Similar presentations:
One or more alternatives lead to a block of possible outcomes with unknown probabilities. Subjective decision-making
1.
How managers can make a decisionin an uncertainty environment?
2.
2One or more alternatives lead to a block of possible
outcomes with unknown probabilities
Subjective decision-making
3.
3…no reliable data…
4.
42 approaches to decision making
under conditions of uncertainty
The Manager uses the
available information and
experience to define
subjective probabilities > risk
conditions
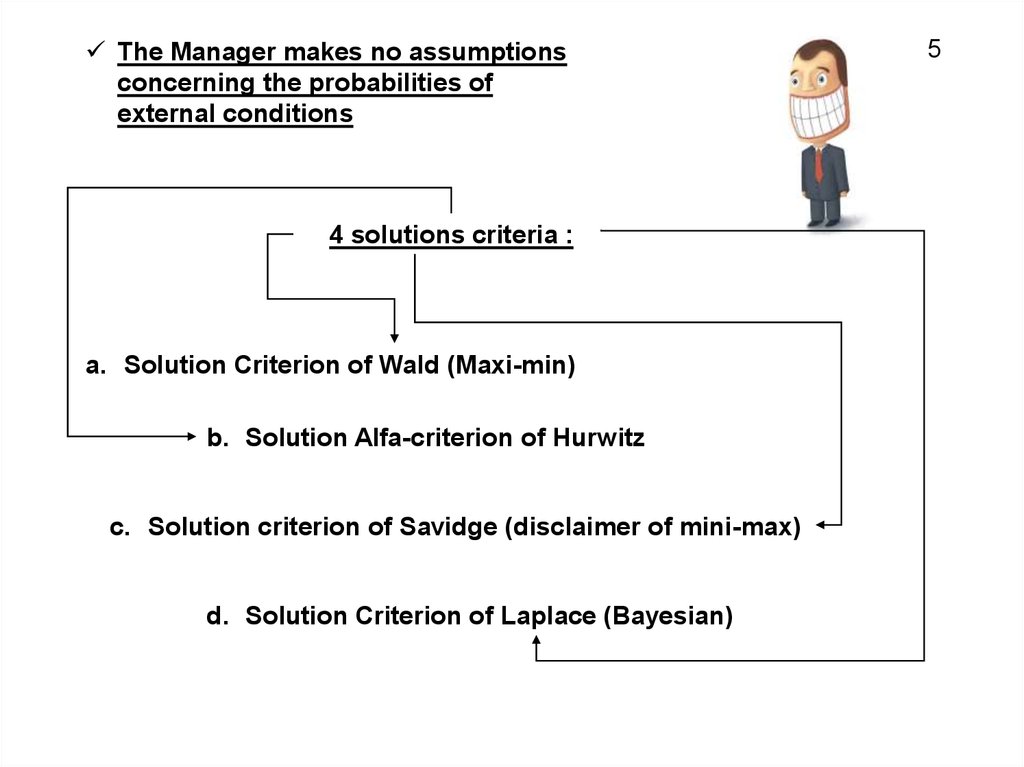
The Manager makes no assumptions
concerning the probabilities of external
conditions
5.
The Manager makes no assumptionsconcerning the probabilities of
external conditions
4 solutions criteria :
a. Solution Criterion of Wald (Maxi-min)
b. Solution Alfa-criterion of Hurwitz
c. Solution criterion of Savidge (disclaimer of mini-max)
d. Solution Criterion of Laplace (Bayesian)
5
6.
6The most suitable
criteria?
7.
7…take into account philosophy, temperament and
viewpoints of the present leadership of the company
8.
8a. Solution Criterion of Wald (Maxi-min)
The criterion of conservatism and attempt to
maximize reliability
External conditions are moody
and freakish
9.
9Define the worst possible result of each
strategy
Choose the strategy that provides the best
of the worst results
10.
11…probability of different states of economy are unknown
Decision matrix
Alternative
strategies
The state of the external environment
Criteria
Maxi-min
Maxi-max
11.
11Strategy S1 is just the most conservative - it implies the
lowest risks, but at the same time promises the lowest
profit
12.
12The criterion is suitable for small commercial
firms whose survival depends on the ability to
avoid losses
13.
13b. Solution Alfa-criteria of Hurwitz
d
Determine the index of the solution for each strategy, which is an
average weighted of its extreme outputs
Weighing factors
the coefficient of optimism alpha
and its addendum 1 -
α, which applies to the maximum return M,
α , which is applicable to the minimum return m
The cost of each strategy:
d i M i (1 )mi
The strategy with the highest value for di selected as
the optimal
14.
14The coefficient of optimism
α is located in the range from 0 to 1
15.
d i M i (1 )miIf a Manager is a
pessimist, he may
decide that α= 0
=> Maxi-Min
15
If the Manager is
optimistic, he
may decide that
α=1
=> Maxi-max
16.
Suppose that a Manager is optimistic and decides that a = 0,7d i M i (1 )mi
17.
17…depends on the amount of
….
….depends on their own relations “Manager for risk”…
18.
18Alpha-Hurwitz criterion: draw attention to the worst and
the best return of the concrete strategies
19.
19c. Solution criterion of Savage (disclaimer of mini-max)
Explores losses incurred as a result of making the wrong
decision
Losses are measured as the absolute difference between
the returns for this strategy, and returns of the most
effective strategy within the same state of the economy.
20.
Within each column, the biggest return is deducted from each of the next 20return in column (including yourself). The absolute difference between the
positions is a measurement of losses
Matrix of losses
21.
21The meaning of measurement of losses:
if we have chosen a strategy that provides the most
value for this condition, then we do not consider
losses
22.
22But if we choose any other strategy, the loss is the
difference between what happens in fact, and the
return that we would get by adopting a more optimal
solution
23.
When I use the criterion of Savidge, I refuseattempt to maximize the profit and choose
the strategy with a satisfactory return but
lower risk
It is useful for the evaluation of a series of projects over
a long period!





















 management
management








