Similar presentations:
Evidence for Evolution
1.
WHAT IS EVOLUTION?“The change in the heritable
characteristics of a population over
time”
Why were Darwin’s early ideas
ridiculed?
Charles Darwin
(1809 – 1882)
Why is evolution still such a
contentious issue?
2.
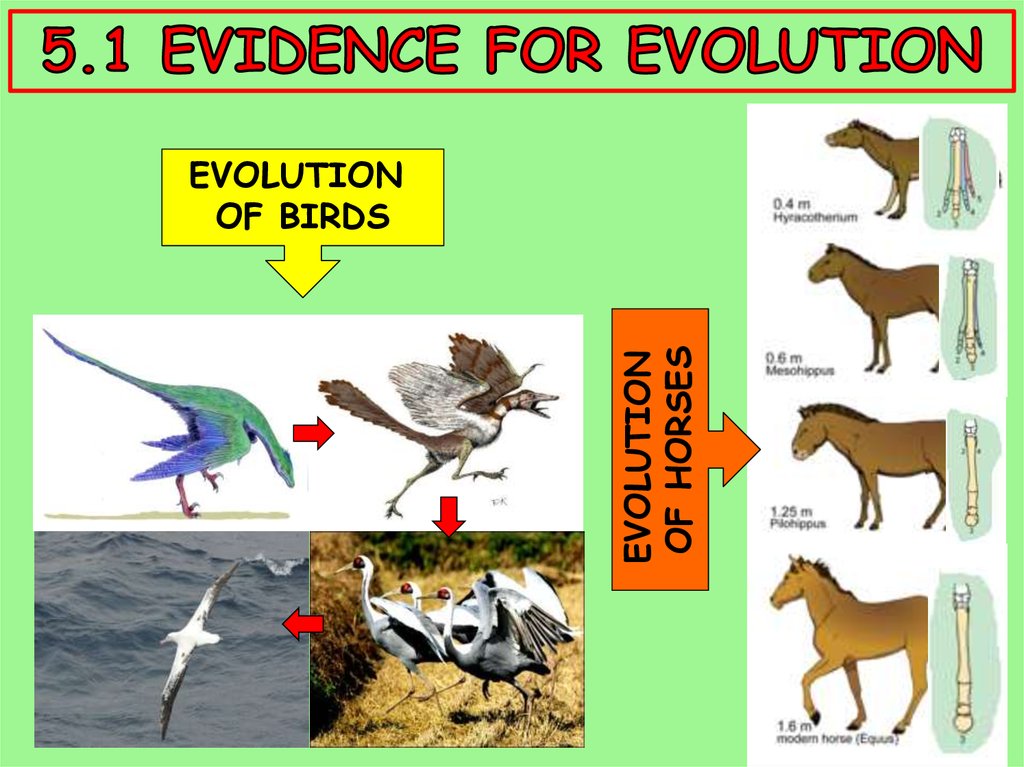
EVOLUTIONOF HORSES
EVOLUTION
OF BIRDS
3.
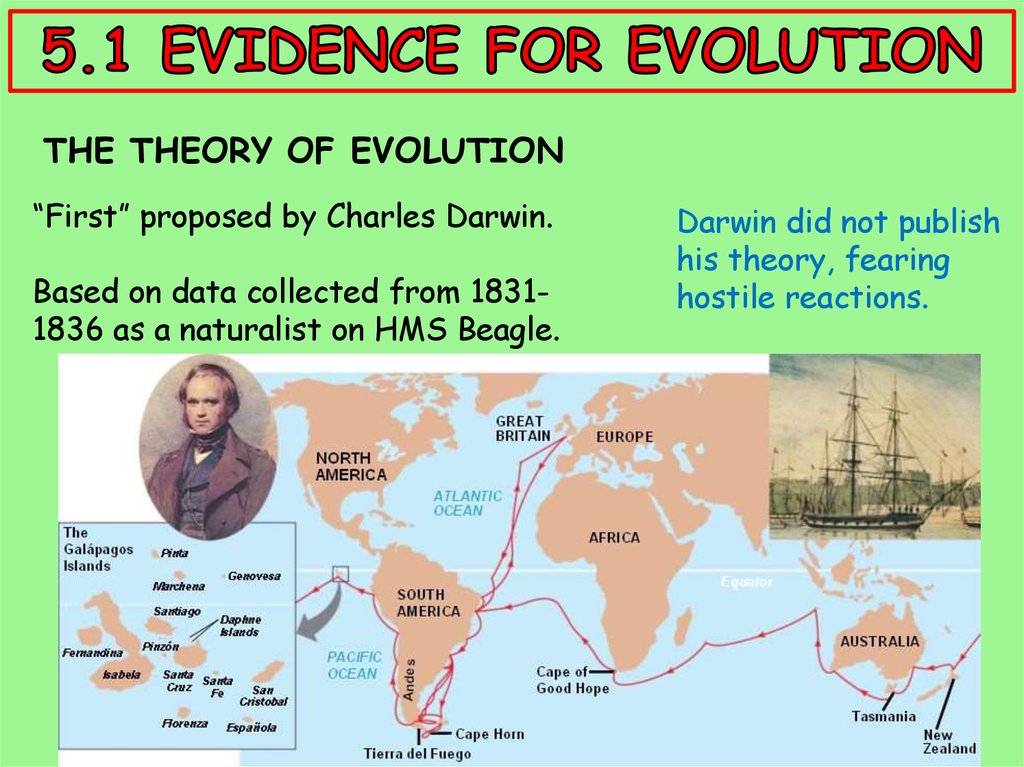
THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION“First” proposed by Charles Darwin.
Based on data collected from 18311836 as a naturalist on HMS Beagle.
Darwin did not publish
his theory, fearing
hostile reactions.
4.
WE SHOULD THANK ALFRED WALLACE…In 1858 Wallace sent Darwin a letter outlining
his theory on evolution.
Darwin was surprised that Wallace’s basic
arguments were the same as his.
Spurred Darwin to publish his theory in his
book in 1859
The theory should really be referred to as
the Darwin-Wallace Theory!
Video biography of Wallace and Darwin
5.
ANALYSING THE EVIDENCERoss & Phoebe debate
evolution
Most biologists accept the theory of evolution based on
evidence from:
Fossils sequence of preserved organisms matches
expectations. Patterns can be seen.
Selective Breeding artificial selection can occur
Homologous Structures similar structures derived from a
common ancestor that may now serve different functions
Patterns of Variation examples of gradual divergence
across a geographical range
6.
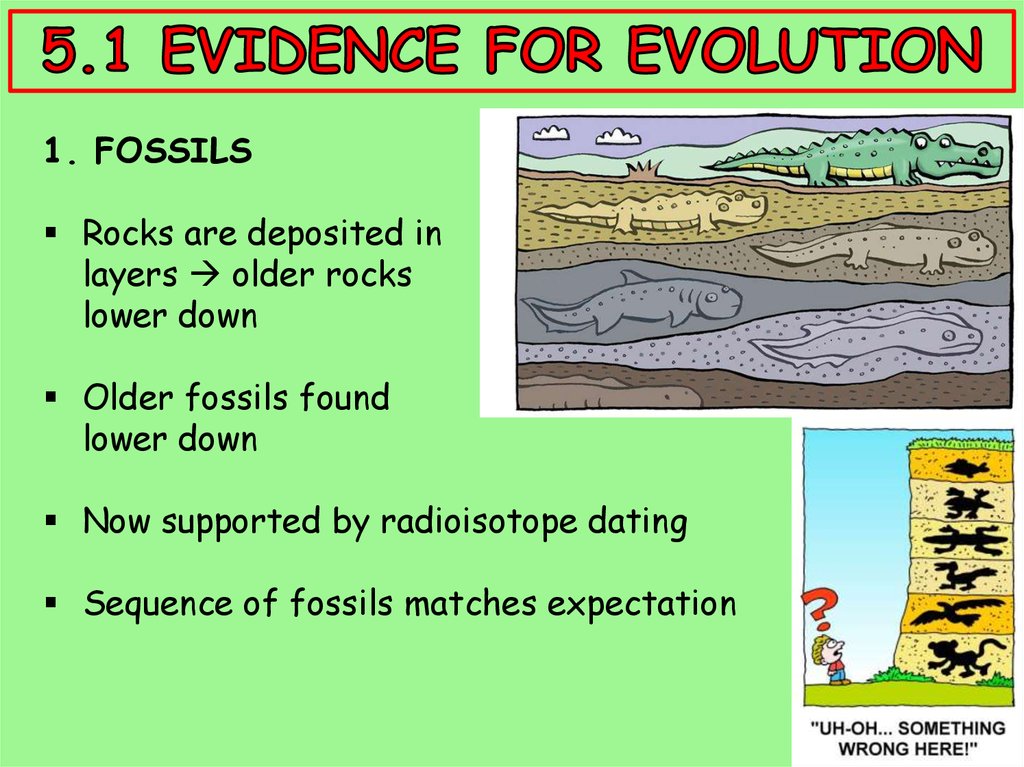
1. FOSSILSRocks are deposited in
layers older rocks
lower down
Older fossils found
lower down
Now supported by radioisotope dating
Sequence of fossils matches expectation
7.
1. FOSSILSBacteria Algae Fungi
Worms Fish
Amphibians Reptiles
Birds Mammals
Ecology Plant fossils
appear before animals;
Plants on land appear before
animals on land
8.
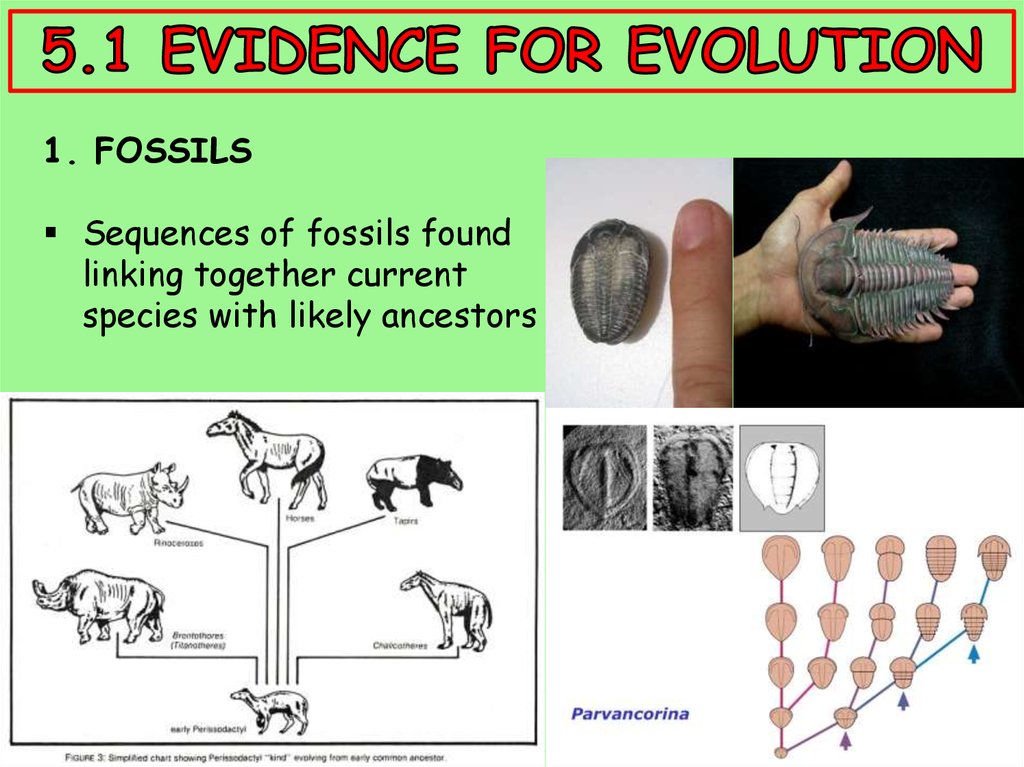
1. FOSSILSSequences of fossils found
linking together current
species with likely ancestors
9.
2. SELECTIVE BREEDINGArtificial selection
Repeatedly select & breed individuals
with desired characteristics
Produced breeds often very different
to the wild species
Short amount of time
+ Selection can cause evolution
- Doesn’t prove evolution occurs naturally
10.
2. SELECTIVE BREEDINGAuroch
from Asia
Belgian
Blue
11.
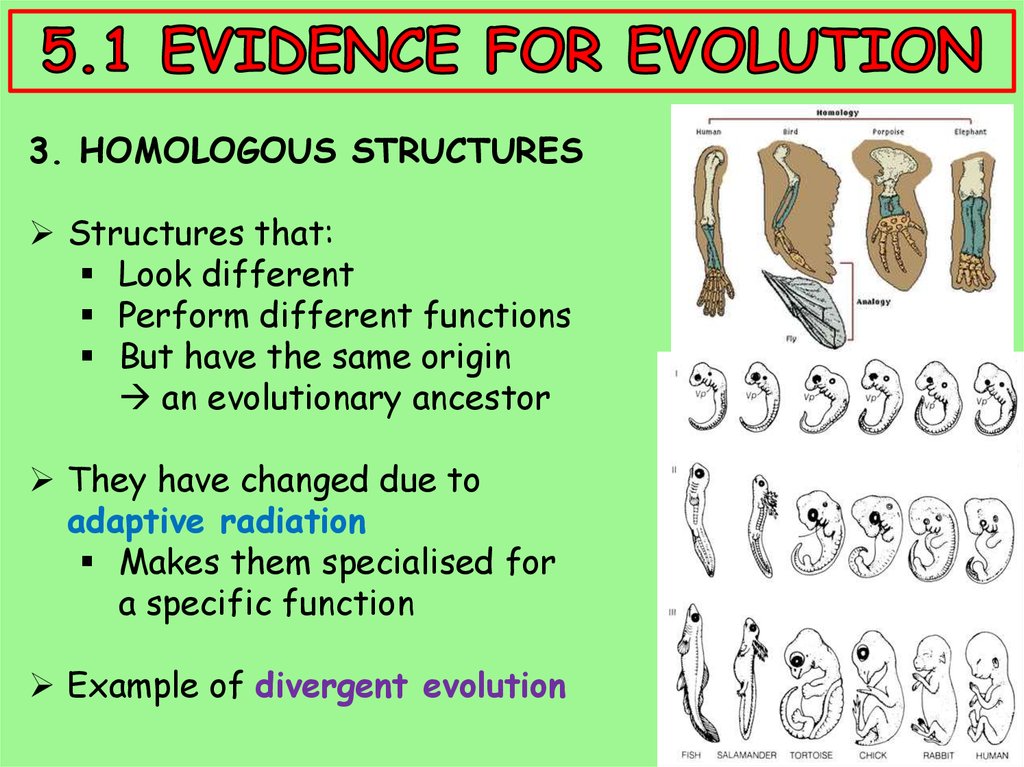
3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURESStructures that:
Look different
Perform different functions
But have the same origin
an evolutionary ancestor
They have changed due to
adaptive radiation
Makes them specialised for
a specific function
Example of divergent evolution
12.
3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURESWorksheet
Activity
Pentadactyl Limb
Same arrangement of bones
Look different as they serve different functions
13.
3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURESVestigial organs
Reduced structures that serve no function
Difficult to explain without evolution
Evolution = structures that no longer have a function so
are being gradually lost
14.
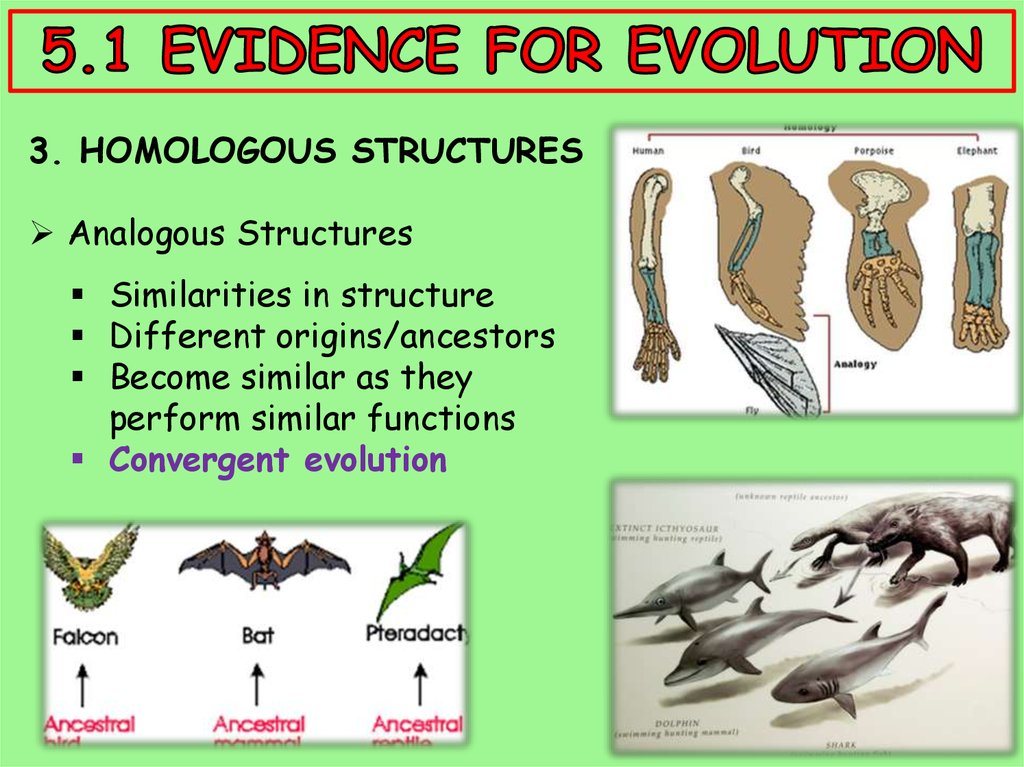
3. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURESAnalogous Structures
Similarities in structure
Different origins/ancestors
Become similar as they
perform similar functions
Convergent evolution
15.
4. BIOGEOGRAPHICSpeciation
2 populations become separated
Cannot interbreed
Natural selection acts differently
Characteristics diverge
After time look recognizably
different
If populations merge again may
not be able to interbreed
They have evolved into separate
species
https://www.youtube.com
/watch?v=tRc9DawVHaU
https://www.youtube.com
/watch?v=Egl-Bcbu5Ow
16.
17.
4. BIOGEOGRAPHICEndemic Species
Only found in one geographical
location
Common on islands
Mainland species migrates
Then diverges (e.g. lava lizard on
Galapagos Islands)
18.
4. BIOGEOGRAPHICGradual Divergence
Should see examples of all stages of divergence
Makes classification
difficult
Refutes belief that
species were created
as distinct types
incapable of change
Instead suggests
evolution












 english
english