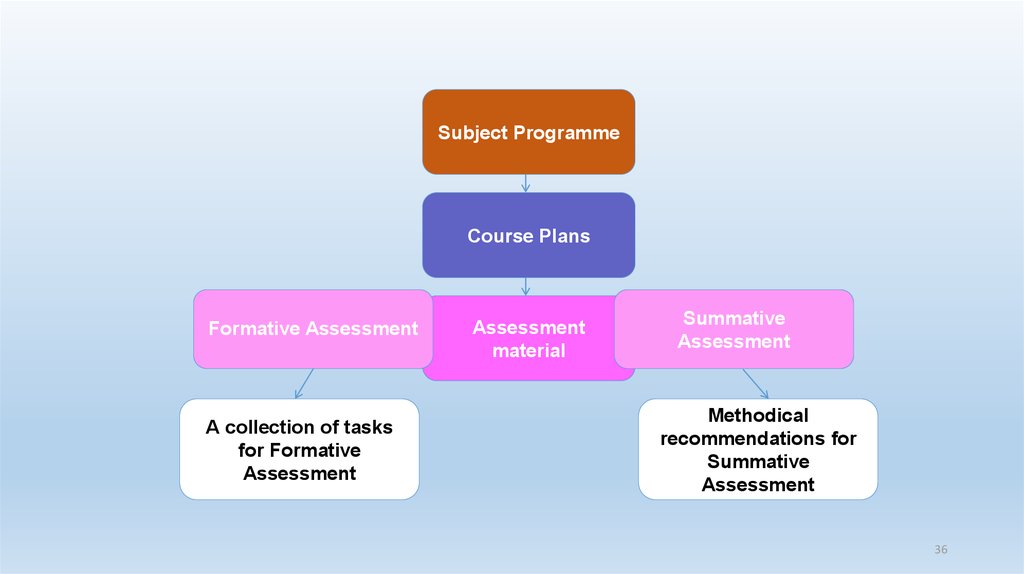
Subject ProgrammeCourse Plans
Formative Assessment
Assessment
material
Summative
Assessment
35
37.
Subject ProgrammeCourse Plans
Formative Assessment
A collection of tasks
for Formative
Assessment
Assessment
material
Summative
Assessment
Methodical
recommendations for
Summative
Assessment
36
38.
Subject ProgrammeCourse Plans
Formative Assessment
A collection of tasks
for Formative
Assessment
Assessment
material
Summative
Assessment
Methodical
recommendations for
Summative
Assessment
37
39. Key skills for the 21st century
• Discuss what skills are relevant fortoday’s learner
• Do you think learning factual knowledge
alone is sufficient?
39
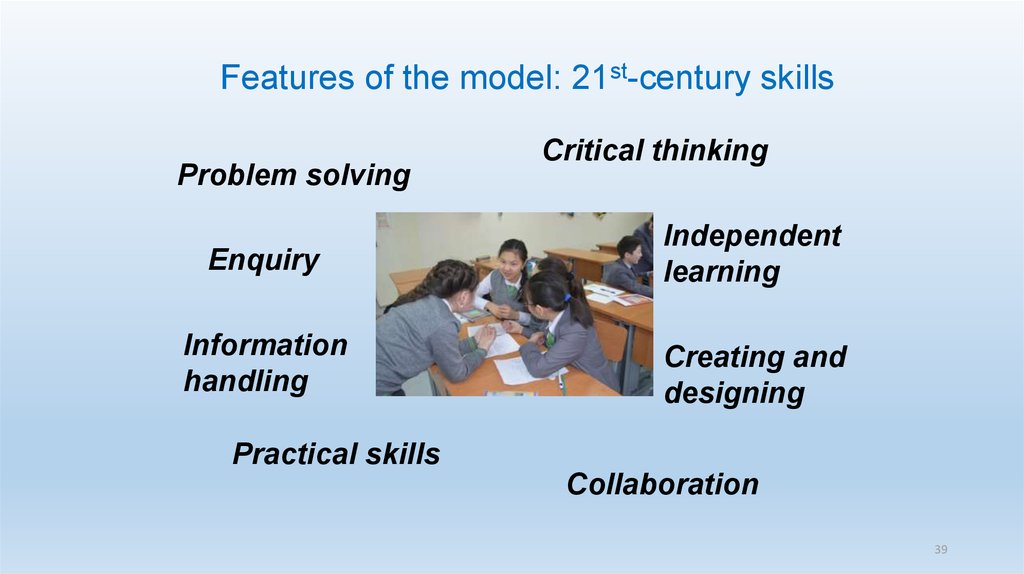
40. Features of the model: 21st-century skills
Problem solvingCritical thinking
Enquiry
Independent
learning
Information
handling
Creating and
designing
Practical skills
Collaboration
39
41. Criterion-referencing
• Norm-referencing: compares a learner’s performance to the rest ofthe group either locally, nationally or internationally
• Criterion-referencing: compares a learner’s performance to a
Learning Outcome or performance standard
• SO criterion-referenced assessment is where an individual’s
performance is compared to a specific Learning Outcome or
performance standard and not to the performance of other learners
41
42.
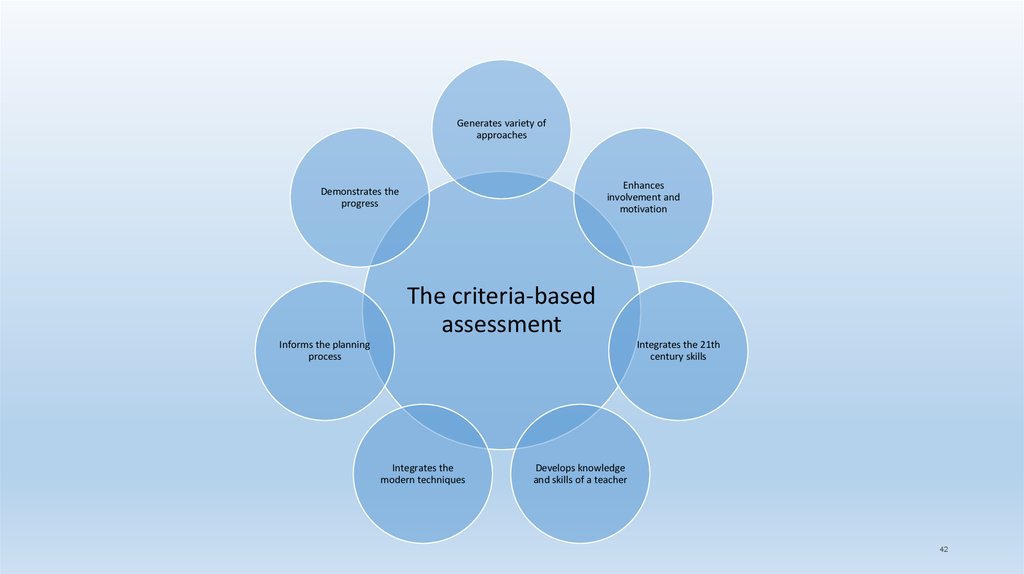
Generates variety ofapproaches
Enhances
involvement and
motivation
Demonstrates the
progress
The criteria-based
assessment
Informs the planning
process
Integrates the 21th
century skills
Integrates the
modern techniques
Develops knowledge
and skills of a teacher
42
43.
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT: PART OF DAILYTEACHING
Learning objectives
(skills and content)
To inform planning
Differentiation
Planning of the learning and
teaching activities
Deciding on when to move
forward
Active learning
Feedback with learners
Syllabus
Did the learners achieve the learning
objectives?
Formative assessment
Collection of tasks for formative assessment
43
44.
‘A criteria-based assessmentmodel compares learners’
achievements with clearly defined,
collectively developed criteria,
which are known to all participants
of the process in advance.’
43
45.
‘Criteria-based assessment is fairerto learners than the traditional
method applied in Kazakhstan.’
44
46.
Overview of the Criteria-based Assessmentmodel
Criteria-based Assessment model
Formative assessment
Summative assessment
47. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
• Type of assessment, which iscarried out after completion of a
certain academic period (term,
trimester, academic year, level of
comprehensive education), as
well as across units / crosscurricular topics of subject
programmes with scoring and
grading.
47
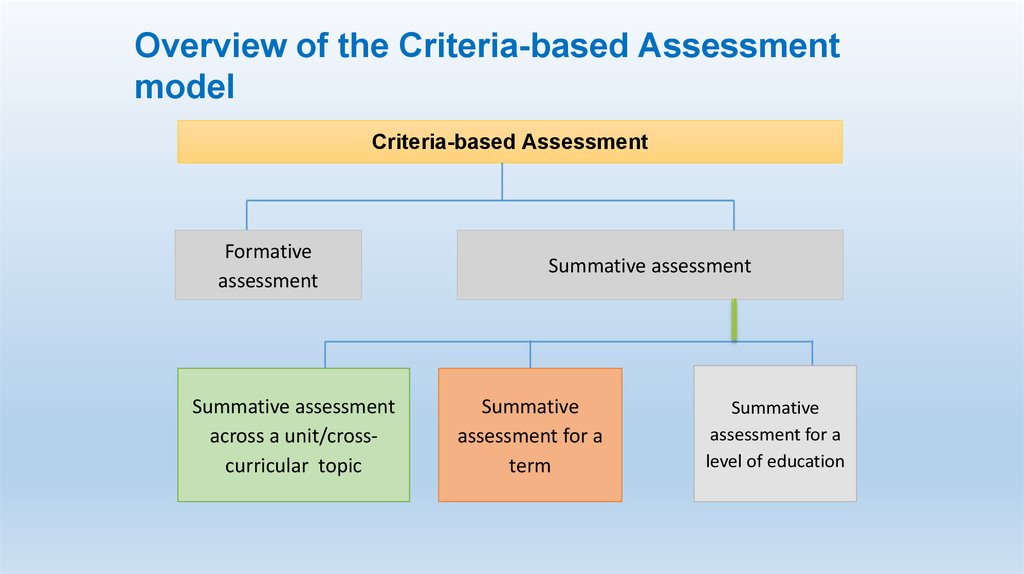
48.
Overview of the Criteria-based Assessmentmodel
Criteria-based Assessment
Formative
assessment
Summative assessment
across a unit/crosscurricular topic
Summative assessment
Summative
assessment for a
term
Summative
assessment for a
level of education
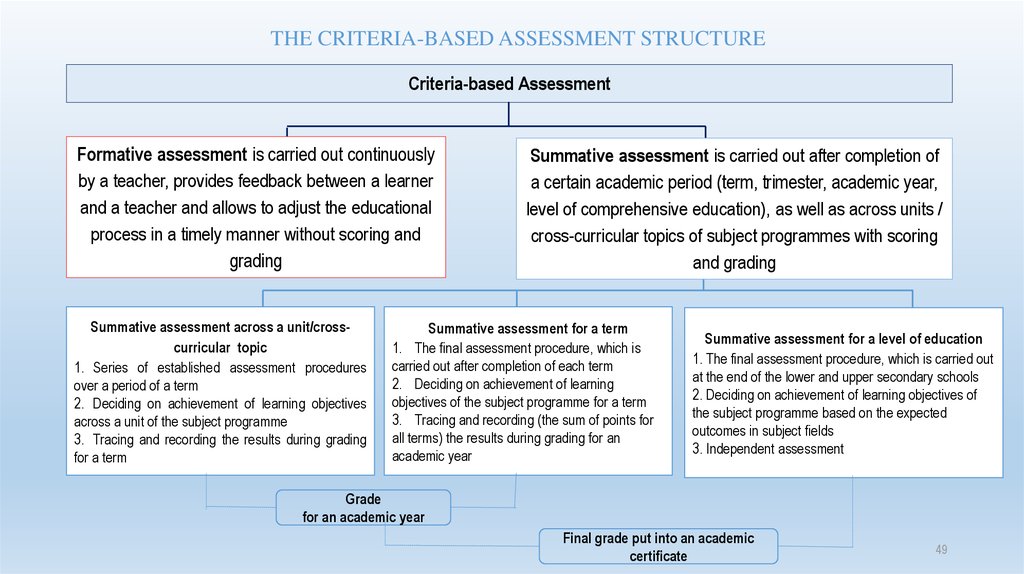
49.
THE CRITERIA-BASED ASSESSMENT STRUCTURECriteria-based Assessment
Formative assessment is carried out continuously
by a teacher, provides feedback between a learner
and a teacher and allows to adjust the educational
process in a timely manner without scoring and
grading
Summative assessment across a unit/crosscurricular topic
1. Series of established assessment procedures
over a period of a term
2. Deciding on achievement of learning objectives
across a unit of the subject programme
3. Tracing and recording the results during grading
for a term
Summative assessment is carried out after completion of
a certain academic period (term, trimester, academic year,
level of comprehensive education), as well as across units /
cross-curricular topics of subject programmes with scoring
and grading
Summative assessment for a term
1. The final assessment procedure, which is
carried out after completion of each term
2. Deciding on achievement of learning
objectives of the subject programme for a term
3. Tracing and recording (the sum of points for
all terms) the results during grading for an
academic year
Summative assessment for a level of education
1. The final assessment procedure, which is carried out
at the end of the lower and upper secondary schools
2. Deciding on achievement of learning objectives of
the subject programme based on the expected
outcomes in subject fields
3. Independent assessment
Grade
for an academic year
Final grade put into an academic
certificate
49
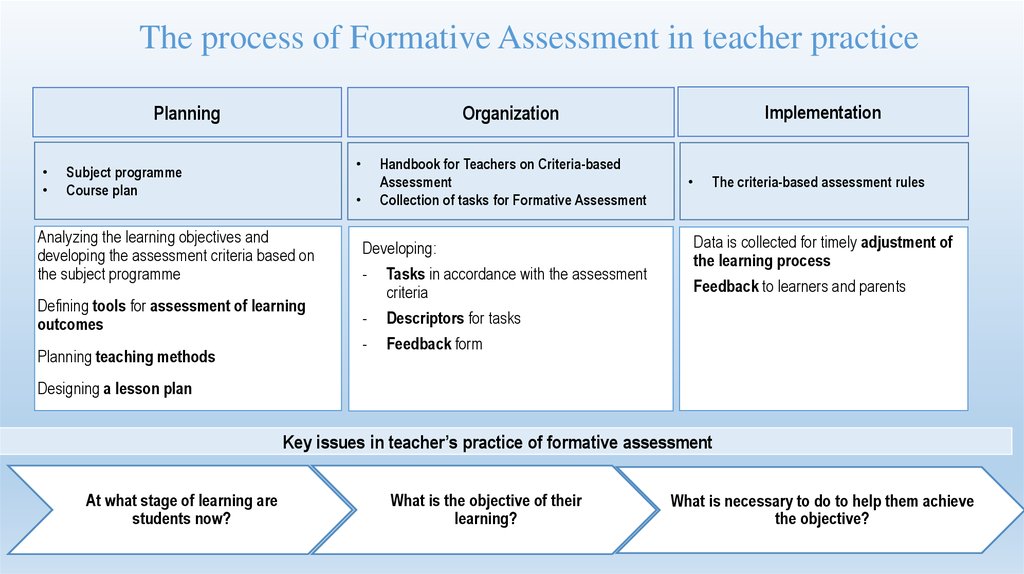
50. The process of Formative Assessment in teacher practice
PlanningHandbook for Teachers on Criteria-based
Assessment
Collection of tasks for Formative Assessment
Subject programme
Course plan
Analyzing the learning objectives and
developing the assessment criteria based on
the subject programme
Developing:
-
Defining tools for assessment of learning
outcomes
Tasks in accordance with the assessment
criteria
-
Descriptors for tasks
-
Feedback form
Planning teaching methods
Implementation
Organization
The criteria-based assessment rules
Data is collected for timely adjustment of
the learning process
Feedback to learners and parents
Designing a lesson plan
Key issues in teacher’s practice of formative assessment
At what stage of learning are
students now?
What is the objective of their
learning?
What is necessary to do to help them achieve
the objective?
50
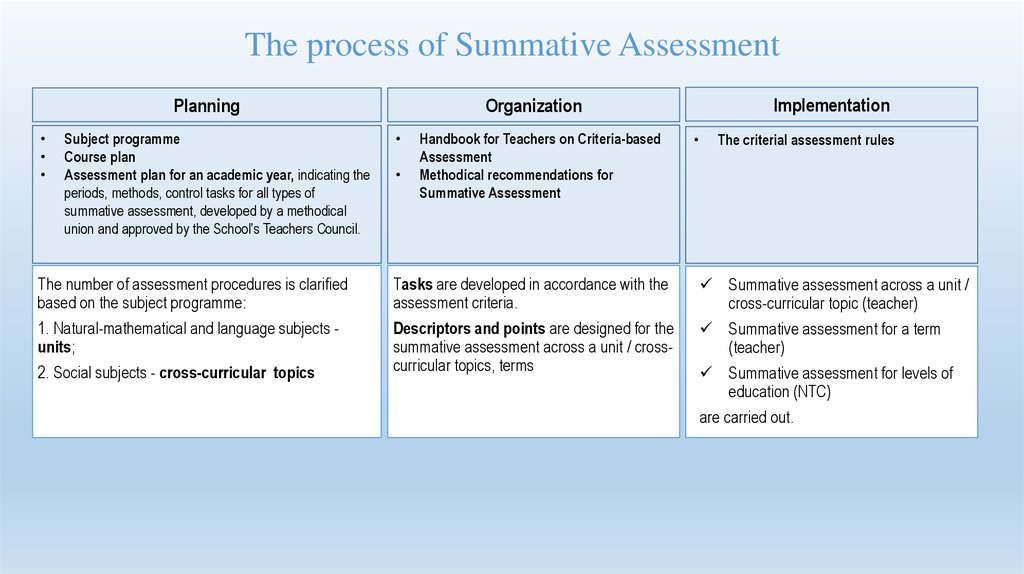
51. The process of Summative Assessment
PlanningSubject programme
Course plan
Assessment plan for an academic year, indicating the
periods, methods, control tasks for all types of
summative assessment, developed by a methodical
union and approved by the School's Teachers Council.
Implementation
Organization
Handbook for Teachers on Criteria-based
Assessment
Methodical recommendations for
Summative Assessment
The criterial assessment rules
The number of assessment procedures is clarified
based on the subject programme:
Tasks are developed in accordance with the
assessment criteria.
Summative assessment across a unit /
cross-curricular topic (teacher)
1. Natural-mathematical and language subjects units;
Descriptors and points are designed for the
summative assessment across a unit / crosscurricular topics, terms
Summative assessment for a term
(teacher)
2. Social subjects - cross-curricular topics
Summative assessment for levels of
education (NTC)
are carried out.
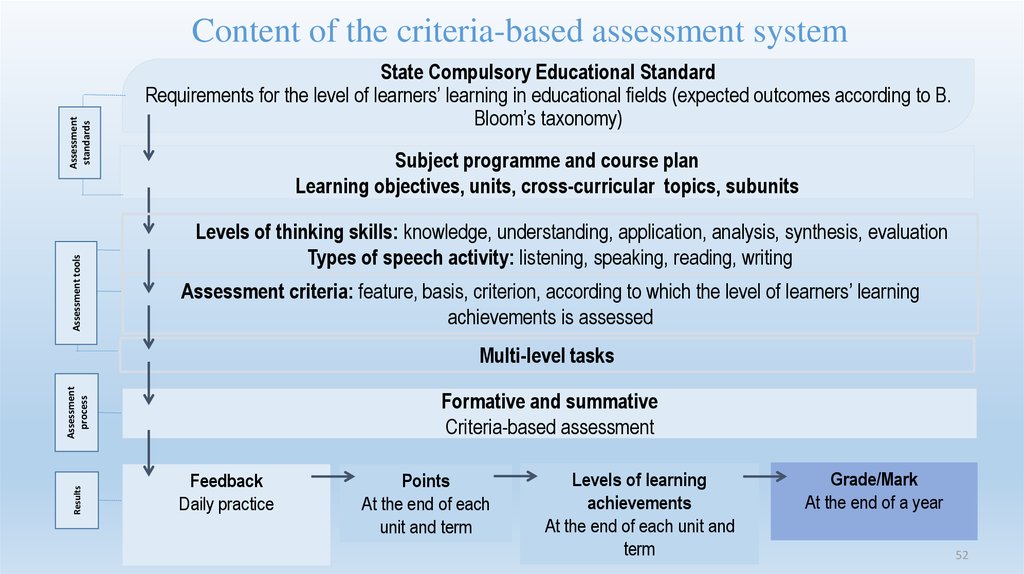
52. State Compulsory Educational Standard Requirements for the level of learners’ learning in educational fields (expected outcomes
Assessment toolsAssessment
standards
Content of the criteria-based assessment system
State Compulsory Educational Standard
Requirements for the level of learners’ learning in educational fields (expected outcomes according to B.
Bloom’s taxonomy)
Subject programme and course plan
Learning objectives, units, cross-curricular topics, subunits
Levels of thinking skills: knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, synthesis, evaluation
Types of speech activity: listening, speaking, reading, writing
Assessment criteria: feature, basis, criterion, according to which the level of learners’ learning
achievements is assessed
Results
Assessment
process
Multi-level tasks
Formative and summative
Criteria-based assessment
Feedback
Daily practice
Points
At the end of each
unit and term
Levels of learning
achievements
At the end of each unit and
term
Grade/Mark
At the end of a year
52
53.
ALGORITHM OF SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTDEVELOPMENT ACROSS A UNIT/ CROSSCURRICULAR TOPIC
*Teacher
Descriptors
Tasks
Subject
programme/
Course plan
Learning
objectives
Level of
thinking
Assessment
criteria
*follows the Methodical Recommendations of the Center of Pedagogical Measurements (CPM) and
National Academy of Education (NAE) (or uses them)
53
54.
ALGORITHM OF TASK DEVELOPMENTFOR SUMMATIVE ASSESMENT ACROSS A
UNIT / GENERAL TOPIC
Unit
Learning
objectives
Assessment
criteria
Levels of
thinking
Levelled tasks
Descriptors
Points
Rubrics
54
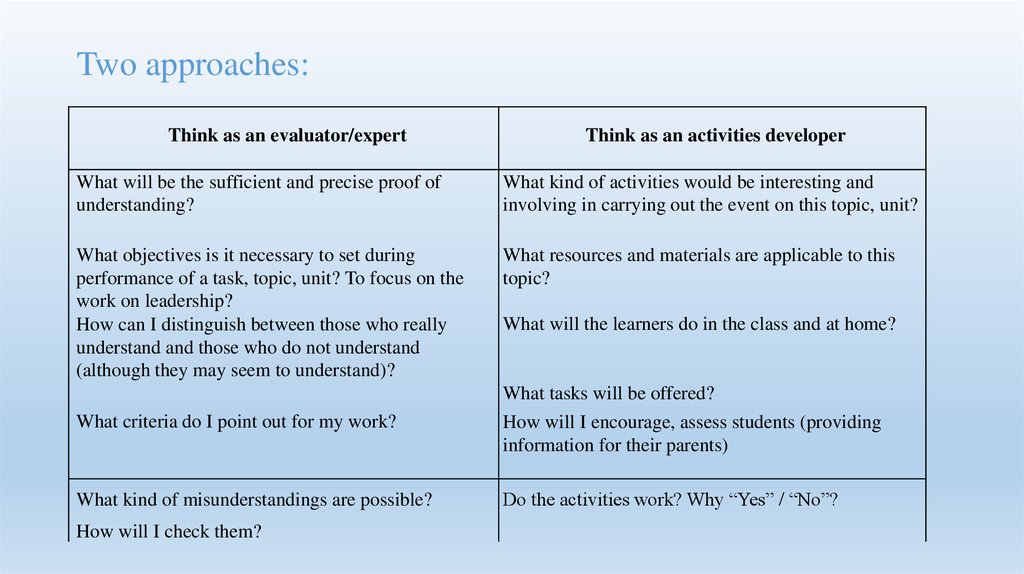
55. Two approaches:
Think as an evaluator/expertThink as an activities developer
What will be the sufficient and precise proof of
understanding?
What kind of activities would be interesting and
involving in carrying out the event on this topic, unit?
What objectives is it necessary to set during
performance of a task, topic, unit? To focus on the
work on leadership?
How can I distinguish between those who really
understand and those who do not understand
(although they may seem to understand)?
What resources and materials are applicable to this
topic?
What will the learners do in the class and at home?
What tasks will be offered?
What criteria do I point out for my work?
How will I encourage, assess students (providing
information for their parents)
What kind of misunderstandings are possible?
Do the activities work? Why “Yes” / “No”?
How will I check them?
56.
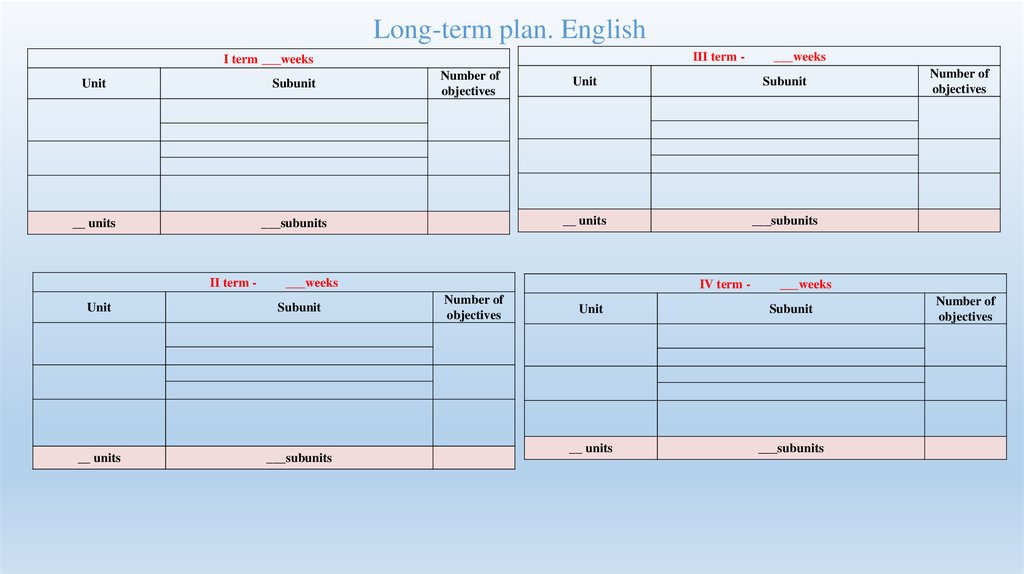
Long-term plan. EnglishІ term ___weeks
Unit
Subunit
__ units
___subunits
ІI term -
III term Number of
objectives
Unit
Subunit
__ units
___subunits
ІV term -
___weeks
Unit
Subunit
__ units
___subunits
Number of
objectives
___weeks
Number of
objectives
___weeks
Unit
Subunit
__ units
___subunits
Number of
objectives
57.
5758.
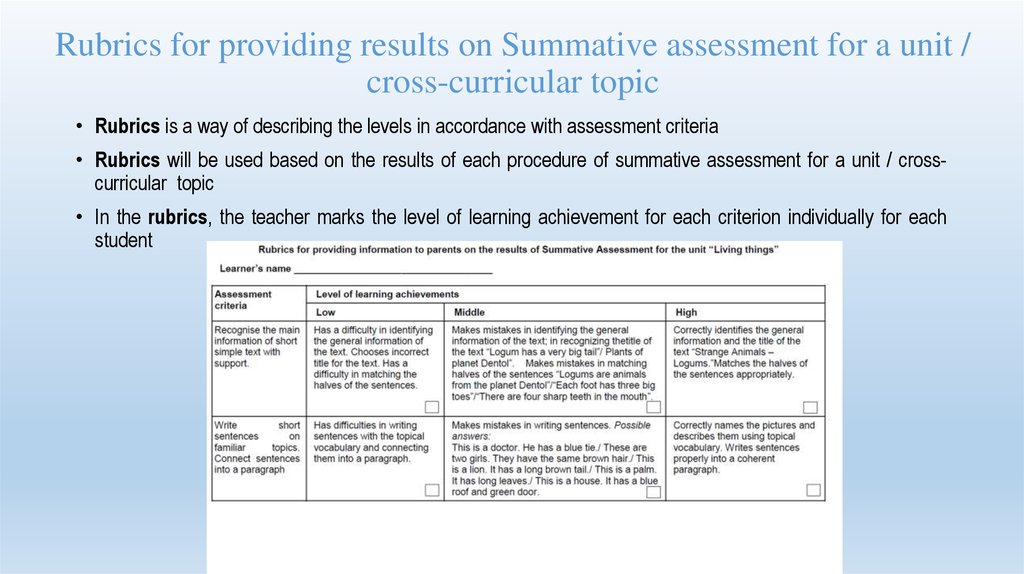
59. Rubrics for providing results on Summative assessment for a unit / cross-curricular topic
• Rubrics is a way of describing the levels in accordance with assessment criteria• Rubrics will be used based on the results of each procedure of summative assessment for a unit / crosscurricular topic
• In the rubrics, the teacher marks the level of learning achievement for each criterion individually for each
student
60. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT ACROSS A UNIT/CROSS-CURRICULAR TOPIC
Summative assessment is carried out:• across units (natural and mathematical subjects,
language subjects);
• across cross-curricular topics (social subjects).
60
61.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR A TERM• Summative assessment for a term is carried out at the end of a term and shows the proof of
understanding, skills and knowledge through grades and points.
• Summative assessment for a term is carried out through the organization of various testing and control
works.
• When compiling summative work for a term, it is necessary to take into account not only knowledge,
understanding and skills, but also the ability of a learner to think at the highest level: it must be taken
into account that it is important to provide learners with tasks enabling assessment, analysis and
synthesis.
• Samples of tasks for Summative assessment for a term are given in Methodical recommendations.
• However, each school may prepare its own tasks for Summative assessment for a term. Teachers can use
a database in which tasks for Summative assessment are collected.
• At the beginning of the school year, the school methodical union makes an Assessment Plan for an
academic year.
62. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR A TERM
• For whom are the tasks intended?• How much time is allowed for the tasks?
• How is SA conducted?
• What is the content of the SA tasks?
• What types of tasks will be used?
• How are the points scored for questions or tasks counted?
• How many tasks do you need to develop?
62
63. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT ACROSS A UNIT / CROSS-CURRICULAR TOPIC
• Tasks for Summative assessment across a unit / cross-curricular topic aredeveloped in accordance with the learning objectives of the unit and the assessment
criteria.
• Methodical unions of schools develop and approve the Summative Assessment
Plan for an academic year.
• Methodical Recommendations with sample tasks for each subject for the
assessment implementation are developed by the CPM and NAE.
63
64.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT FOR A TERMTask: Identify the similarities and differences between the
summative assessment for a unit / cross-curricular topic and
the summative assessment for a term.
summative
assessment for
a unit / crosscurricular topic
summative
assessment for a
term
65. Moderation
Discussion process of the results of summative works of learners in order to establishcommon assessment standards.
Moderation is intended:
For teachers to discuss the results of learners’ summative works in order to standardize the
assessment.
Moderation is carried out:
With participation of teachers working in the same parallels;
They discuss preliminary assessments of work on a particular subject for the purpose of
performing the same approach in applying the scoring table.
It is important to know:
Based on moderation, the result of Summative assessment for a term can be changed.
The chairperson of moderation can be both the head of the Methodical union, and any
subject teacher.
66.
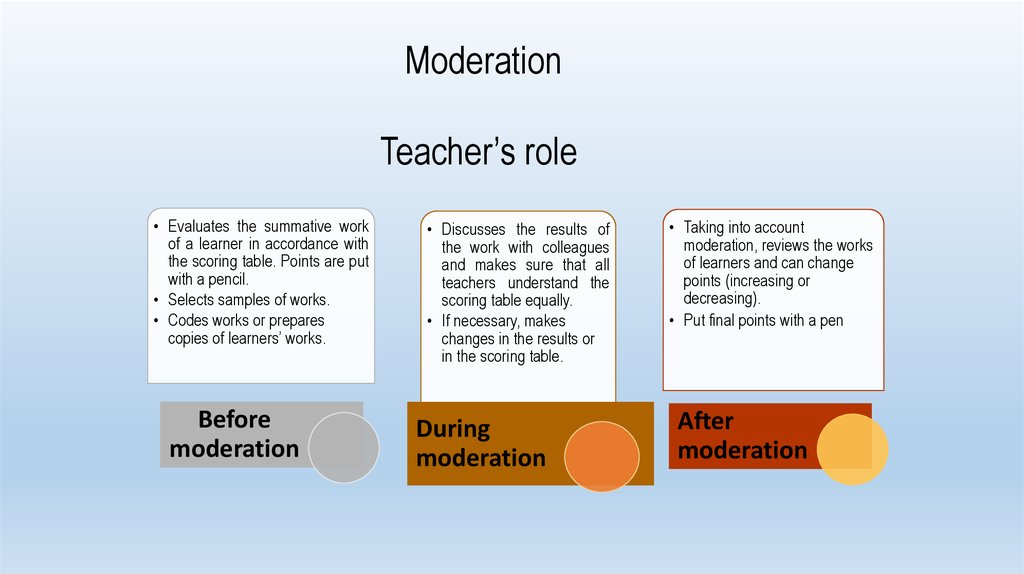
ModerationTeacher’s role
• Evaluates the summative work
of a learner in accordance with
the scoring table. Points are put
with a pencil.
• Selects samples of works.
• Codes works or prepares
copies of learners’ works.
Before
moderation
• Discusses the results of
the work with colleagues
and makes sure that all
teachers understand the
scoring table equally.
• If necessary, makes
changes in the results or
in the scoring table.
During
moderation
• Taking into account
moderation, reviews the works
of learners and can change
points (increasing or
decreasing).
• Put final points with a pen
After
moderation
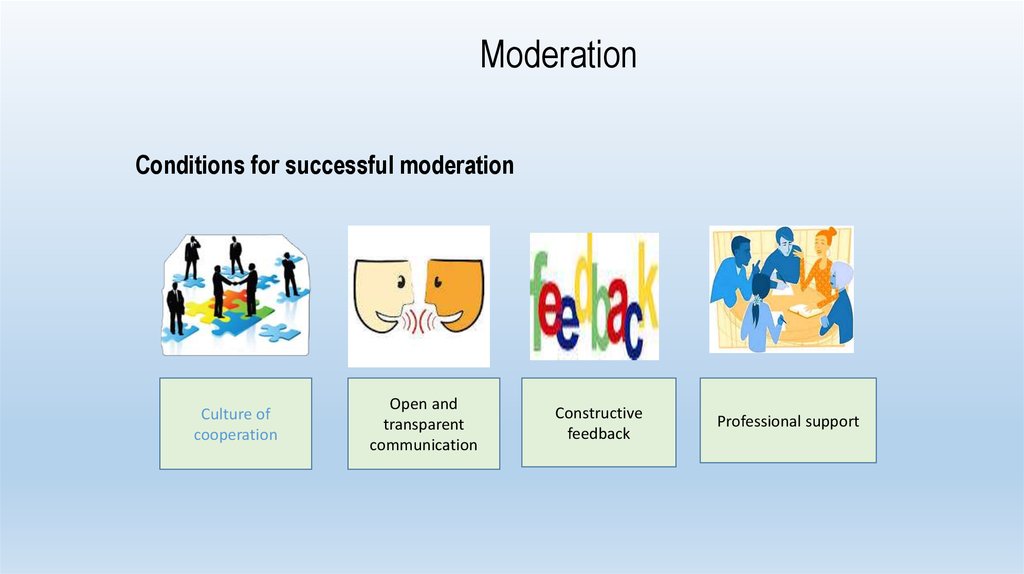
67. Conditions for successful moderation
ModerationConditions for successful moderation
Culture of
cooperation
Open and
transparent
communication
Constructive
feedback
Professional support
68.
69.
70.
71.
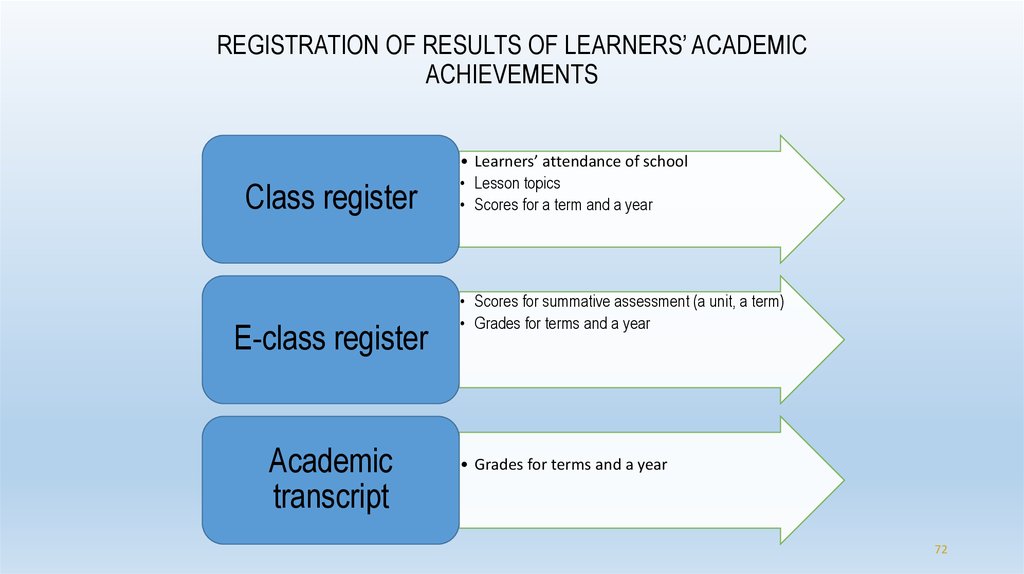
72. REGISTRATION OF RESULTS OF LEARNERS’ ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENTS
Class registerE-class register
Academic
transcript
• Learners’ attendance of school
• Lesson topics
• Scores for a term and a year
• Scores for summative assessment (a unit, a term)
• Grades for terms and a year
• Grades for terms and a year
72















































 english
english








