Similar presentations:
Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
1. Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
Nina Zlateva, Ph. D.1
2. Integrated Marketing Communication Strategy
2Integrated Marketing
Communication Strategy
The
marketing communication system;
Marketing communication mix;
Integrating the marketing communication mix;
Steps in developing effective communication;
Marketing communications media possibilities;
Marketing communication budget;
Socially responsible marketing communications;
3. Objectives of promotional activities
3Objectives of promotional
activities
Building
awareness;
Creating interest;
Providing information;
Stimulate demand;
Differentiate product;
Reinforce the brand;
4. Major targets of promotional campaigns
4Major targets of promotional
campaigns
The
actual audience;
Influencers;
Distribution channel members;
Other companies;
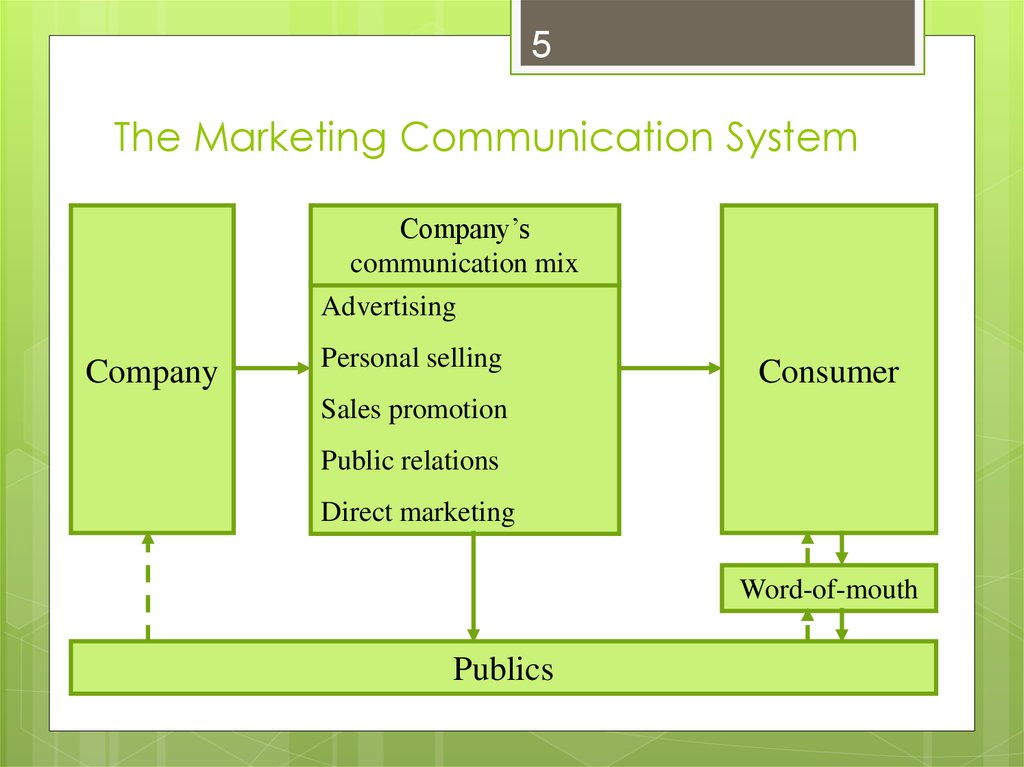
5. The Marketing Communication System
5The Marketing Communication System
Company’s
communication mix
Advertising
Company
Personal selling
Consumer
Sales promotion
Public relations
Direct marketing
Word-of-mouth
Publics
6. Marketing Communication Mix
6Marketing Communication Mix
Advertising – any paid form of non-personal presentation
and promotion of a product by an identified sponsor;
Personal selling – personal presentation by a firm’s sales
force for the purpose of making sales and building customer
relationships;
Sales promotion – short-term incentives to encourage the
purchase of a product;
Public relations – building good relations with company’s
various publics by obtaining favourable publicity, building
up good corporate image, and building or heading off
unfavourable rumours, stories, events;
Direct marketing – direct communications with carefully
targeted individual consumers to both obtain an immediate
response and cultivate lasting customer relations;
7. Important considerations in promotional decisions
7Important considerations in
promotional decisions
Stage
in the product Lifecycle;
Nature of the product;
Cultural sensitivity;
Legal and regulatory conditions;
Competitor actions;
Target market composition;
8. Types of promotional strategies
8Types of promotional
strategies
Push
strategy - A push promotional
strategy involves taking the product
directly to the customer via whatever
means, ensuring the customer is aware of
your brand at the point of purchase.
Pull strategy - A pull strategy involves
motivating customers to seek out your
brand in an active process. "Getting the
customer to come to you“.
9. Managing promotion through the product life cycle
9Managing promotion through
the product life cycle
Introduction
– provide detailed
information about the product;
Growth – increase brand awareness and
foster customer loyalty;
Maturity – create product differentiation
and highlight specific benefits and
features;
Decline – remind that the product exists;
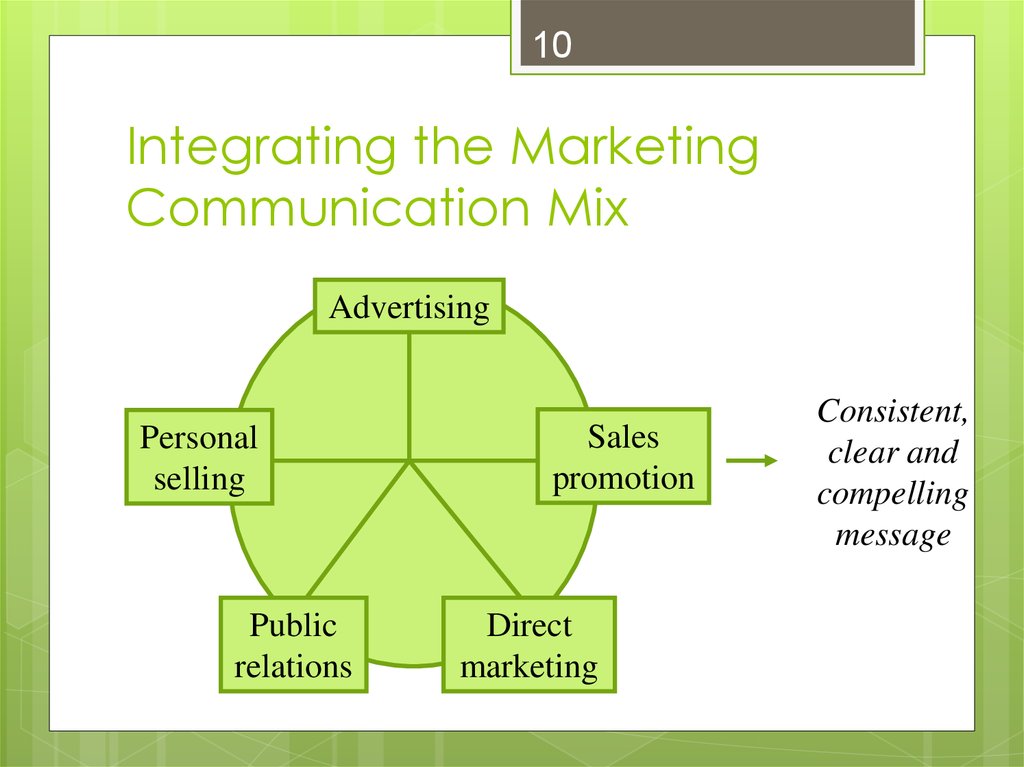
10. Integrating the Marketing Communication Mix
10Integrating the Marketing
Communication Mix
Advertising
Personal
selling
Public
relations
Sales
promotion
Direct
marketing
Consistent,
clear and
compelling
message
11. Growing importance of IMC
11Growing importance of IMC
Taking advantage of synergy among promotional
tools;
Looking for alternative ways to communicate with
target audiences;
Penetrating the skepticism and capturing the
attention of new generations;
Shifting of marketing budget from media
advertising to other forms of promotion;
Rapid growth of database marketing;
Rapid growth of internet;
Developing and sustaining brand identity and
equity;
12. Steps in Developing Effective Communication
12Steps in Developing Effective
Communication
Identifying the target audience;
Determining communication objectives – depending on
the buyer-readiness stage: awareness, knowledge, liking,
preference, conviction, purchase;
Designing a message:
- message content (what to say?) – rational,
emotional or moral appeals;
- message structure (how to say it?) – to make a
conclusion or leave it to the audience, one-sided or twosided arguments, presenting the strongest arguments first
or last;
- message format – headline, copy, illustration,
colour;
13. Steps in Developing Effective Communication (Continued)
13Steps in Developing Effective
Communication
(Continued)
Choosing media
- personal communication channels – face to
face, phone, chat, consumer advocates, family
members, friends, neighbours, co-workers, etc.
- non-personal communication channels – media
(print media: newspapers, magazines, direct mail;
broadcast media: radio, television; display media:
billboards, signs, posters; online media: Internet),
atmospheres, events
- message source – the company, the brand
name, the salesperson of the brand, or the actor in the
ad who endorses the product
Collecting feedback
14. Marketing Communications Media Possibilities (Pickton & Broderick, 2005)
14Marketing Communications Media
Possibilities (Pickton & Broderick, 2005)
Press
– newspapers (daily, weekly, local, regional,
national); magazines (weekly, monthly, quarterly,
annual, general interest, special interest, consumer,
trade, association, company, club); directories
Television – local, regional, national, international,
terrestrial, cable, satellite, video, teletext
Cinema – local, regional, national
Radio – local, regional, national, international
15. Marketing Communications Media Possibilities (Continued)
15Marketing Communications
Media Possibilities
(Continued)
Posters
– transport (on buses, taxis, trains, boats,
poster vans); outdoor (billboards, bins, posts,
benches, flyers, aerial banners, sport ground sites);
indoor (at POS and at exhibitions – on windows,
shopping trolleys, counters, shelves, hanging signs,
on stands and displays, on notice boards, in public
toilets)
Internet – websites, e-mails, blogs
Direct mail – letters, leaflets
16. Marketing Communications Media Possibilities (Continued)
16Marketing Communications
Media Possibilities
(Continued)
People/word-of-mouth
– sales staff, other
employees, customers/consumers, members of the
media, members of the trade, other publics
Leaflets and brochures – annual financial reports,
special offer fliers, press releases, etc.
Stationery – business cards, letterheads, memos, fax
invoices, receipts, envelopes, pencils, pens,
paperclips, etc.
Packaging – all forms and types
17. Marketing Communications Media Possibilities (Continued)
17Marketing Communications
Media Possibilities
(Continued)
Merchandise
items – calendars, diaries, giftware,
greeting cards, labels, bookmarks, clothing items,
nameplates, badges, cups, sport equipment, etc.
Point-of-sale displays (POS) – shelf displays, bins,
carousels, posters, videos, exhibition boards, stands
Livery and signage – signage in and on shops offices,
buildings; vehicle signage (cars, vans, lorries, trains,
planes); uniforms and working clothes; sign posts,
illuminated signs, display signs
Others – postal service, telephone, beer mats, floor
mats, balloons, golf tees and golf holes, back of
receipts/tickets, bags, flags, PR stunts/events, CDs,
DVDs, etc.
18. Marketing Communication Budget
18Marketing Communication
Budget
Maximum
expenses method;
Affordable method;
Percentage-of-sales method;
Competitive-parity method;
Objective-and-task method;
















 marketing
marketing








