Similar presentations:
DNA and Replication
1. DNA and Replication
12. Replication Facts
•DNA has to be copied before a celldivides (before mitosis)
•New cells will need identical DNA
strands
•Replication of DNA is copying of
DNA
2
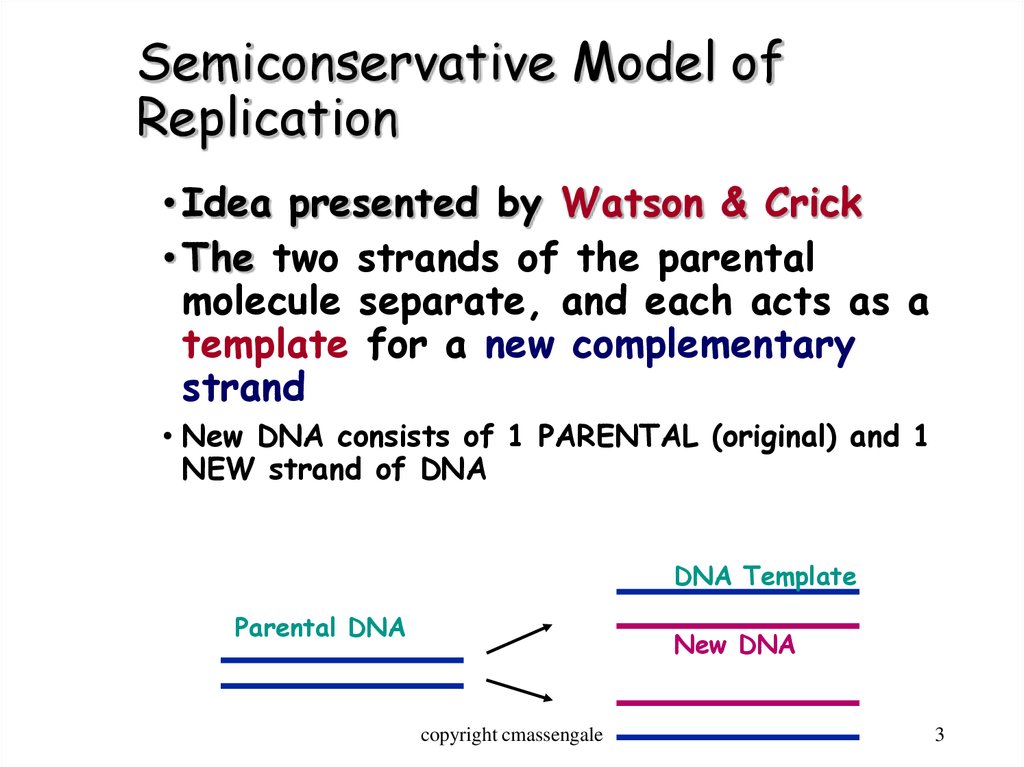
3. Semiconservative Model of Replication
• Idea presented by Watson & Crick• The two strands of the parental
molecule separate, and each acts as a
template for a new complementary
strand
• New DNA consists of 1 PARENTAL (original) and 1
NEW strand of DNA
DNA Template
Parental DNA
New DNA
copyright cmassengale
3
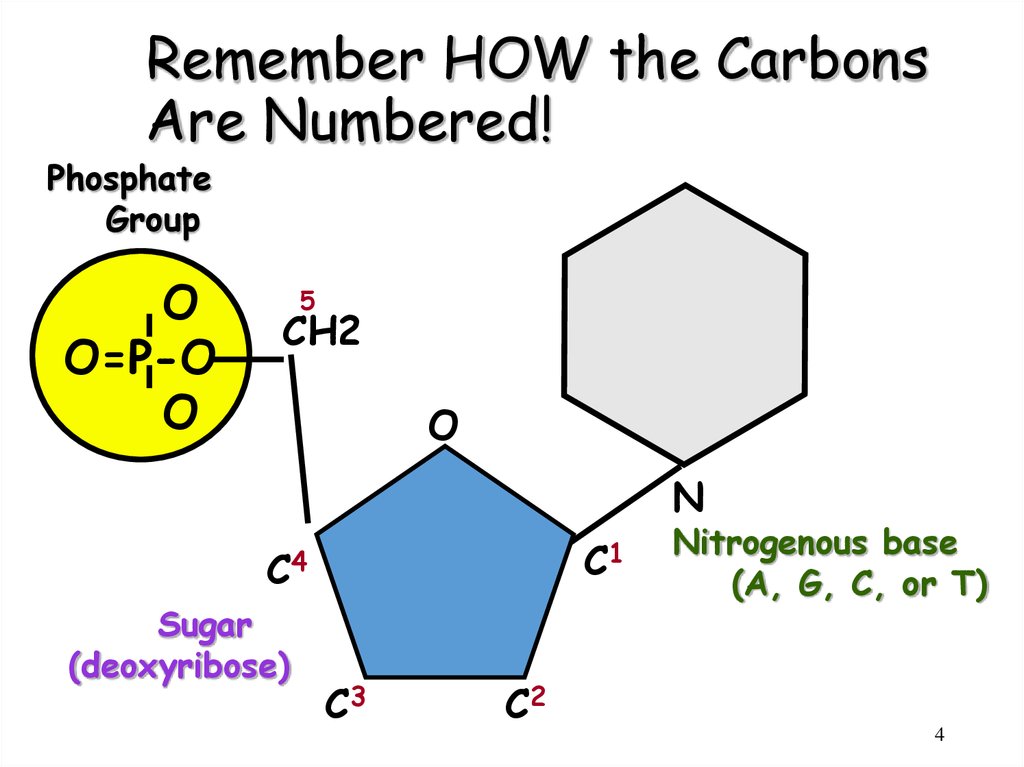
4. Remember HOW the Carbons Are Numbered!
PhosphateGroup
O
O=P-O
O
5
CH2
O
N
C1
C4
Sugar
(deoxyribose)
C3
C2
Nitrogenous base
(A, G, C, or T)
4
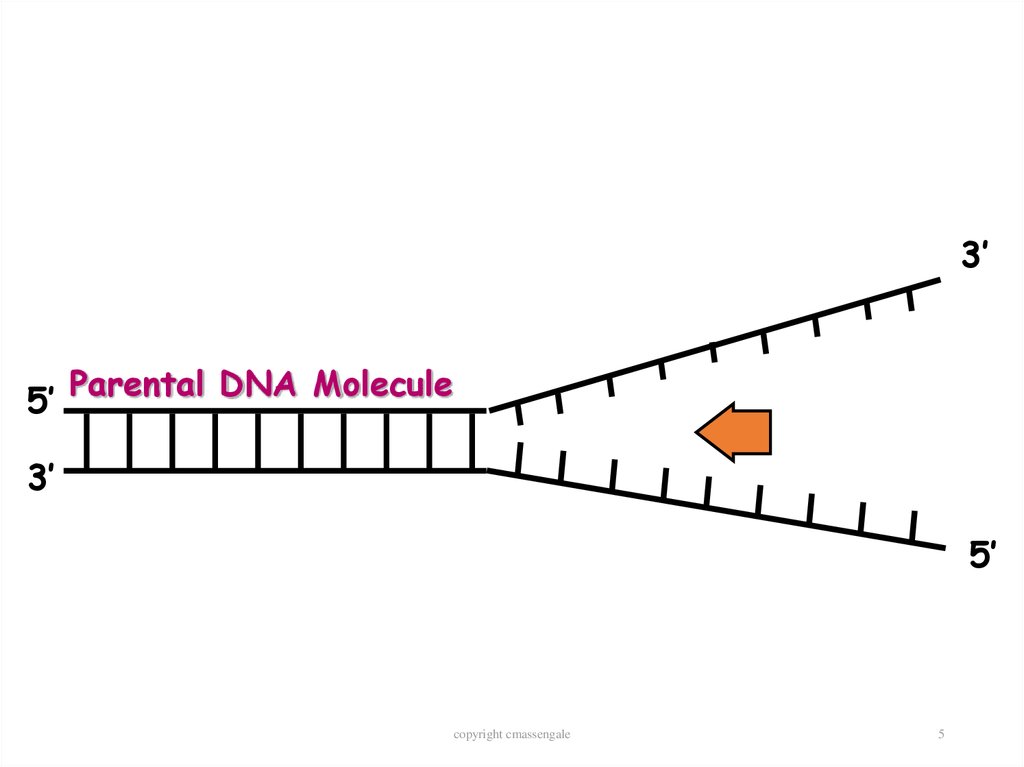
5.
3’5’
Parental DNA Molecule
3’
5’
copyright cmassengale
5
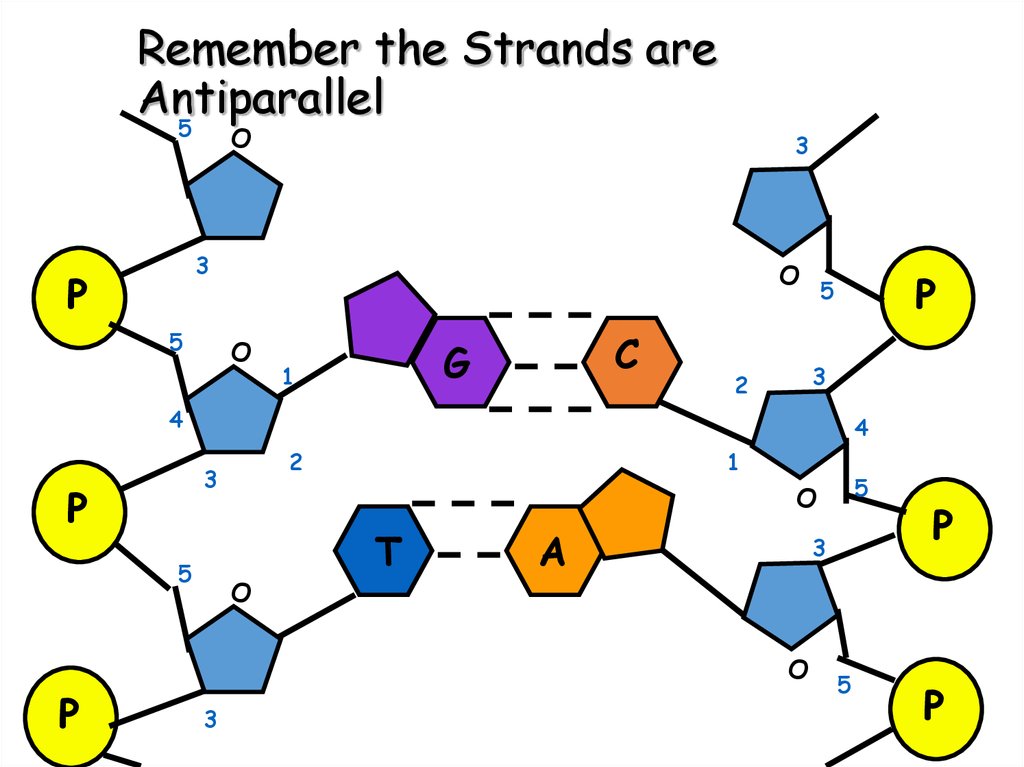
6. Remember the Strands are Antiparallel
5O
3
3
P
5
O
O
C
G
1
P
5
3
2
4
4
P
5
P
2
3
1
O
T
A
3
O
3
5
O
5
P
P
6
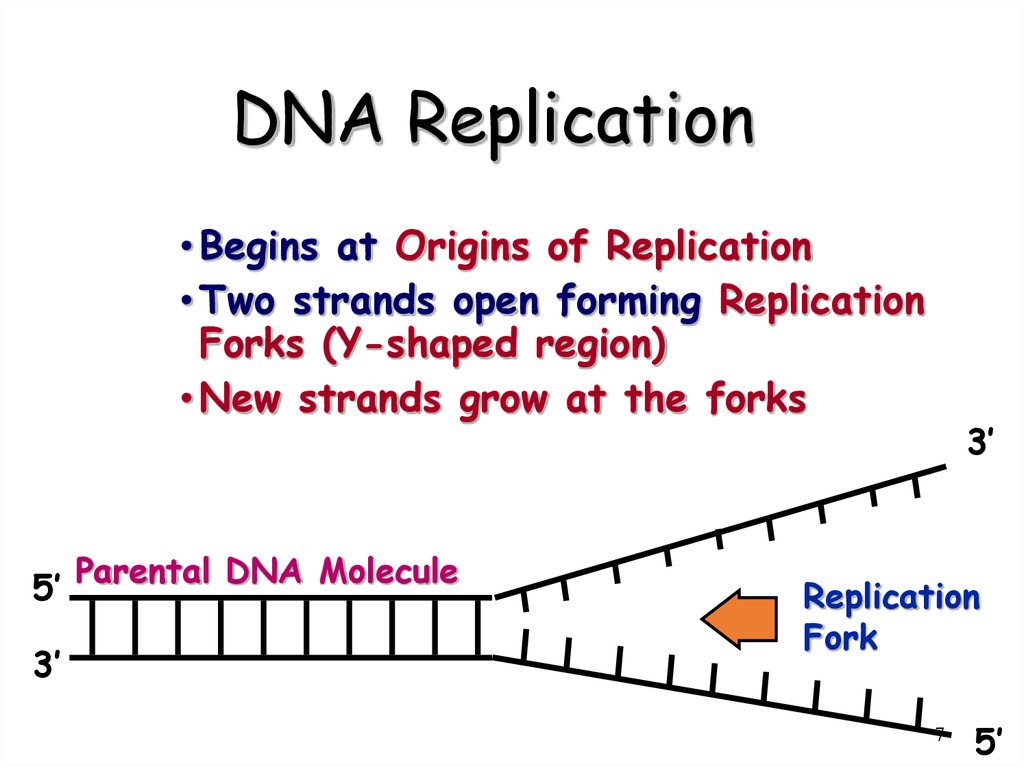
7. DNA Replication
• Begins at Origins of Replication• Two strands open forming Replication
Forks (Y-shaped region)
• New strands grow at the forks
5’ Parental DNA Molecule
3’
3’
Replication
Fork
7
5’
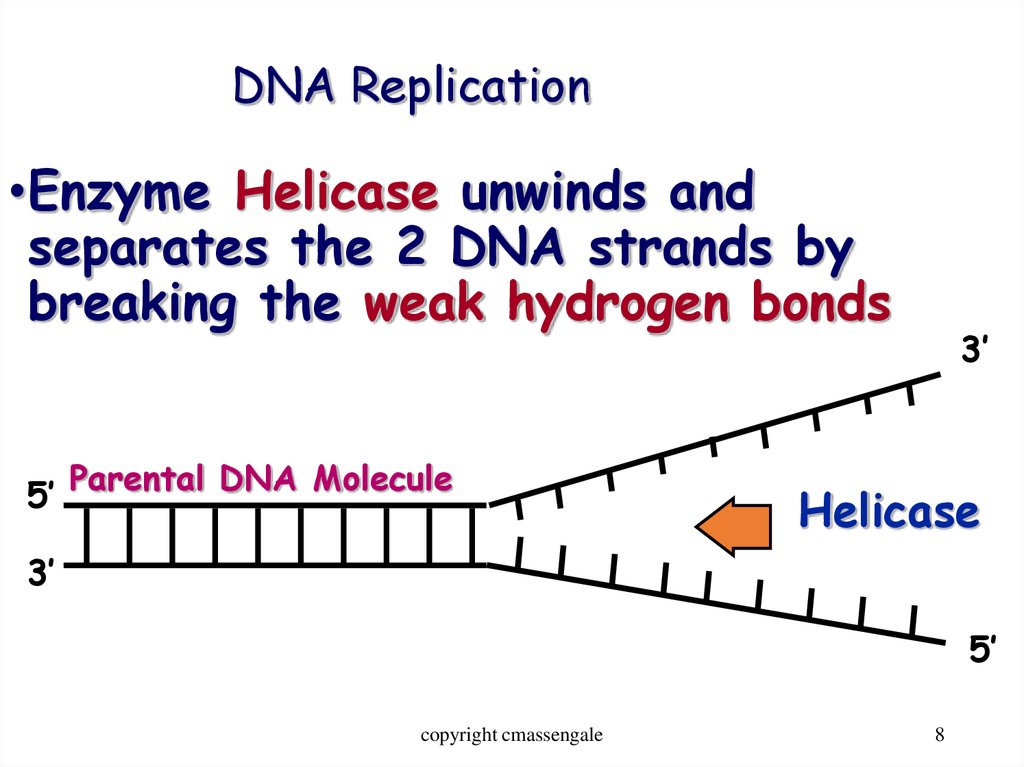
8. DNA Replication
•Enzyme Helicase unwinds andseparates the 2 DNA strands by
breaking the weak hydrogen bonds
5’ Parental DNA Molecule
3’
Helicase
3’
5’
copyright cmassengale
8
9. DNA Replication
• Before new DNA strands can form,there must be RNA primers present
to start the addition of new
nucleotides
• Primase is the enzyme that
synthesizes the RNA Primer
• DNA polymerase can then add the
new nucleotides
copyright cmassengale
9
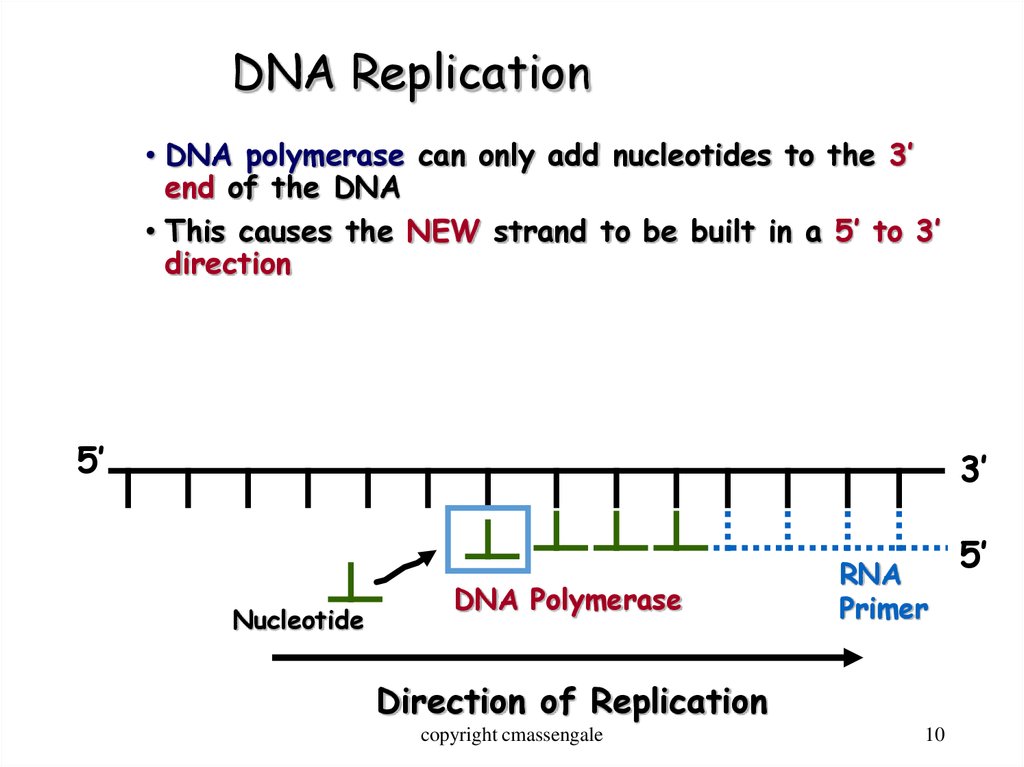
10. DNA Replication
• DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3’end of the DNA
• This causes the NEW strand to be built in a 5’ to 3’
direction
5’
3’
Nucleotide
DNA Polymerase
RNA
Primer
Direction of Replication
copyright cmassengale
10
5’
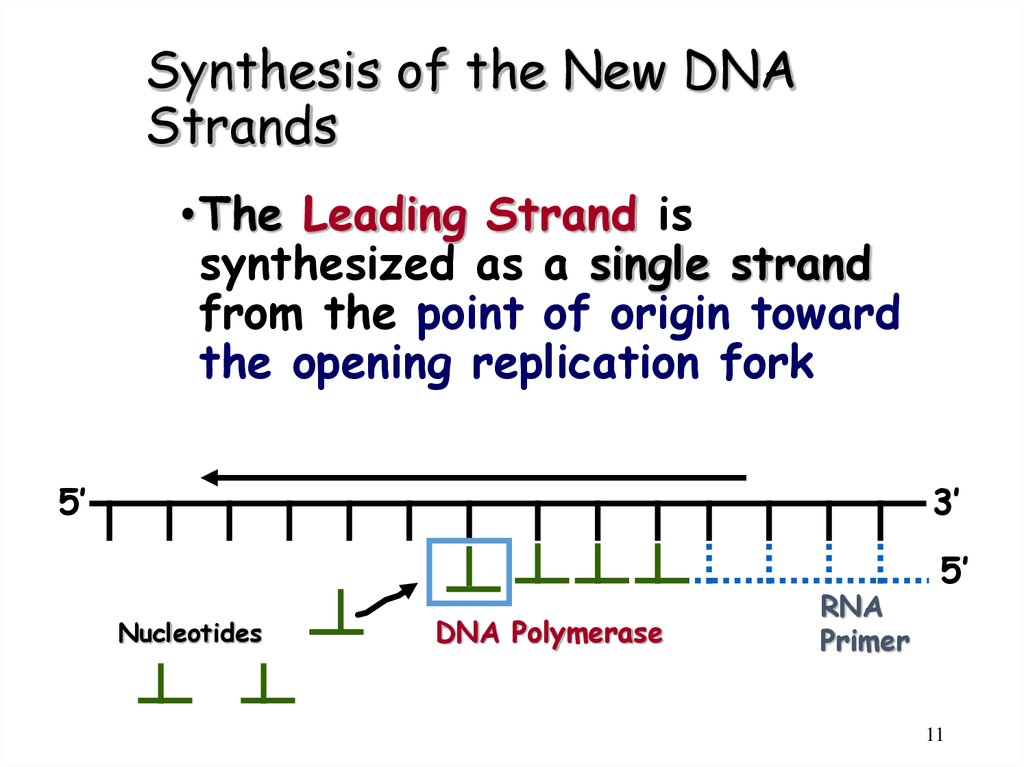
11. Synthesis of the New DNA Strands
•The Leading Strand issynthesized as a single strand
from the point of origin toward
the opening replication fork
5’
3’
Nucleotides
DNA Polymerase
RNA
Primer
5’
11
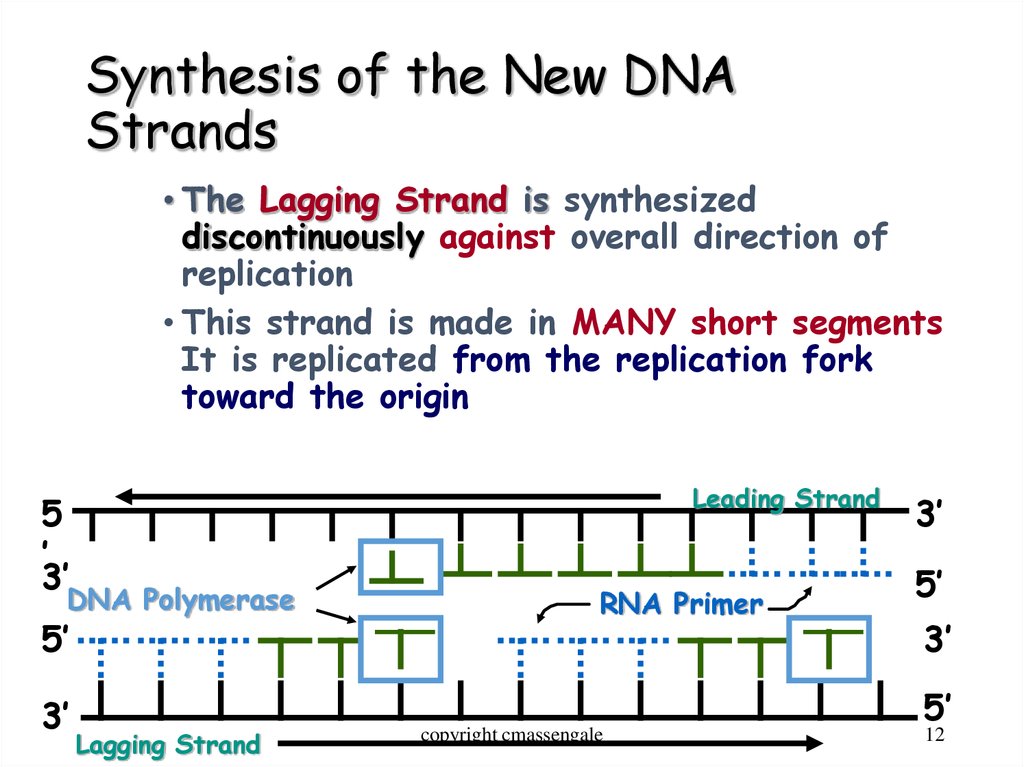
12. Synthesis of the New DNA Strands
• The Lagging Strand is synthesizeddiscontinuously against overall direction of
replication
• This strand is made in MANY short segments
It is replicated from the replication fork
toward the origin
Leading Strand
5
’
3’
DNA Polymerase
5’
3’
Lagging Strand
RNA Primer
copyright cmassengale
3’
5’
3’
5’
12
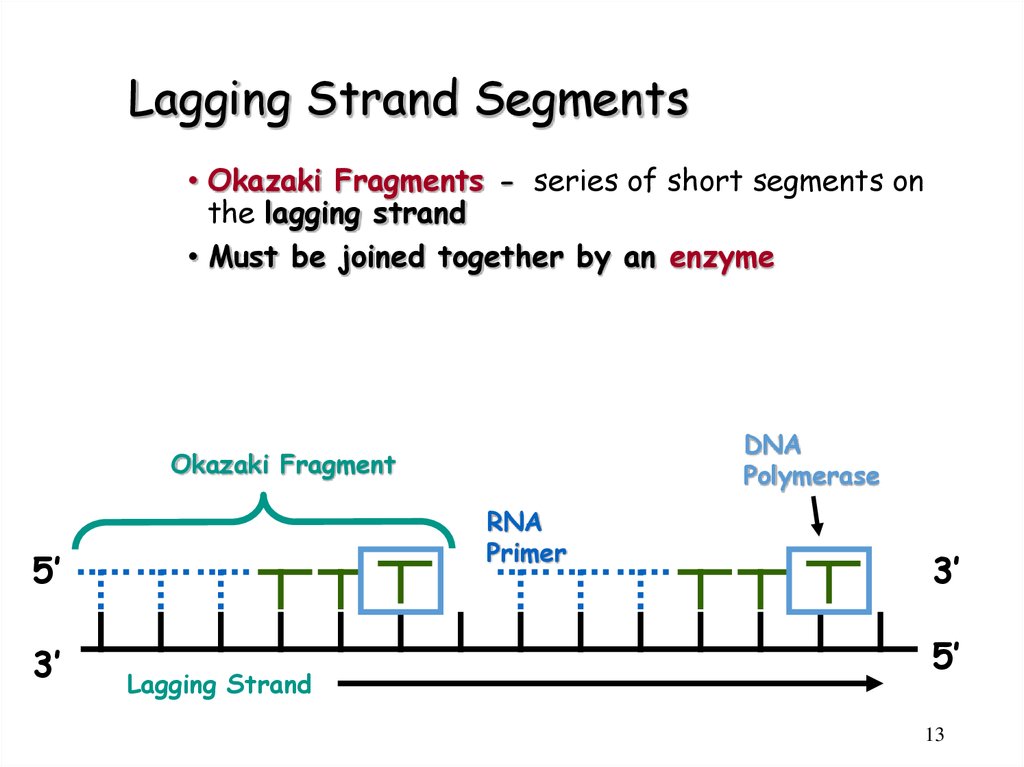
13. Lagging Strand Segments
• Okazaki Fragments - series of short segments onthe lagging strand
• Must be joined together by an enzyme
DNA
Polymerase
Okazaki Fragment
RNA
Primer
5’
3’
Lagging Strand
3’
5’
13
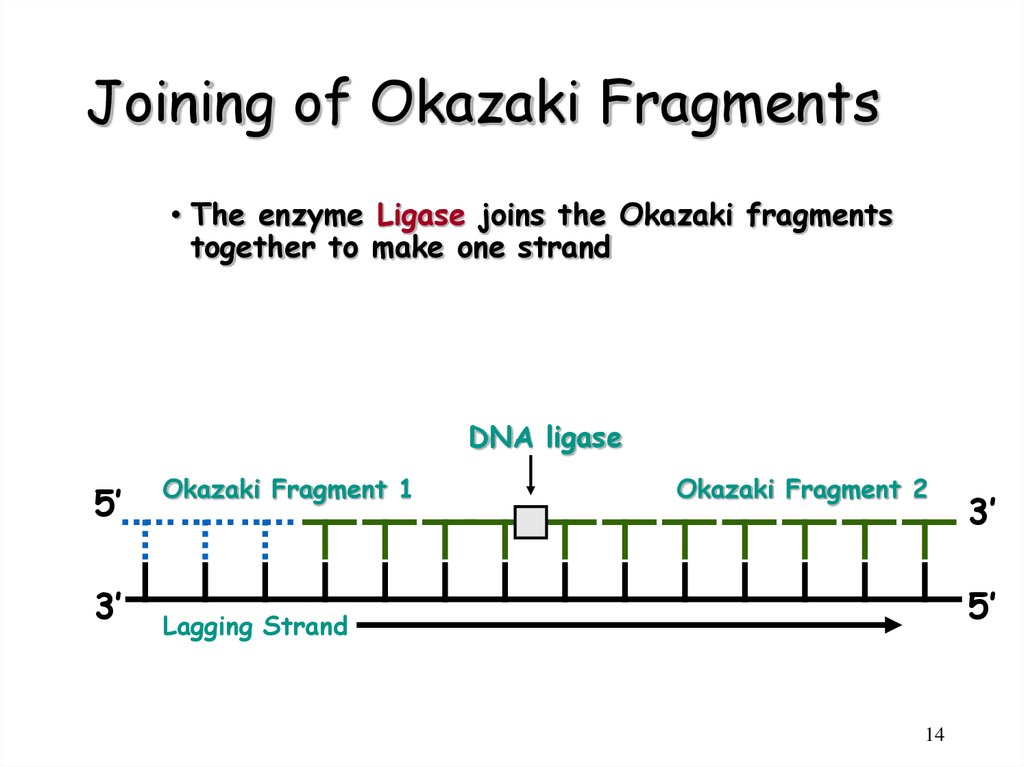
14. Joining of Okazaki Fragments
• The enzyme Ligase joins the Okazaki fragmentstogether to make one strand
DNA ligase
5’
3’
Okazaki Fragment 1
Okazaki Fragment 2
3’
5’
Lagging Strand
14
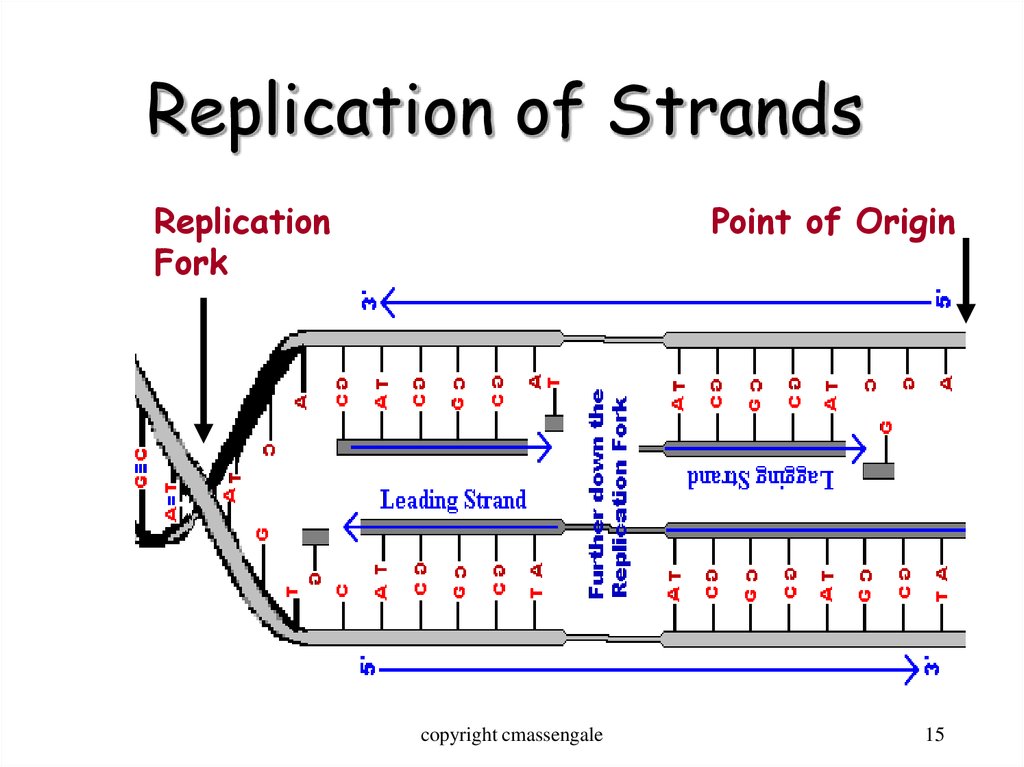
15. Replication of Strands
ReplicationFork
Point of Origin
copyright cmassengale
15
16.
copyright cmassengale16



 biology
biology