Similar presentations:
History of the kazakhstan architecture
1. History of the kazakhstan architecture
HISTORY OF THEKAZAKHSTAN
ARCHITECTURE
Lecture 1
2. Lecture 1. Ancient times
1.Main stages of development of Kazakhstan material culture2. Geographical, cultural and historical regions of Kazakhstan
3. The most ancient monuments in the territory of Kazakhstan:
- sites and caves;
- settlements and dwellings;
- memorial and cult constructions;
- megaliths
3. Main stages of Architecture development in Kazakhstan
1. Ancient times(140 000 BC– V c. BC);
2. Medieval
(VI – XIX c. AD)
3. New and Newest times
(XX-XXI c.)
4. Ancient times
1. PALEOLITH, NEOLITH(140 000-5000 BC)
2. BRONZE ERA
(5000-1000 BC)
3. EARLY NOMADS ERA
(VII c. BC – V c. AD)
5. Medieval times
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
Period of Turkic khaganates (VI-IX centuries);
Karakhanid’s Era (X-XII centuries);
The Mongolian period (XIII – 1st part of the XV
century);
Period of the Kazakh khanates (2nd part of the
XV-XVIII centuries);
Kazakhstan as a part of the Russian Empire (XIX
– the head of the XX century);
6. New and Newest times
1.Soviet period (ХХ c.);
2.
Independence period (since 1990).
7. Geographical, cultural and historical regions – architectural schools of Kazakhstan
1.2.
3.
4.
Central and Northern Kazakhstan
Eastern Kazakhstan
Southern and Southeast
Kazakhstan
Western Kazakhstan
8. Paleolithic monuments (140,000-40,000 BC)
The most ancient workshop ZhetykonyrCaves (Kazy-Kurt, Karatau, Bayan-Aul, Karkaraly,
Ulytau (Central Kazakhstan); Bukhtarma, New
and Nikolsky caves (Eastern Kazakhstan)
Settlements Kanay (Eastern Kazakhstan), Kalkan
(Southeast Kazakhstan).
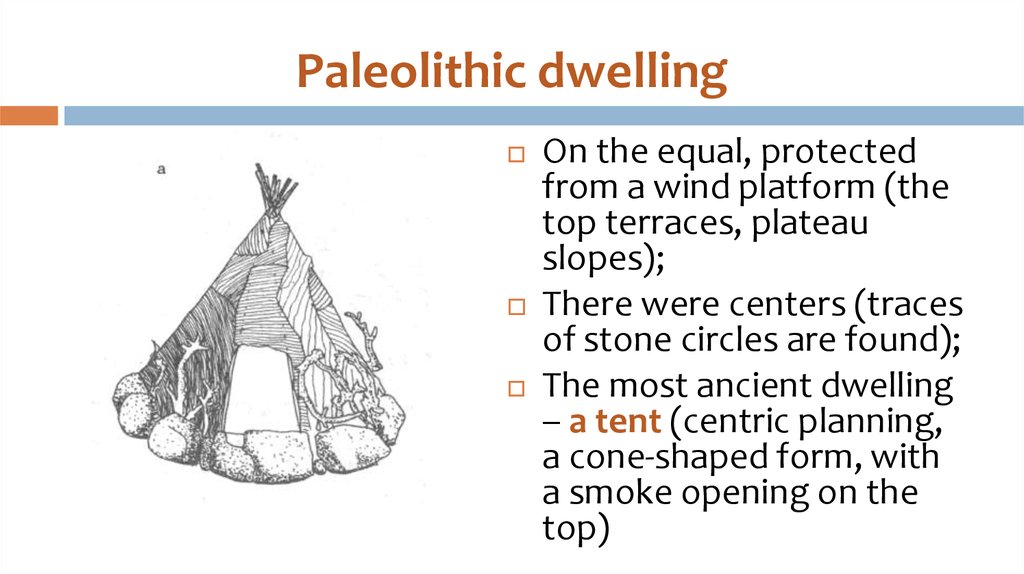
9. Paleolithic dwelling
On the equal, protectedfrom a wind platform (the
top terraces, plateau
slopes);
There were centers (traces
of stone circles are found);
The most ancient dwelling
– a tent (centric planning,
a cone-shaped form, with
a smoke opening on the
top)
10. Aydakharly cave (Ulytau mountains, Central Kazakhstan)
11. Neolithic monuments
Types of Neolythic sites:Spring (Satchy-kyz, Eastern Kazakhstan region)
River (Makhandzhar, Nothern Kazakhstan
region)
Lake (Shatpakol, Atyrau Region)
Cave (Karaungur, Southern Kazakhstan region)
12. Botay Settlement (3,000-2,000 BC)
The Ayirtau district ofNothern Kazakhstan
region, the area is 15
hectares;
About 250 dwellings are
dug out;
Numerous remains of the
cultivated horse are
found
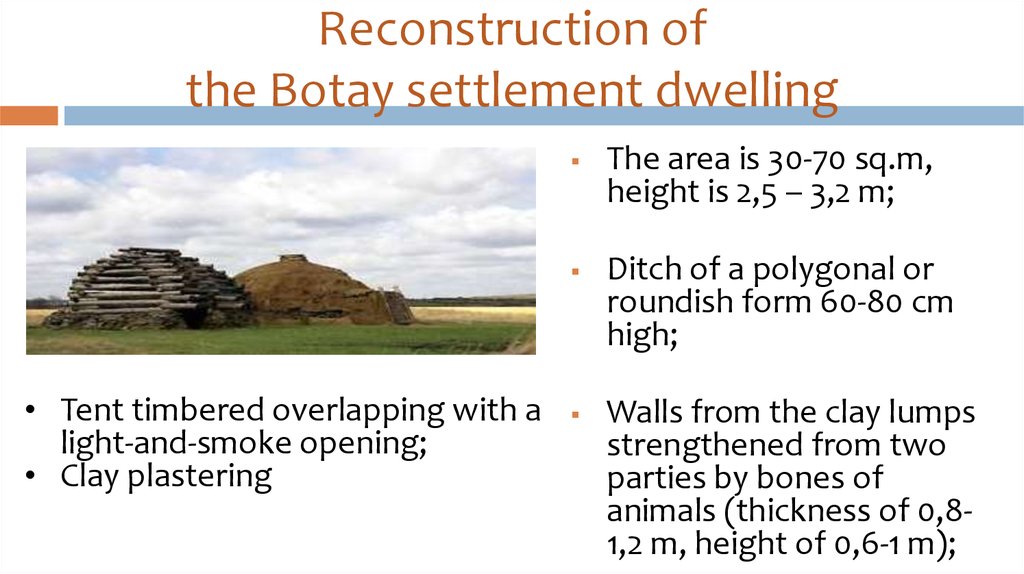
13. Reconstruction of the Botay settlement dwelling
• Tent timbered overlapping with alight-and-smoke opening;
• Clay plastering
The area is 30-70 sq.m,
height is 2,5 – 3,2 m;
Ditch of a polygonal or
roundish form 60-80 cm
high;
Walls from the clay lumps
strengthened from two
parties by bones of
animals (thickness of 0,81,2 m, height of 0,6-1 m);
14. Settlements of Andronov culture (XVIII-XII c. BC)
Alekseev settlement (Kostanay region);Sadchikov settlement (Kostanay region);
Atasu settlement (Jana-Arka district of the Karaganda
region);
Settlements of Buguly 1,2,3; Akbauyr, Shortandy-Bulak,
Senkebay (Shet district of the Karaganda region);
Tagibay settlement (Bayan-Aul district).
In total more than 60 settlements and 200 large burial
grounds are revealed.
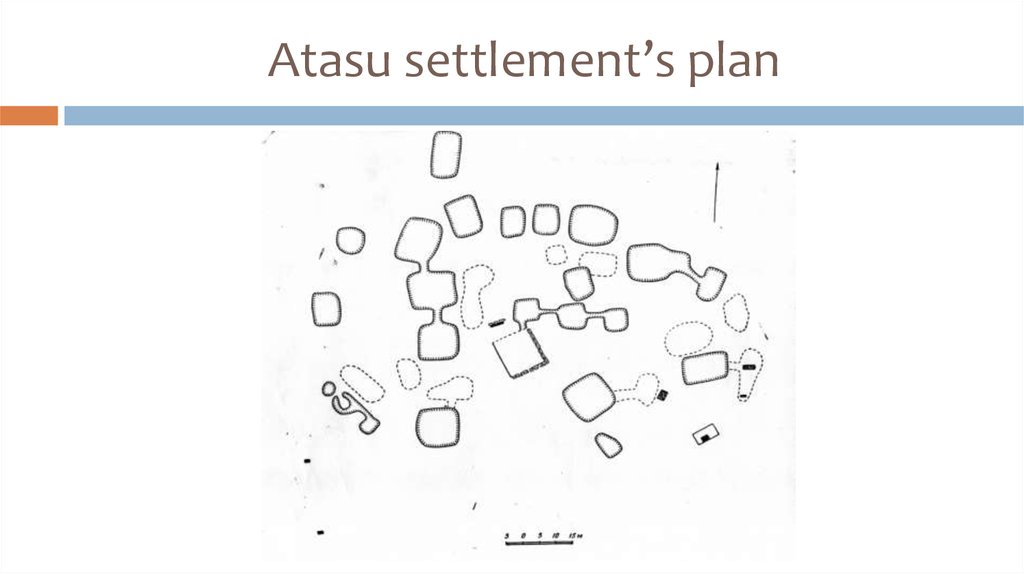
15. Atasu settlement (XV-XII c.BC)
The area is about 15 hectares;Has ring-shaped planning with an open central area;
The remains of 35 structures are found (22 –
inhabited semi-dugouts of 80-250 sq.m);
Rectangular and square planning of dwellings, some
rooms are connected by underground corridors;
Overlapping on wooden columns; 4 central columns
bear a pyramidal-and-step tent.
16. Atasu settlement’s plan
17. Atasu. Facing of the dwelling walls
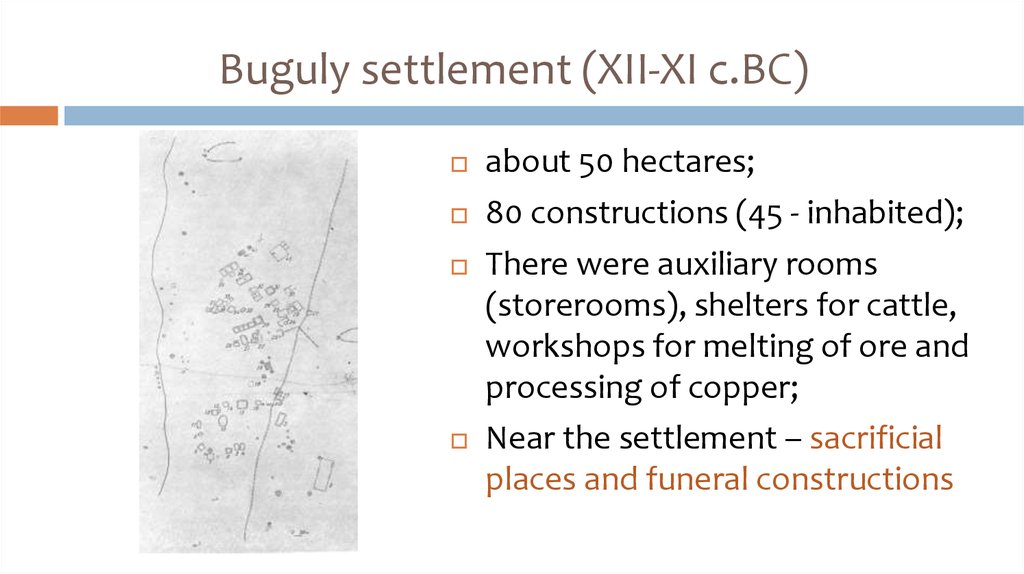
18. Buguly settlement (XII-XI c.BC)
about 50 hectares;80 constructions (45 - inhabited);
There were auxiliary rooms
(storerooms), shelters for cattle,
workshops for melting of ore and
processing of copper;
Near the settlement – sacrificial
places and funeral constructions
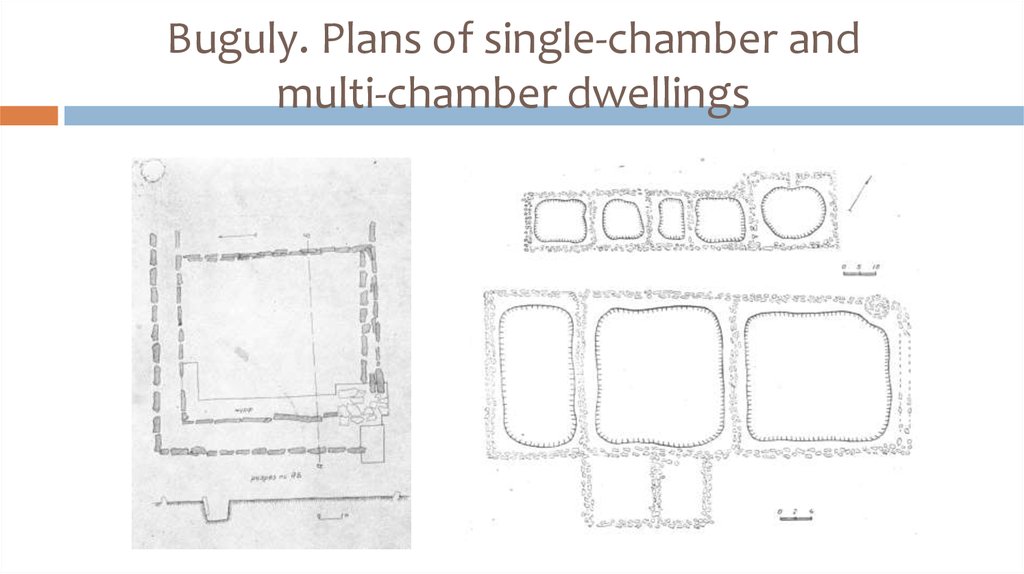
19. Buguly. Plans of single-chamber and multi-chamber dwellings
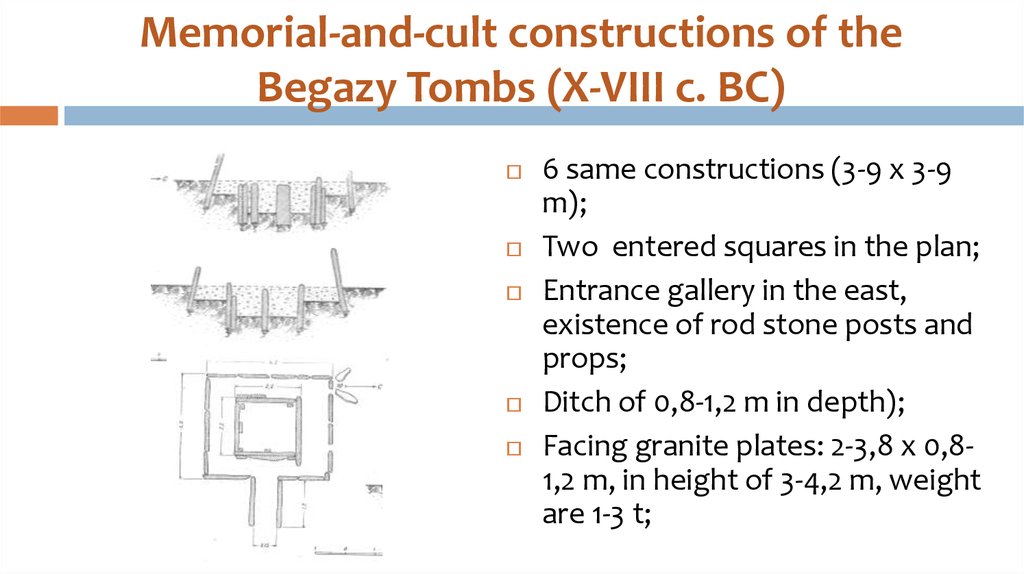
20. Memorial-and-cult constructions of the Begazy Tombs (X-VIII c. BC)
6 same constructions (3-9 x 3-9m);
Two entered squares in the plan;
Entrance gallery in the east,
existence of rod stone posts and
props;
Ditch of 0,8-1,2 m in depth);
Facing granite plates: 2-3,8 x 0,81,2 m, in height of 3-4,2 m, weight
are 1-3 t;
21.
22.
23.
24.
25. Shagalaly settlement (Central Kazakhstan, XII-IX c. BC)
Semi-dugouts up to 500sq.m;
Rectangular, oval, 8-like
plans;
The 8-like structure consists
of two roundish rooms
(D=10m), are connected by
pass 2 m long, 1 m wide;
Roof on wooden columns;
In dwellings there were wells
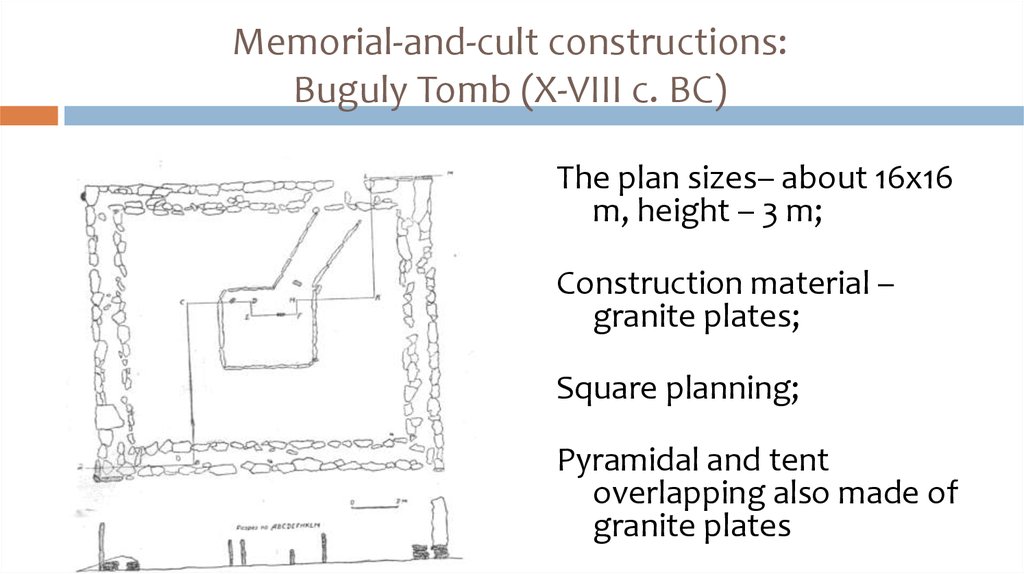
26. Memorial-and-cult constructions: Buguly Tomb (X-VIII c. BC)
The plan sizes– about 16х16m, height – 3 m;
Construction material –
granite plates;
Square planning;
Pyramidal and tent
overlapping also made of
granite plates
27. Megalithic structures
Avenues of menhirs (the single: alyp-tas, dau-tas,bagana-tas, sym-tas; groups: korgan-tas, rope-tas);
Kotan-tas – ring-shaped protections made of the big
stone blocks with an embankment or without;
Stone boxes Besik-tas;
Dolmens (square or rectangular in the plan);
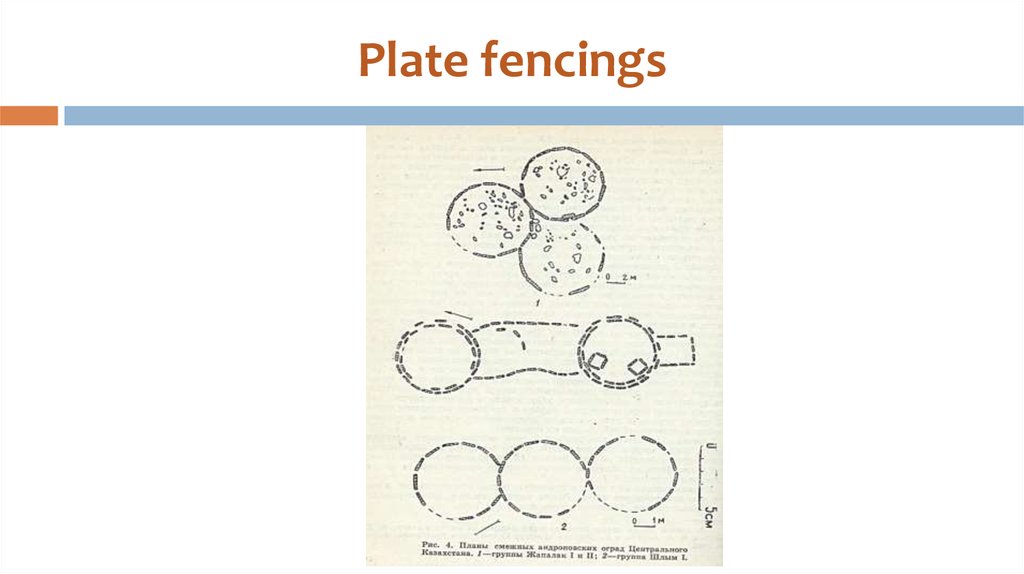
Zist;
Cromlechs and plate fencings.
28. Avenue of menhirs (Kanat-tas). Korpetay mountains (Karkaraly district, Karaganda region)
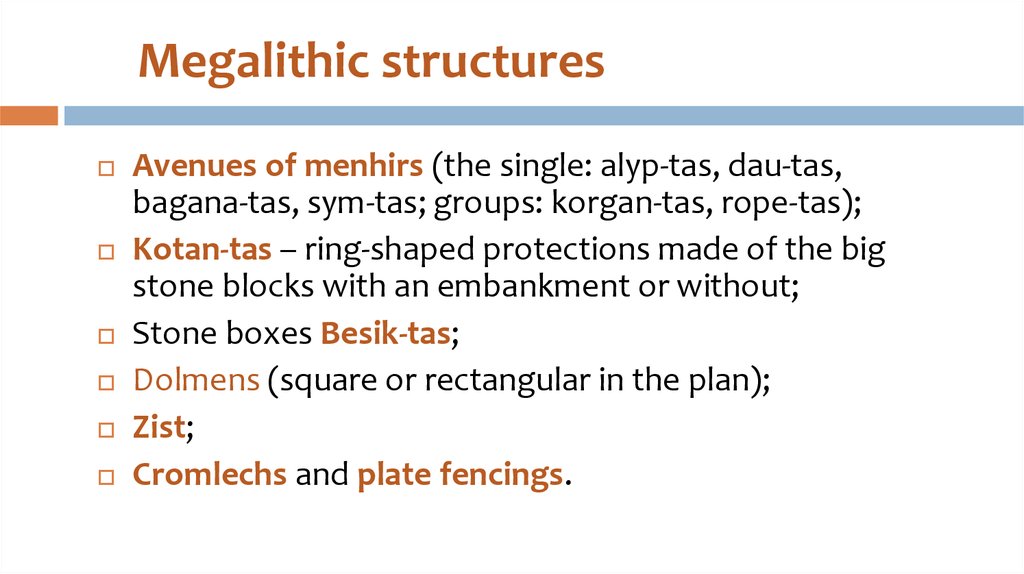
29. Plate fencings
30.
31. The Dolmen. Sangru settlement
32. The Zist. Sangru settlement
33. The Zist. Akchatau mountains
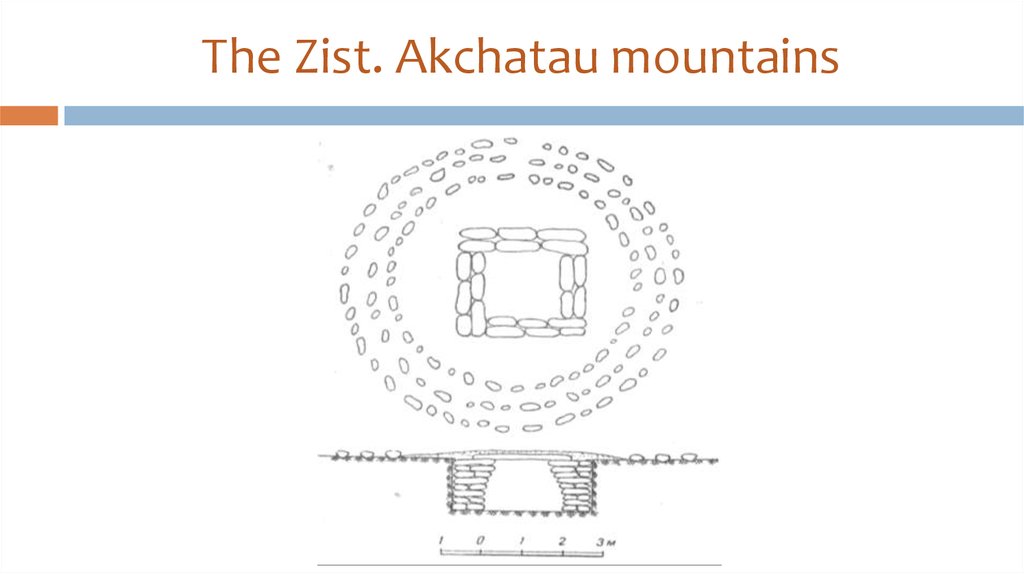
34. Aksu-Ayuly tomb (Shet district, Karaganda region)
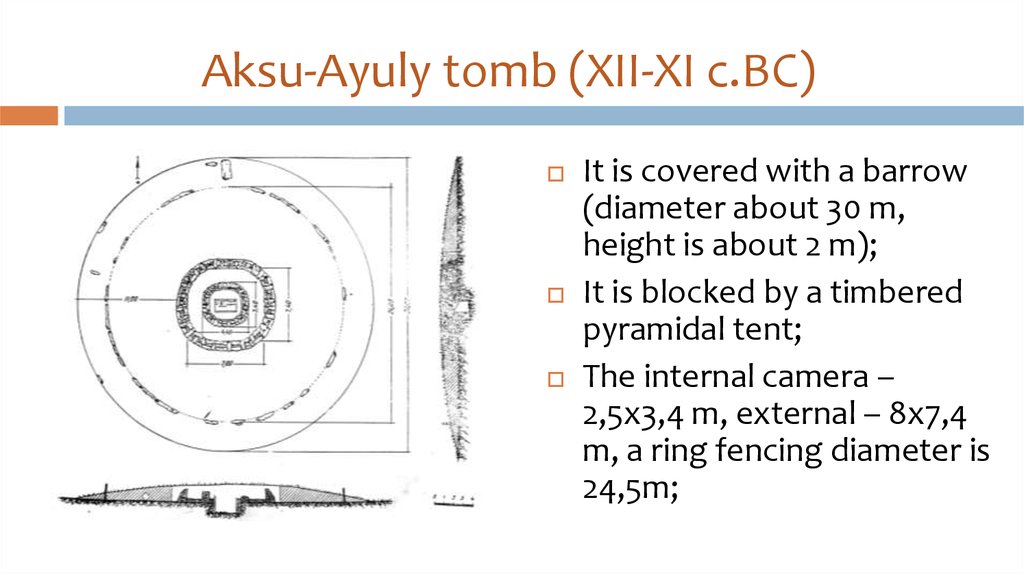
35. Aksu-Ayuly tomb (XII-XI c.BC)
It is covered with a barrow(diameter about 30 m,
height is about 2 m);
It is blocked by a timbered
pyramidal tent;
The internal camera –
2,5х3,4 m, external – 8х7,4
m, a ring fencing diameter is
24,5m;
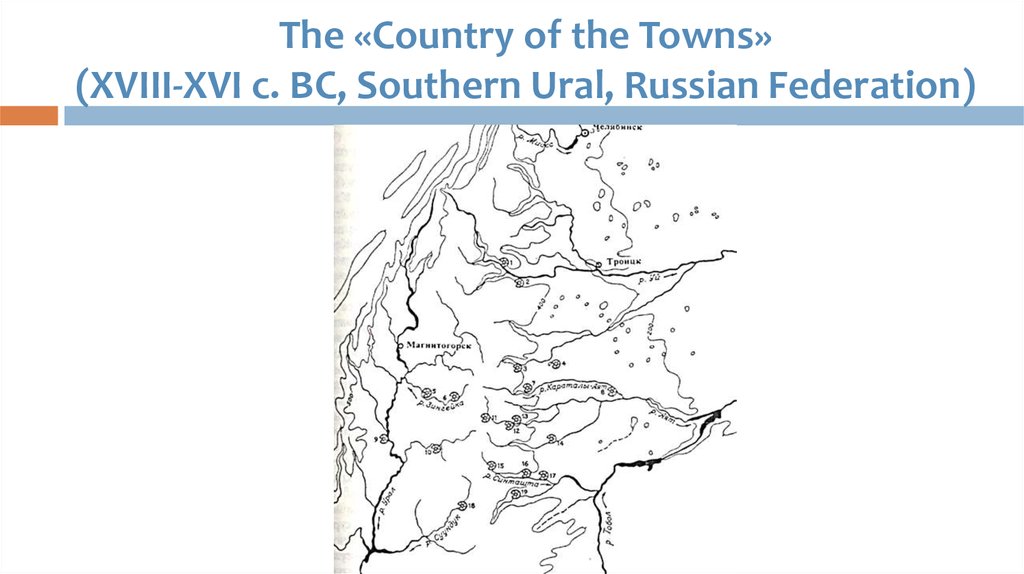
36. The «Country of the Towns» (XVIII-XVI c. BC, Southern Ural, Russian Federation)
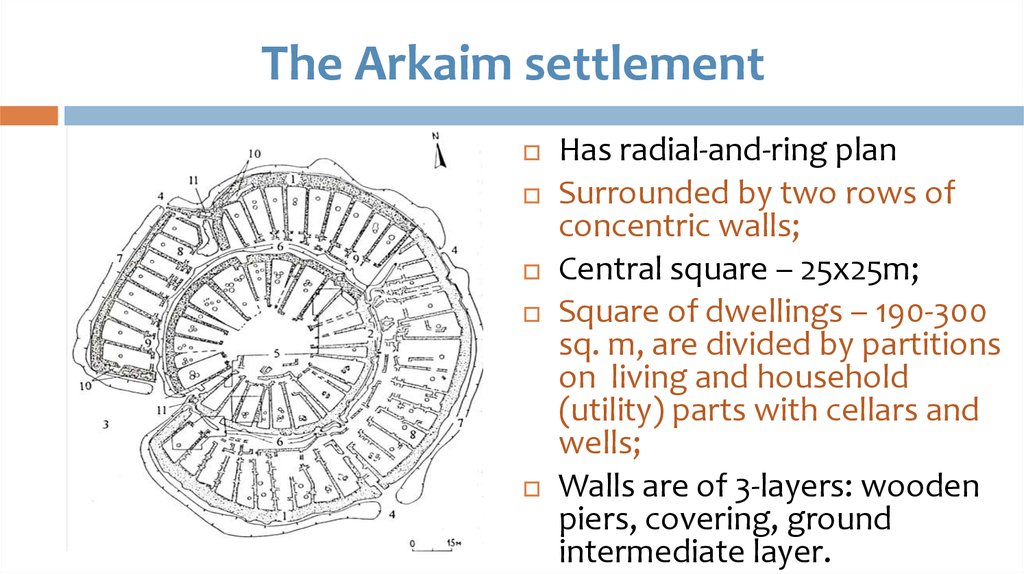
37. The Arkaim settlement
Has radial-and-ring planSurrounded by two rows of
concentric walls;
Central square – 25x25m;
Square of dwellings – 190-300
sq. m, are divided by partitions
on living and household
(utility) parts with cellars and
wells;
Walls are of 3-layers: wooden
piers, covering, ground
intermediate layer.
38. The Toqsanbay settlement (3,000-2,000 BC, Beyneu district of Mangistau region)
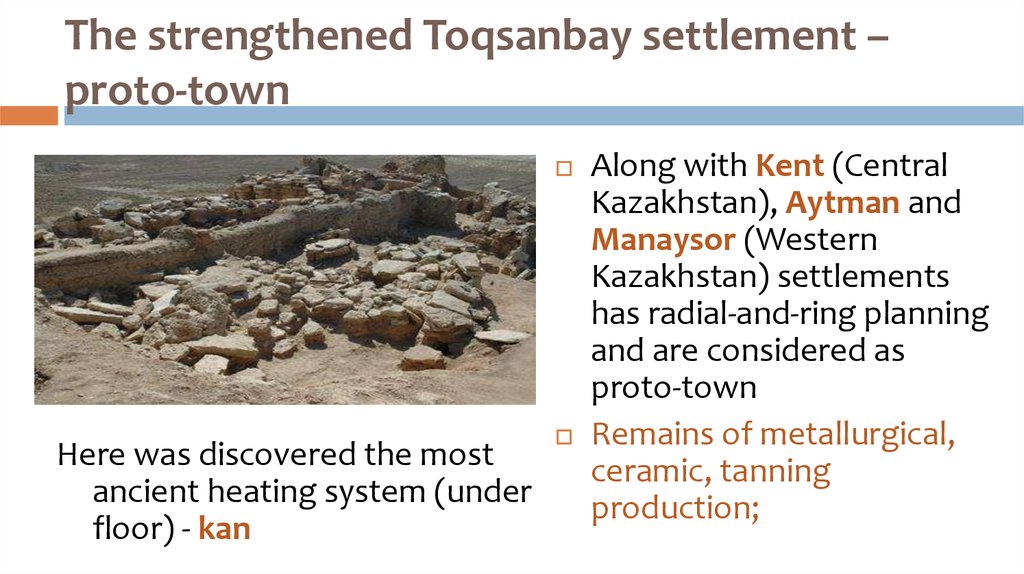
39. The strengthened Toqsanbay settlement – proto-town
Here was discovered the mostancient heating system (under
floor) - kan
Along with Kent (Central
Kazakhstan), Aytman and
Manaysor (Western
Kazakhstan) settlements
has radial-and-ring planning
and are considered as
proto-town
Remains of metallurgical,
ceramic, tanning
production;























 history
history








