Similar presentations:
Refrigeration Fundamentals. Part 1. Heat and Heat Transfer
1. Refrigeration Fundamentals
Part 1Heat and Heat Transfer
2. What is Refrigeration?
2 Sect. 13. DEFINITION
‘Refrigeration’……is the transfer of heat from a place where it is
‘not wanted’…
… to a place where it is ‘unobjectionable’.
3 Sect. 1
4. HEAT REMOVAL
Ifheat is removed from inside the
container ‘faster’ than it enters...
…The internal temperature becomes colder.
4 Sect. 1
5. WHAT IS HEAT?
A Form of EnergyIt Exists ‘Everywhere’
It Exists at ‘All Temperatures’…Except…
– Absolute Zero (-459º F / -273º C)
5 Sect. 1
It can be Moved from ‘Place to Place’
6. WHAT ARE REEFERS?
Machines that ‘Move Heat’6 Sect. 1
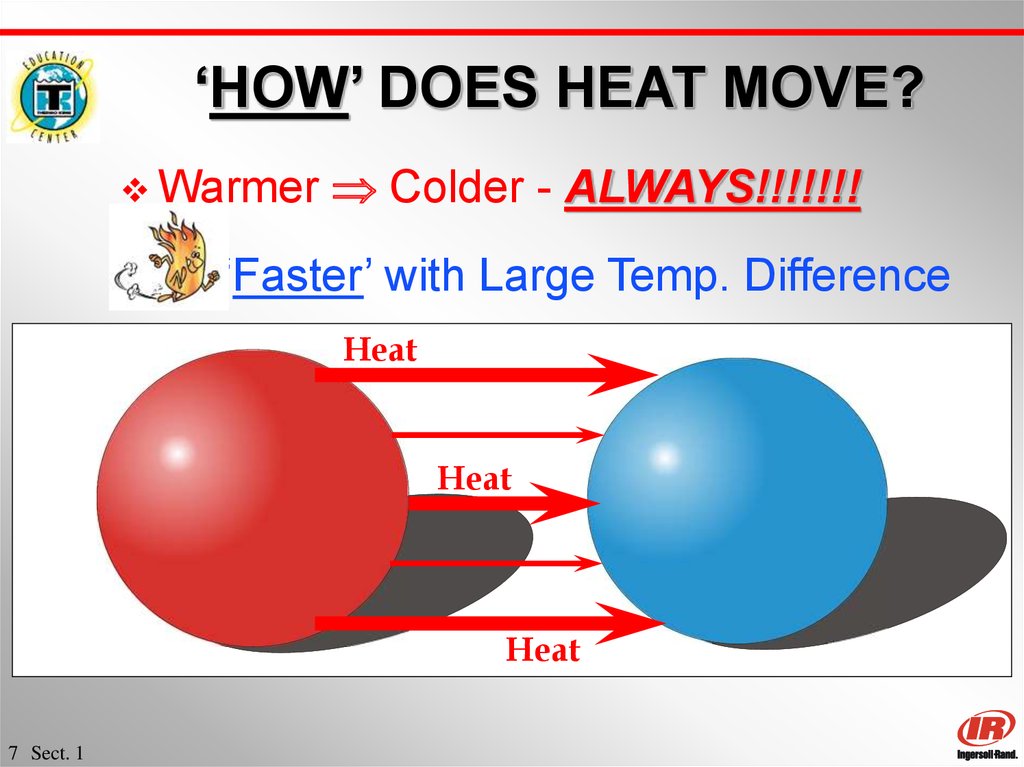
7. ‘HOW’ DOES HEAT MOVE?
WarmerColder - ALWAYS!!!!!!!
‘Faster’ with Large Temp. Difference
Heat
Heat
Heat
7 Sect. 1
8. ‘HOW’ DOES IT MOVE?
Heat can move three (3) ways….1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Radiation
8 Sect. 1
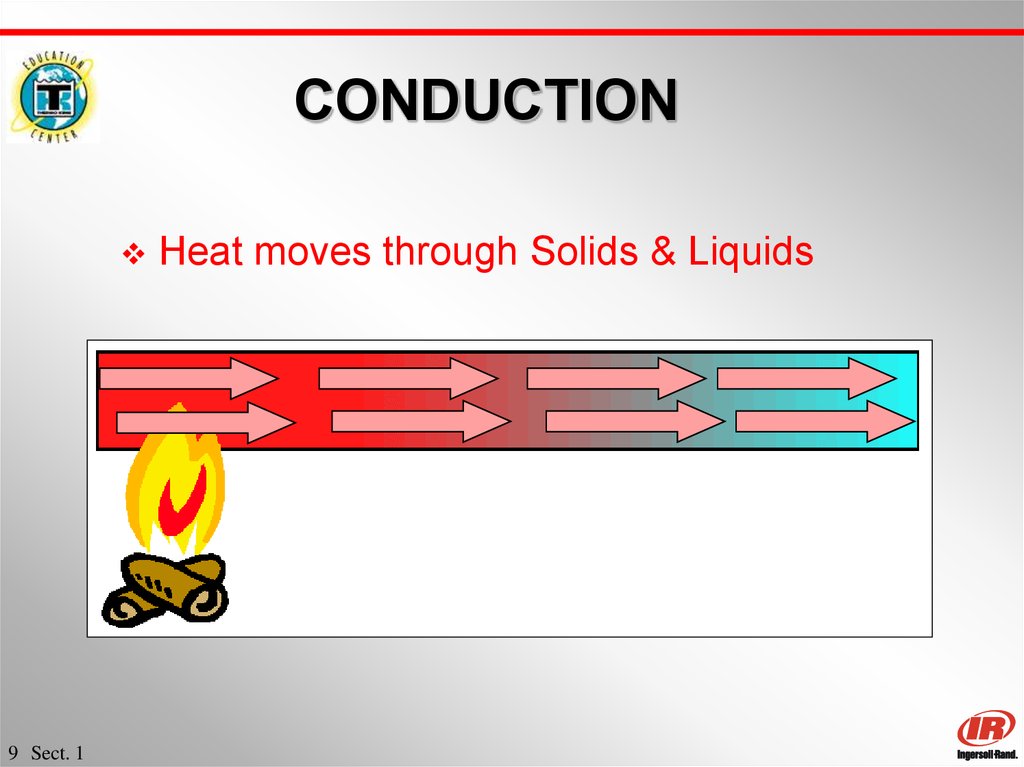
9. CONDUCTION
9 Sect. 1Heat moves through Solids & Liquids
10. CONDUCTION
10 Sect. 1Heat will move Between Solids and / or
Fluids in direct contact with one another
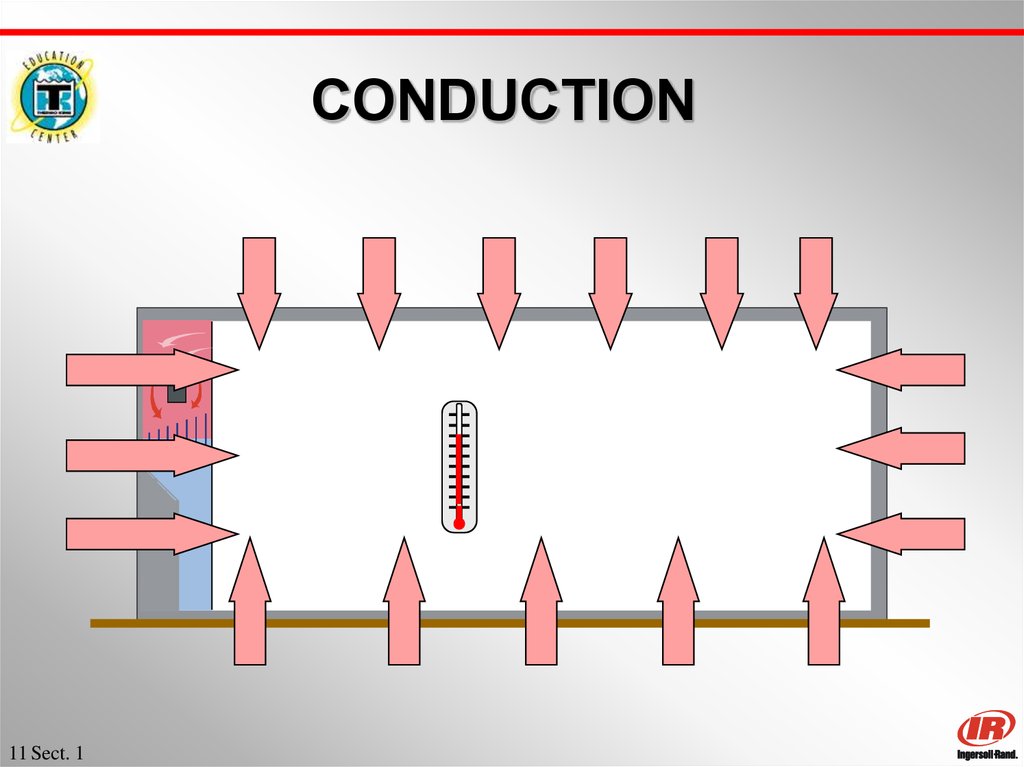
11. CONDUCTION
11 Sect. 112. Any other Examples of Conduction?
12 Sect. 113. CONVECTION
Definition - Heat transfers via thecirculation (movement) of a fluid.
i.e…..
– Air is a fluid
– Refrigerant Liquid & Vapor are fluids
Types
– ‘Natural’ Convection
– ‘Forced’ Convection
13 Sect. 1
14. ‘NATURAL’ CONVECTION
Warm Air RisesHeater
Cool Air Falls
14 Sect. 1
15. ‘NATURAL’ CONVECTION
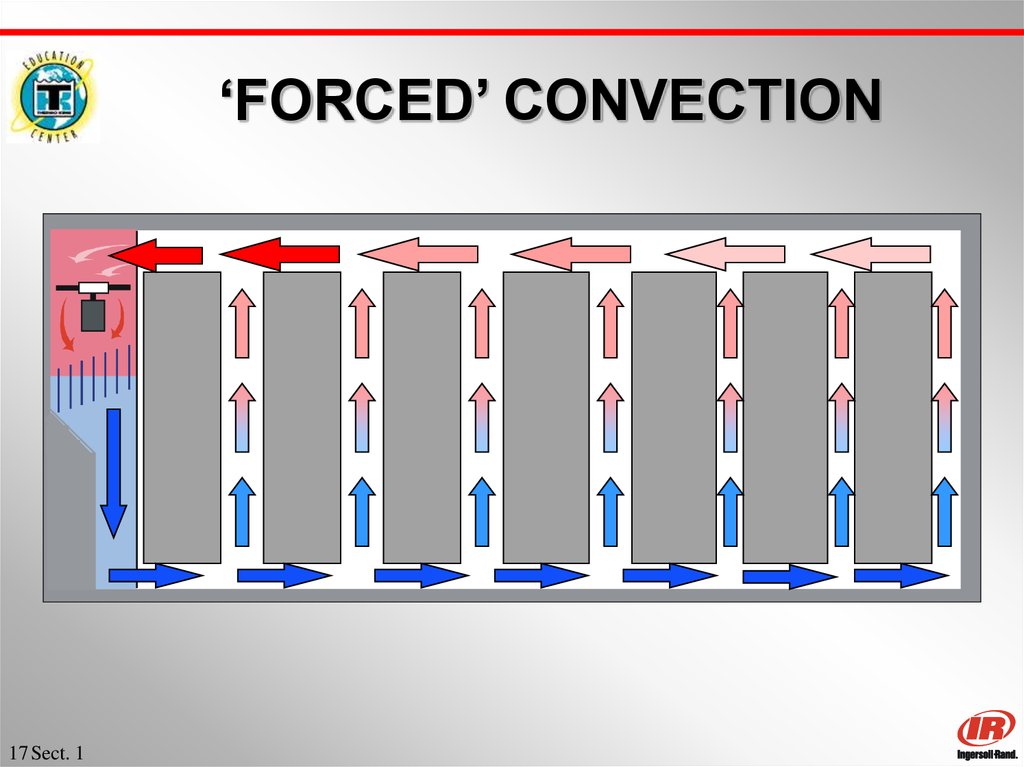
15 Sect. 116. ‘FORCED’ CONVECTION
16 Sect. 117. ‘FORCED’ CONVECTION
17 Sect. 118. Any other Examples of Convection?
18 Sect. 119. RADIATION
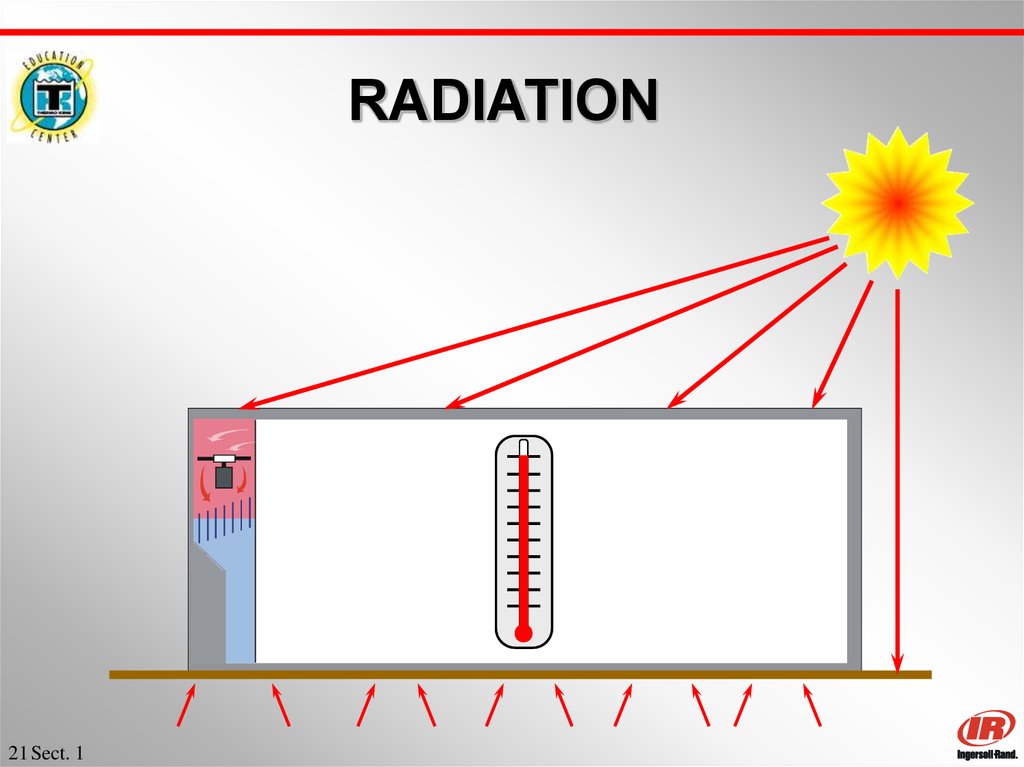
Movesin Straight Lines… like light
Does not heat the air it passes through
Raises temperature of the substance
that absorbs it
Dark colors absorb ‘more’ heat…
Light colors absorb ‘less’ heat
19 Sect. 1
20. RADIATION
20 Sect. 121. RADIATION
21 Sect. 122. Any other Examples of Radiation?
22 Sect. 123. HEAT TRANSFER SYSTEMS
combine ‘Conduction’ AND‘Convection’ to move heat. i.e….
Usually
23 Sect. 1
24. TERMS TO REMEMBER
RefrigerationHeat
Box
24 Sect. 1
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
25. HOW IS HEAT ‘MEASURED’?
Four (4) Ways….1.
2.
3.
4.
25 Sect. 1
Temperature
Sensible Heat
British Thermal Unit (BTU)
Specific Heat
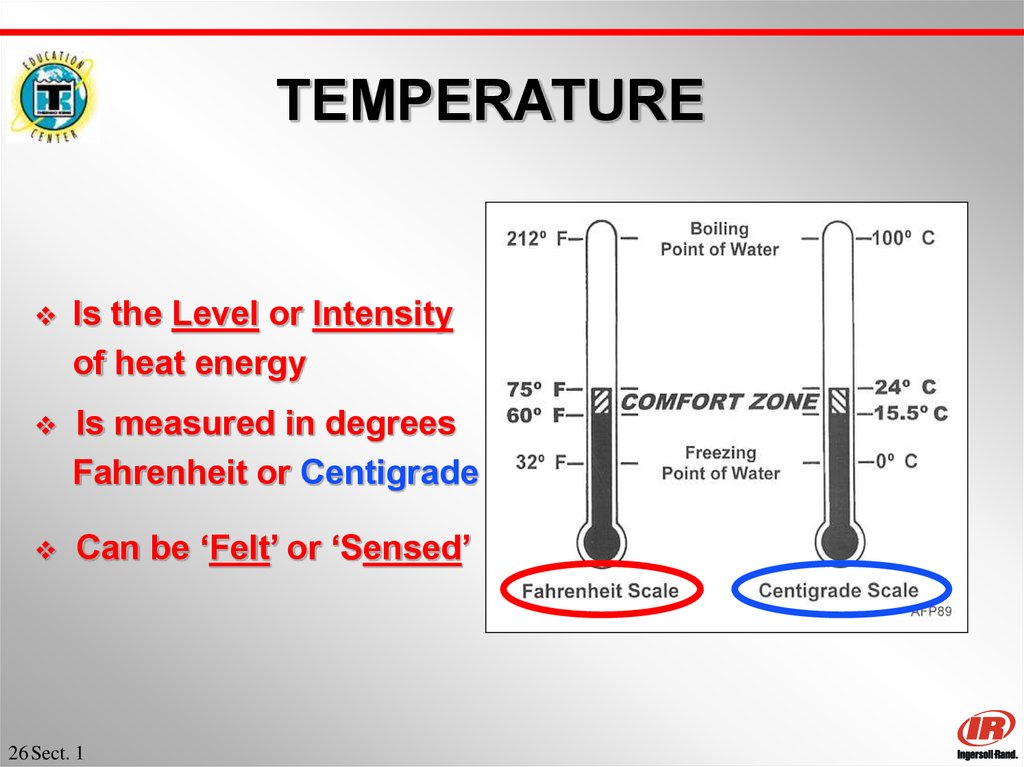
26. TEMPERATURE
Is the Level or Intensityof heat energy
Is measured in degrees
Fahrenheit or Centigrade
Can be ‘Felt’ or ‘Sensed’
26 Sect. 1
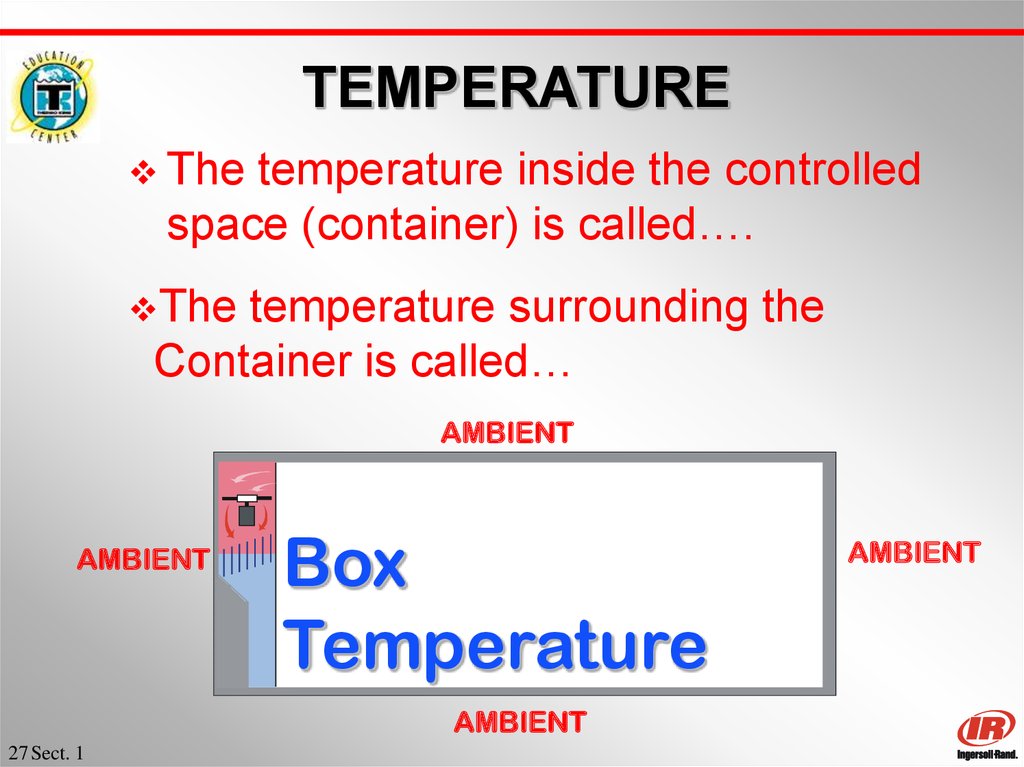
27. TEMPERATURE
Thetemperature inside the controlled
space (container) is called….
The
temperature surrounding the
Container is called…
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Box
Temperature
AMBIENT
27 Sect. 1
AMBIENT
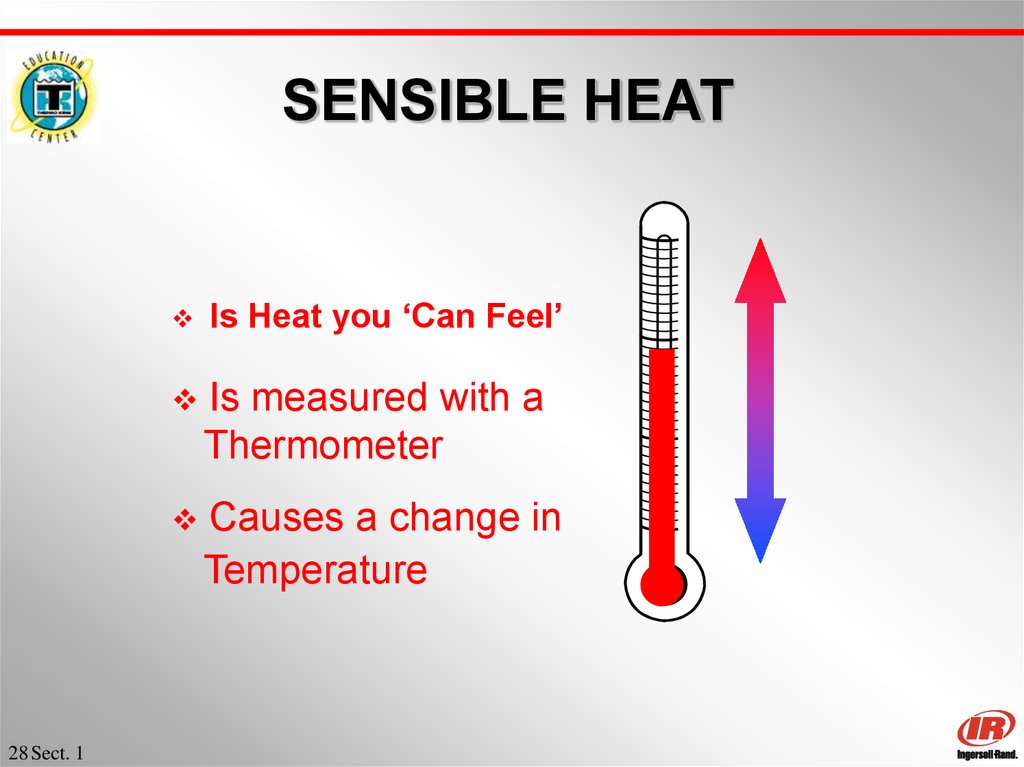
28. SENSIBLE HEAT
28 Sect. 1Is Heat you ‘Can Feel’
Is measured with a
Thermometer
Causes a change in
Temperature
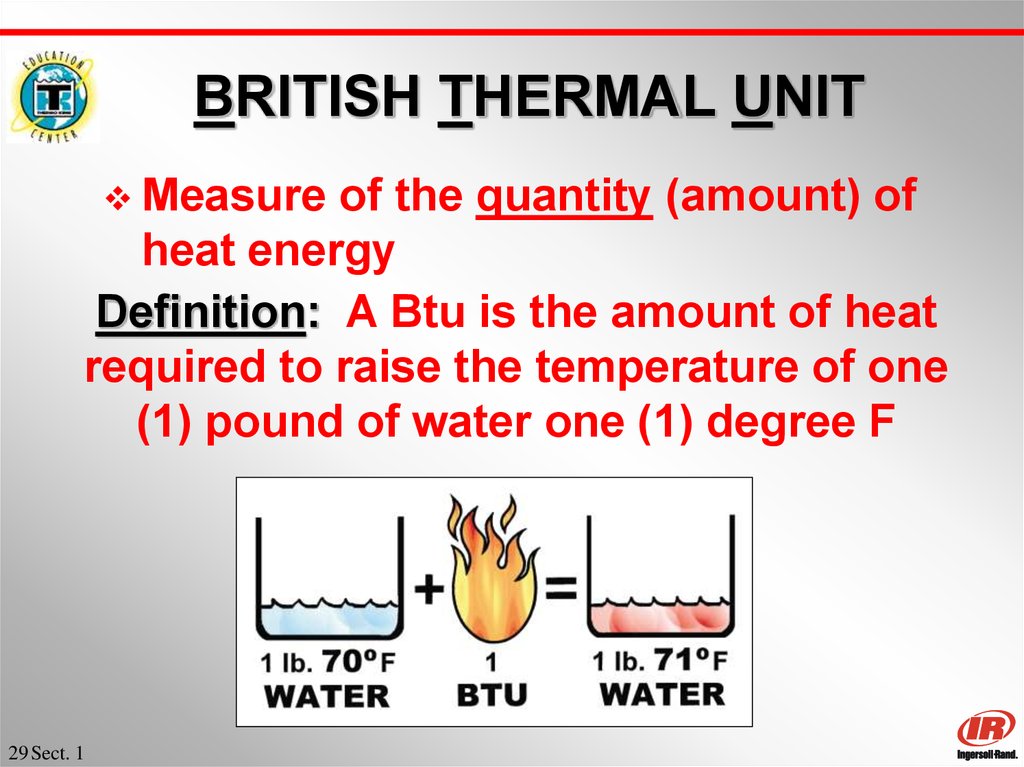
29. BRITISH THERMAL UNIT
Measureof the quantity (amount) of
heat energy
Definition: A Btu is the amount of heat
required to raise the temperature of one
(1) pound of water one (1) degree F
29 Sect. 1
30. SPECIFIC HEAT
Amountof heat required to raise the
temperature of one (1) pound of a ‘Specific
Substance’ one (1) degree F. i.e. 0.75
Compared
to Water (1.0)
The less heat required to change substance
temp., the lower the Specific Heat
The more heat required to change
substance temp., the higher the Specific Heat
30 Sect. 1
31. SPECIFIC HEAT EXAMPLES
Water - 1.0Aluminum - .22
Honey - .35
Cheese - .50
31 Sect. 1
Fresh Beef - .75
Vegetables - .90
Cucumbers &
Watermelon - .97
32. TERMS TO REMEMBER
TemperatureBox Temperature
Ambient
Temperature
32 Sect. 1
Sensible Heat
Btu
Specific Heat
33.
Questions?33 Sect. 1























 physics
physics








