Similar presentations:
VBA development technology. (Lecture 6)
1. VBA development technology
2. Main steps during task solving
goal of the task;mathematical model;
algorithm;
structure of the data;
GUI design;
code writing;
implementation with IDE;
application analysis;
testing;
performing of a program;
analysis of results.
3. Control names
Name of a control is set up with Nameproperty.
Default names are:
UserForm1; TextBox1, TextBox2; Label1,
Label2.
Prefix naming:
<prefix><Basename>
frmCheck; lblPrice; txtPrice; cmdCalculate
4. Common prefixes
Object typePrefix
Label
lbl
TextBox
txt
CommandButton
cmd
CheckBox
chk
OptionButton
opt
Frame
fra
ListBox
lst
ComboBox
cbo
Image
img
PictureBox
pic
OLE Container
ole
Form
frm
5. Naming rules
No more than 40 symbols.Names should be easy to read and
understand
txtNewPrice, txtNew_Price
No spaces, dots and other special
symbols instead underscore
6. Dot notation
<NameOfObject>.<Property>txtPrice.Text = 0
txtPrice.BackColor = vbYellow
txtPrice.Visible = False
Each control has its own default property which may be used
without dot notation, e.g.
txtCost.Text = txtPrice.Text*txtQuantity.Text
is the same as
txtCost = txtPrice * txtQuantity
in case if all controls are TextBoxes.
7. Variables and constants
Variables areConstants are
used for constant
variables like PI
(3.14) etc.
Const operator is
used to describe
such variables
used to store
interim values
Dim operator is
used to describe
such variables
8. Variable description
[Public|Private] Dim <VariableName> As<Data type>
Data type – set of possible values for this
variable
Dim operator reserves
memory field of specific
type for corresponding
data type.
Dim i As Integer
…
i=0
…
i=i+1
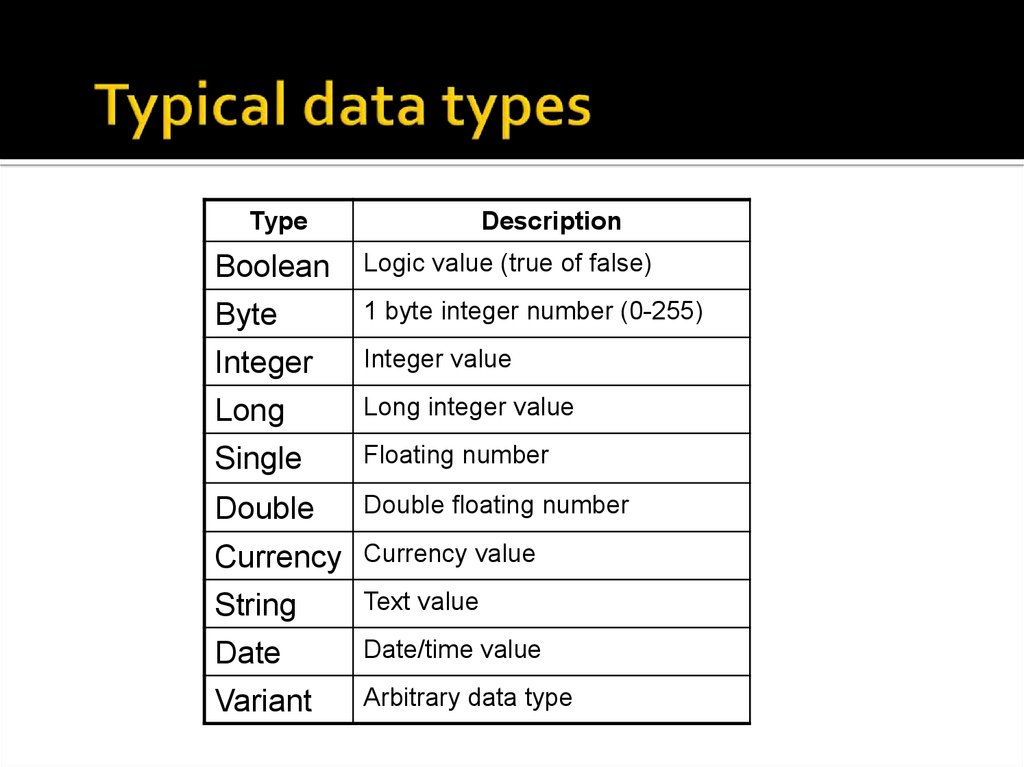
9. Typical data types
TypeDescription
Boolean
Logic value (true of false)
Byte
1 byte integer number (0-255)
Integer
Integer value
Long
Long integer value
Single
Floating number
Double
Double floating number
Currency Currency value
String
Text value
Date
Date/time value
Variant
Arbitrary data type
10. Constant description
[Public|Private] Const <name>= ValueConst PI = 3.14159265
Const Rate$ = 22.45
Const CompanyName= “Microsoft”
…
Embedded into VBA constants start
L = 2 * PI * R
with vb prefix.
…
vbRed – red color
vbSunday – sunday
vbCrLf – new line
vbYesNo – Yes and No buttons
10
11. Boolean data type
The statement – is a sentence which can be true or false.Statement
Simple
2 <= x
x <= 5
2
2
Complex
5
x
5
x
2 <= x and x <= 5
2
5
x
12. Logical operations
Operand – value that takes part in operationsLogical NOT is statement that is opposite to operand:
5 > 2 =True
Not (5 > 2) = False
Logical AND is a statement when both its operands
are true, e.g.
a < x < b is the same as (a < x) And (x < b)
Logical OR is a statement when at least one of its
operands is true.
(i=5) Or (i = n)
13. Date and time datatype
8 bytes in memoryDefault USA format:
#m/d/yy h:mm:ss#
#9/23/06 19:40#
14. Functions to work with data
FunctionDescription
Now
Current date and time
Date
Current date
Year(Date)
Year in Date argument
Month(Date)
Month in Date argument
Day(Date)
Day in Date argument
WeekDay(Date)
Day of week in Date argument (Sunday is 1,
saturday – 7)
DateAdd(interval,
quantity, Date)
Addition of intervals to Date argument
DateDiff(interval,
Date1, Date2 )
Quantity of time intervals between two dates
15. Interval values for DateAdd and DateDiff
ValueDescription
Value
Description
yyyy
Year
d
Day
q
Quarter
h
Hours
m
Month
n
Minutes
ww
Week
s
Seconds
• DateAdd("m",3,Date) – add 3 months to date,
• DateDiff("ww",#1.01.2001#,Date) – amount of
weeks between date and begin of century.
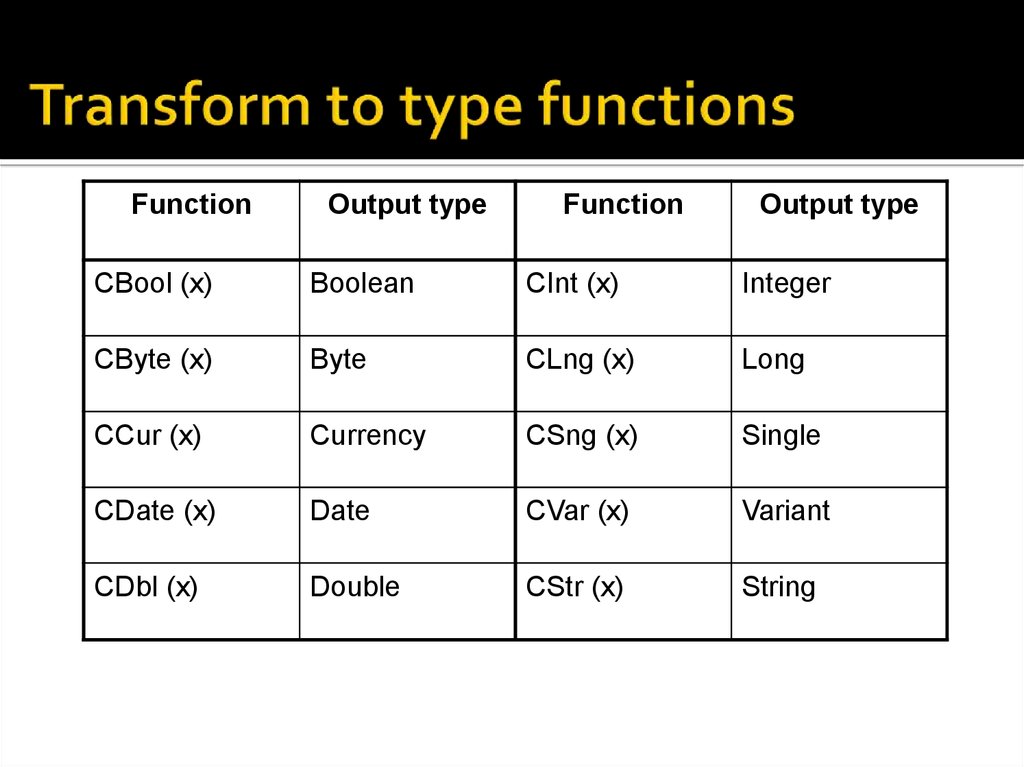
16. Transform to type functions
FunctionOutput type
Function
Output type
CBool (x)
Boolean
CInt (x)
Integer
CByte (x)
Byte
CLng (x)
Long
CCur (x)
Currency
CSng (x)
Single
CDate (x)
Date
CVar (x)
Variant
CDbl (x)
Double
CStr (x)
String
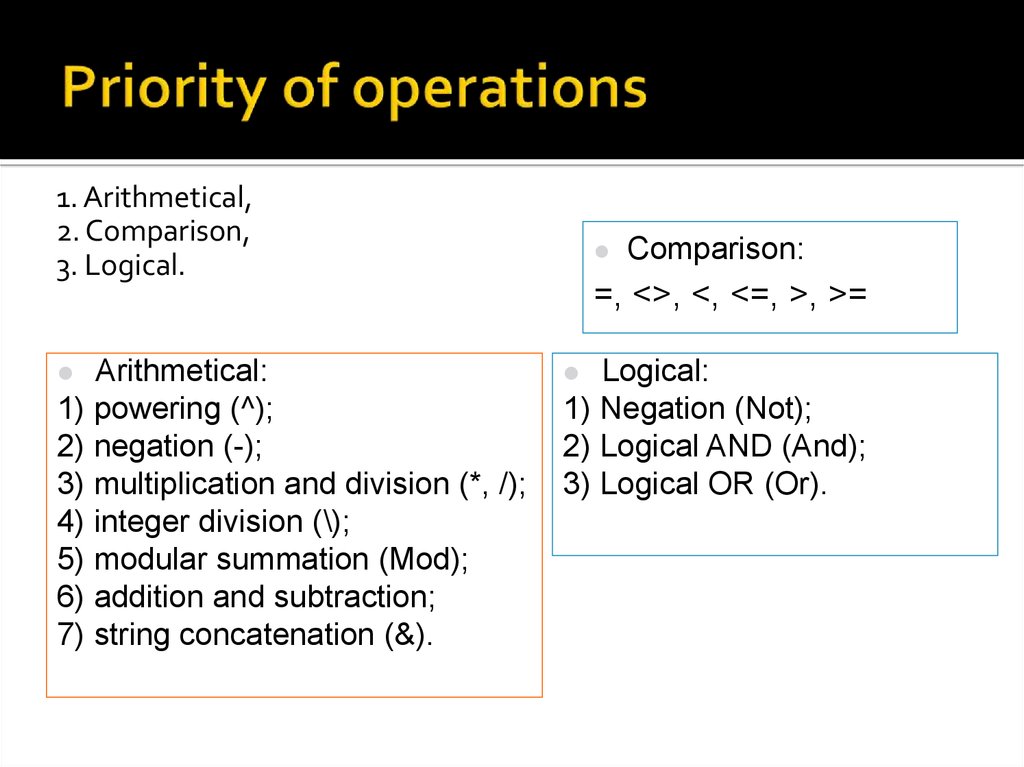
17. Priority of operations
1. Arithmetical,2. Comparison,
3. Logical.
Arithmetical:
1) powering (^);
2) negation (-);
3) multiplication and division (*, /);
4) integer division (\);
5) modular summation (Mod);
6) addition and subtraction;
7) string concatenation (&).
Comparison:
=, <>, <, <=, >, >=
Logical:
1) Negation (Not);
2) Logical AND (And);
3) Logical OR (Or).
18. Variable assignment
variable = valueFirstly value on the right side is calculated,
then result is assigned to variable.
txtCost = txtPrice * txtQuantity
19. Application with different data types
Data type isassigned using Dim
operator.
You may use only
variables those
were described
with Dim earlier.
Option Explicit
operator allows
VBA environment
to look about this
rule
20. Назначение условного оператора
Разветвляющийсяпроцесс – из
нескольких вариантов
выбирают только
один, причем выбор
зависит от условия.
21. Conditional operator
One-line model isused when each
branch contains no
more than single
operator
Block model is used
when at least one
branch has more
than one operator
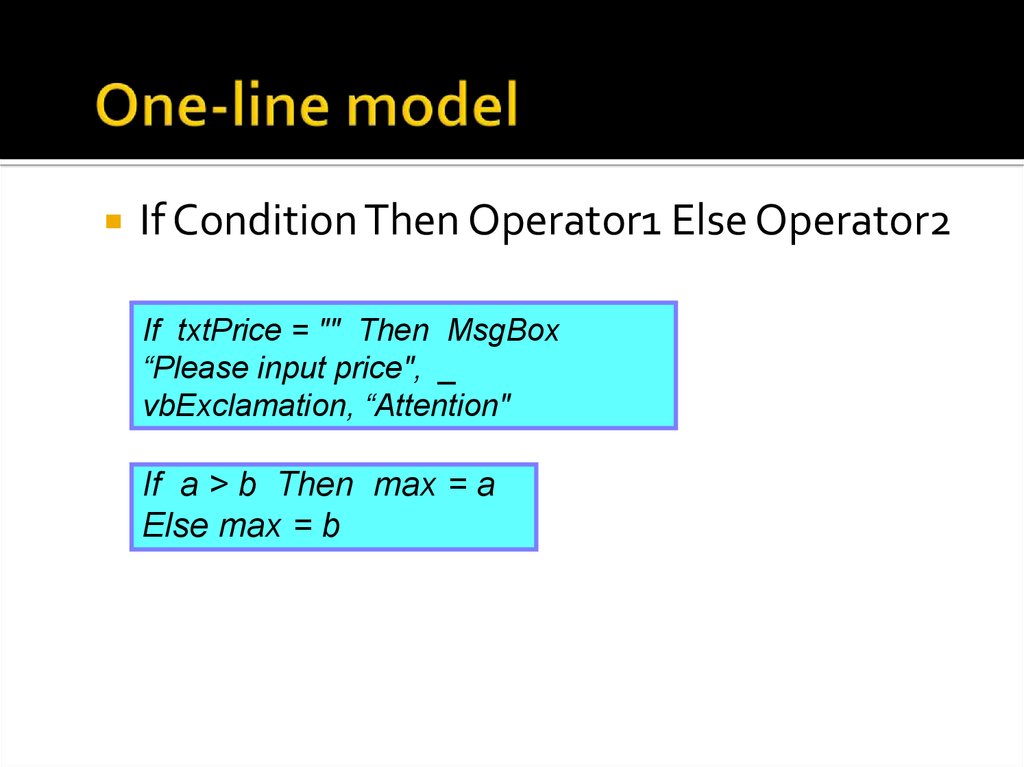
22. One-line model
If Condition Then Operator1 Else Operator2If txtPrice = "" Then MsgBox
“Please input price", _
vbExclamation, “Attention"
If a > b Then max = a
Else max = b
23. Block model
If Condition ThenOperators1
Else
Operators2
End If
If Condition1 Then
Operators1
ElseIf Condition2
Operators2
…
[Else
If Condition Then
Operators
End If
OperatorsN]
End If



















 programming
programming english
english








