Similar presentations:
Integrated approaches to sustainable development practice
1. INTEGRATED APPROACHES TO SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT PRACTICE
Policy Coherence: Migration, Trade, Aid, and DevelopmentMilena Novy-Marx, Ph.D.
John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation
February 26, 2008
2. Overview
1. Impacts of Trade and Migration on Development2. Policy Coherence: Why it Matters
3. Examples of Incoherence
United Kingdom and Migration of Health Workers
Philippines
Agricultural policy in wealthy countries
US, Mexico, and North American Free Trade Agreement
4. Solutions
UK Commonwealth Code of Practice
Global Forum for Migration and Development
5. Conclusion
6. Discussion Questions
3. Impacts of Trade on Development
Presumption that freer trade promotes economicgrowth and development
Comparative
Advantage
Increased efficiency
Freer trade will not promote growth absent basic
founding conditions
Market
imperfections in poorest countries
Lack of basic infrastructure, credit markets
Undeveloped human resources, disease burden, low
agricultural productivity
4. Migration and Development
Worldwide: 200 million international migrants or 3%of global population
Increasing complexity of migration
Half of all migrants are women
Wage and demographic and imbalances between
“North” and “South” create push and pull factors
Paradigm shift to potential positive impacts of migration
on development
Lack of international regime for managing movement of
people, protecting migrants’ rights
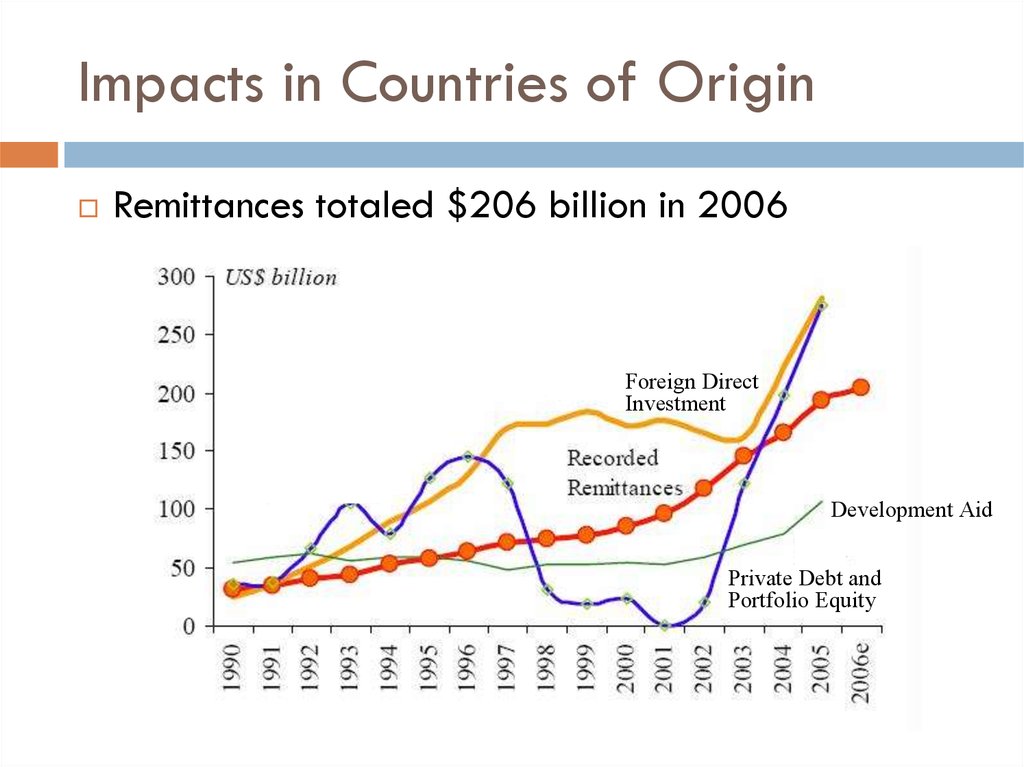
5. Impacts in Countries of Origin
Remittances totaled $206 billion in 2006Foreign Direct
Investment
Development Aid
Private Debt and
Portfolio Equity
6. Impacts in Countries of Origin and Destination
Countries of OriginRemittances – poverty reduction
Release pressure on local labor markets
Brain Drain
Diaspora: Transfers of Knowledge, Investment, Skills,
Contacts, Philanthropy
Countries of Destination
Supply of needed labor (high and low-skilled)
Tax revenue
Multicultural vitality
Migrants vulnerable to abuse
7. Trade and Migration
Differences and Similarities between flows of goodsand people
Complexity of migration due to human dimension
Gains from trade and migration are not evenly
distributed
8. Policy Coherence: Why?
Policy Coherence is the systematic promotion of mutuallyreinforcing policy actions by governments
Policies on trade, aid, development and migration can be
complements
Yet often countries’ policies work at cross purposes
Examples of policy incoherence:
United Kingdom’s (UK) health workforce
Philippines
Developed countries’ agricultural policy
US and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
9. United Kingdom: Health Workers
UK: Migration policy recruits Malawian nursesUK’s aid agency provides aid to Malawi’s health
sector
$120
million in 2004, $34 million for health in 2005
Recruitment from other low-income countries (Africa)
10. Countries with critical health worker shortages
Eventually ethical guidelines established forrecruitment by national health system
11. Philippines
Promoting emigration of doctors and nurses leads toa domestic shortage in health workers
Emigration as national development strategy has
compromised some development outcomes
Decline in health standards
Dependence on remittance/migration model
12. Developed countries’ agriculture, trade, and aid policies
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development(OECD) development assistance promotes trade and
agriculture
Agriculture a key sector for many low-income countries
Yet OECD domestic agriculture and trade policies work at
cross-purposes to these goals
Subsidies for agricultural production
Tariffs on agricultural goods from low-income countries
Increase in non-tariff barriers
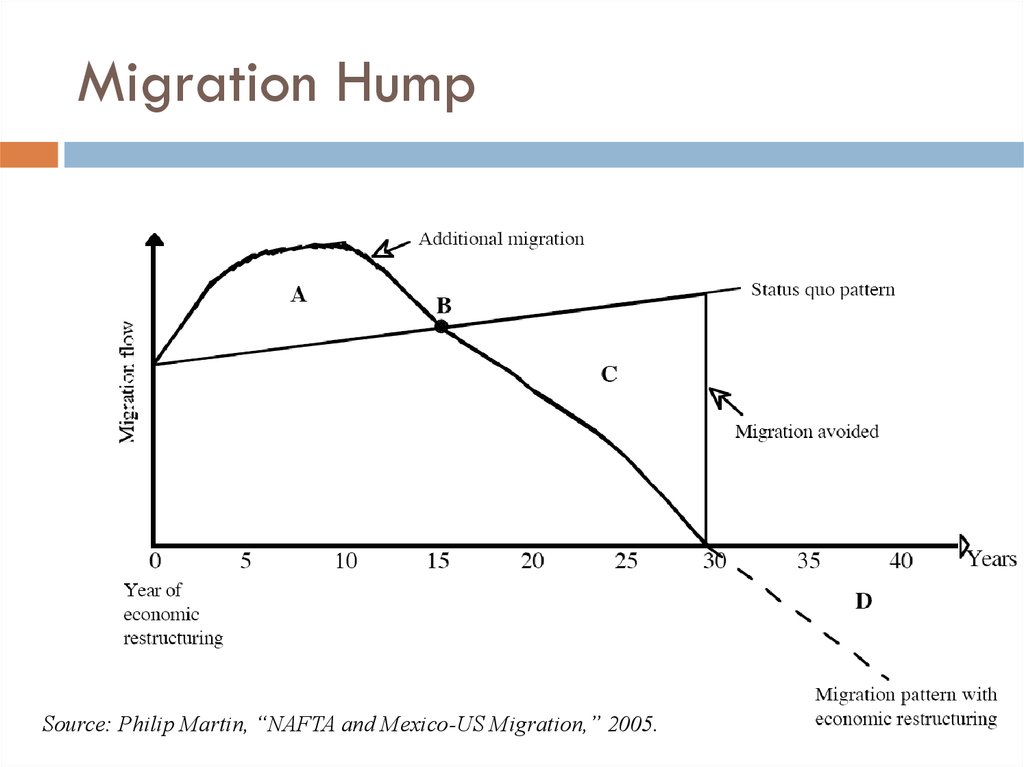
13. US and Mexico: North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
US increased border enforcement to cut migrationwhile the free trade pact increased it
NAFTA does not address migration, subsidies
NAFTA raised pressure for migration to US
Dislocation of farmers
In short-term, freer trade increases migration
In long-term, trade and migration may be
substitutes
14. Migration Hump
Source: Philip Martin, “NAFTA and Mexico-US Migration,” 2005.15. A Policy Solution: United Kingdom
Commonwealth Code of PracticeRestricts recruitment by national health service
Innovative arrangements: hospital twinnings, training
Malawi
UK increases aid to country’s health sector for more
training, higher salaries
Migration of nurses to the UK declines
Challenges:
Balancing right to move with health needs of poorest
Recruitment continues by private sector
16. Global Forum on Migration and Development
Nascent effort to coordinate policies on migrationand development within and between countries
Inter-governmental and civil society meetings to
exchange information and best practices
Non-binding
Governments establish focal points within Ministries
Next Forum in Manila October 2008
17. Policy Recommendations
Governments should:Establish focal points or departments in Ministries
Develop formal consultations between Ministries/agencies
Developing national policies/plans for coherence
Incorporate migration and trade in Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers
(PRSPs)
Improve international coordination
Many challenges remain:
Political commitment
Policy goals often unclear
Effective government institutions and administration
Financial and human resources
Private sector can complement or work against coherence
18. Conclusion
Better coordinated policies on aid, migration andtrade can be complementary, creating synergies for
development
Challenges to implementation
19. Discussion Questions
What are examples of policy incoherence in your country?Has policy coherence improved in any areas?
Is policy coherence primarily an issue for developed countries?
What lessons can be drawn from the cases discussed?
How should development be defined and measured? By the
well being of individuals from a country, regardless of
residence? Or by per capita income of those remaining incountry?
Should individuals have the right to migrate?
20. INTEGRATED APPROACHES TO SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT PRACTICE
Policy Coherence: Migration, Trade, Aid andDevelopment Lecture
Milena Novy-Marx


















 economics
economics








