Similar presentations:
Social production. The problem of choice in the economy
1. Theme: Social production. The problem of choice in the economy
Production and main elements. The resources and factors ofproduction. The system of economic relations.
The problem of choice in resource-limited settings.
Production possibilities curve.
The need resource-saving technologies. Prospects of
Kazakhstan in the development of resource-saving
technologies.
2.
Social production - the process of creating wealth byconverting natural resources to meet human needs. To
expand this concept more fully, it is necessary to consider
the factors of production.
In political economy, there are 2 sets of social production:
the neoclassical and the Marxist.
Neoclassical believed that there are four factors of
production. This capital, labor, land and entrepreneurship.
Representatives of Marxist theory - that the production
process is primarily a labor process which is carried out
under the influence of a social formation.
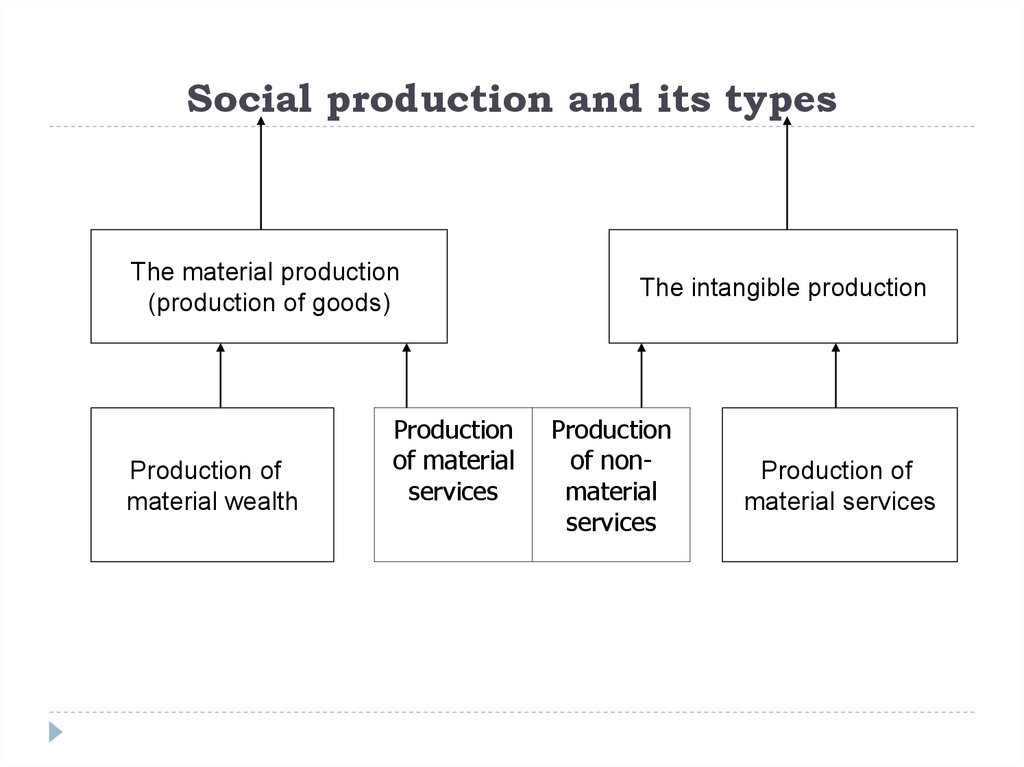
3. Social production and its types
The material production(production of goods)
Production of
material wealth
Production
of material
services
The intangible production
Production
of nonmaterial
services
Production of
material services
4.
PRODUCTION OF GOODS - production is directly linked to thecreation of material wealth that satisfy certain needs of man and
society. Material production is opposed to non-productive sphere,
which is not aimed at the production of material values. This division
is mainly characteristic of Marxist theory.
THE INTANGIBLE PRODUCTION - associated with the
provision of non-material services (health, education)
PRODUCTION OF MATERIAL WEALTH - it is a certain kind
of human activity, a certain way of procuring the means of life
necessary to meet the material and spiritual needs
PRODUCTION OF MATERIAL SERVICES is inseparably
connected with material objects: transport changes the position of
objects in space, trade - they belong to anyone.
PRODUCTION OF NON-MATERIAL SERVICES
(knowledge, safety, health, positive emotions) much more detached
from material objects. There are not subject to the impact of other
things, but immediately people
5. The composition and the structure of public production
Public productionThe productive forces
of society
Work force
The labor
objects
Means of
production
Means of labor
Production (economic) relations
The socio-economic
relations
The Organizational
and economic
relations
6.
The productive forces of society - it is a set ofinterdependent personal and real (physical) factors of
production.
The means of production - the totality of the
means of labor and objects of labor. The means of
production and human labor are inextricably linked and
interdependent. The means of production, and people who
have certain production experience, skills to work and lead
these means of production into effect, constitute the
productive forces.
Condition of the economy depends on the level of
development of its productive forces. The level of
productive forces determines the dynamics of the growth
of national wealth and productivity of social labor.
7.
The structure of the productive forces include:1. People.
People engaged in the process of material production, are
the subject of labor. In the material production of the work of
people is always directed at a certain person outside a natural
substance that is processed and the change in the production
process. This land, minerals, metals, objects of flora and fauna,
minerals and so on. All that directed the work of people, it is
the objects of labor.
2. The means of production.
To work on the subject of work with a view to its
conversion into the desired product, people must have the
instruments of labor, warehouse, transport systems,
communication systems, control systems and planning,
production technology, scientific organization of labor, and so
on. All of this constitutes a means of labor.
8.
The relations of production (productioneconomic relations) - the relationship between people,folding into a the process of social production and social
movement of the product from production to
consumption. The term "relations of production" has been
developed by Karl Marx.
The relations of production are the basis in relation
to the politics, ideology, religion, morality, and others.
Relations
of
production
impact
on
development of the productive forces, accelerating
or slowing down their development. The relations
of production cause the distribution of production
and distribution of funds in the structure of human
social production (the class structure of society).
9.
Socio-economic and organizational-economic relationsconstitute the relations of production, which is closely
associated with the productive forces.
Socio-economic relations by developing on the basis of
feasibility, are expressed in human relations. Determining the
structure of the socio-economic relations are relations over
the ownership of the means of production, resources and
production results. These relationships define the relationship
of distribution and consumption of manufactured goods.
By the organizational - economic relations are the forms
and methods of management, common to all sectors of the
economy. Among them, stand out today: 1) the market system,
the center of which commodity-money relations, 2)
Entrepreneurship, in the center of which - the effective
management of the economy. General organizational and
economic relations - a relationship in the field of monetary,
pricing, finance and credit, marketing, management, banking, etc.
10. The problem of choice in the economy. Production possibilities curve
Economic resources that can be used in the community tomeet the needs, are always limited, are qualitative and quantitative
limits. The ability to bypass the restrictions private fundamentally
change nothing. Limited resources is the fundamental problem of
economics: if the resources were available in unlimited quantities,
then all the goods required to meet the needs of the community,
would be made in sufficient quantities.
Limited resources requires the definition of production
capacity. Manufacturing capabilities - it is the largest production
volume, which is achieved with the full use of resources. Since
resources are limited, then the society is forced to make
technological choices when deciding which needs should be met,
and what - no. Thus, limited resources specifies alternate their use
necessitates an alternative choice from among mutually exclusive
options. From the set of feasible options for the use of resources
selected the most appropriate for the purposes of the society.
11. The problem of choice in the economy. Production possibilities curve
An alternative choice between resource utilization trendscan be recognized at a scale of production capacity
(tabular form) or in the form of a production possibility
curve (graphic form).
you can use the following example, which leads Paul
Samuelson. Suppose two kinds of goods needed to
produce - and gun oil. All resources can be directed to
the production of a single good or the good of both, but
in a certain ratio (Table 1).
12. The problem of choice in the economy. Production possibilities curve
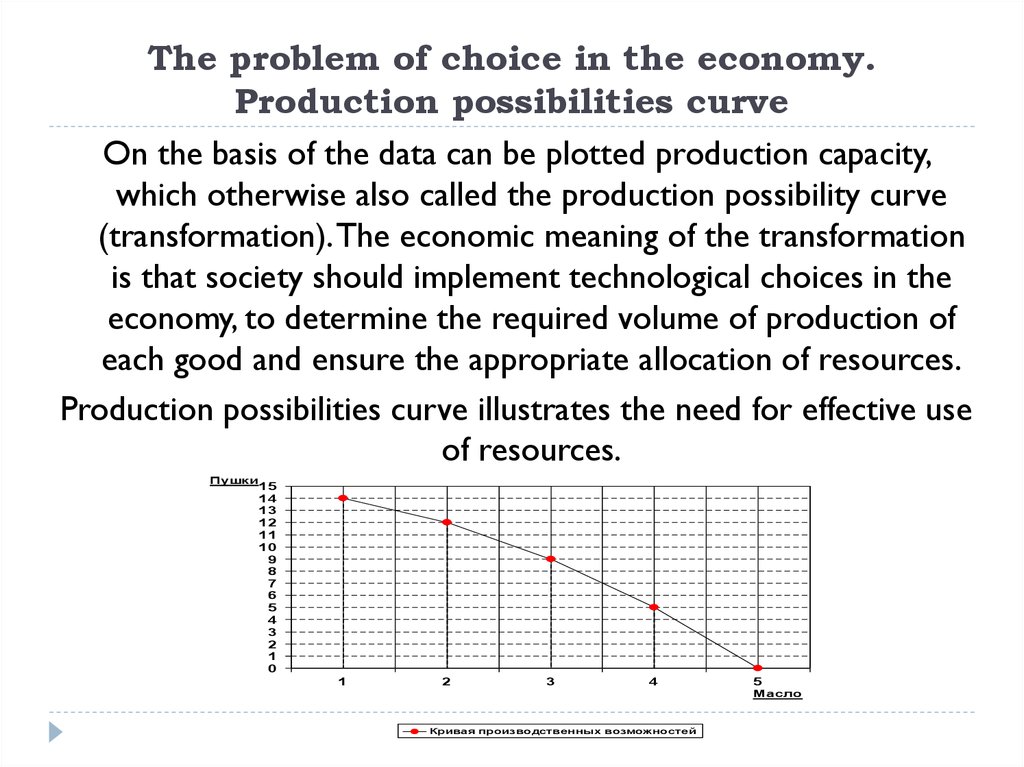
On the basis of the data can be plotted production capacity,which otherwise also called the production possibility curve
(transformation). The economic meaning of the transformation
is that society should implement technological choices in the
economy, to determine the required volume of production of
each good and ensure the appropriate allocation of resources.
Production possibilities curve illustrates the need for effective use
of resources.
Пушки
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
Масло
Кривая производственных возможностей
13. The problem of choice in the economy. Production possibilities curve
Limited resources suggests the need definitions(estimated) production capacity. Production opportunities this is the maximum volume of production, which is achieved
at the full use of the resources of the company. As resources
are limited, society is forced to permanently make a choice, ie.
Decide what needs are satisfied, and what are - no.
Thus, the restriction RESOURCES DETERMINES THEIR
USE alternatively, necessitates ALTERNATE selection among
mutually exclusive possibilities (alternatives). From multiple
acceptable way to utilize resources choose the most optimal
in terms of society's goals.
14. The problem of choice in the economy. Production possibilities curve
Economic sense of transformation consists that societymust implement the technological choice in the economy,
determine the necessary volume of production of each
guards and provide the relevant resource allocation.
Thus, the essence of the problem of choice is that if
each economic resource used to meet diverse needs is
limited, there is always the problem of its alternative use and
the search for a better combination of scarce resources.













 economics
economics








