Similar presentations:
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
1.
LECTURE 2The land and the people
UNITED KINGDOM OF
GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND
Plan to the lecture
1. Geographical position
2. Climate
3. The State system
4. Industry
5. The main parts of the country
2.
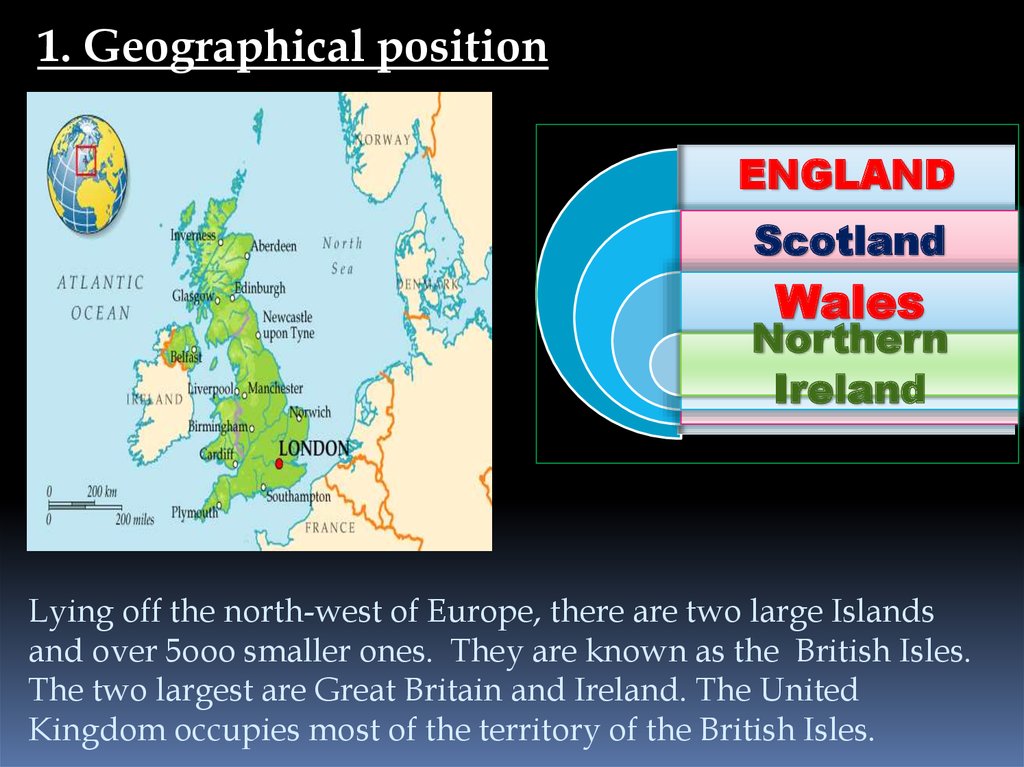
1. Geographical positionENGLAND
Scotland
Wales
Northern
Ireland
Lying off the north-west of Europe, there are two large Islands
and over 5ooo smaller ones. They are known as the British Isles.
The two largest are Great Britain and Ireland. The United
Kingdom occupies most of the territory of the British Isles.
3.
Geographically, the islandof Great Britain is
subdivided into two main
regions – Lowland Britain
and Highland Britain.
Lowland Britain comprises
southern and eastern
England. Highland Britain
consists of Scotland, most
of Wales, the Pennines, and
the Lake District.
The highest mountains are
in Scotland and Wales: Ben
Nevis is 1,343 metres and
Snowdon is 1,085 metres.
4.
2. ClimateThe weather is so changeable that the English often say that
they have no climate but only weather. Therefore it is
natural for them to use the comparison "as changeable as
the weather" of a person who often changes his mood or
opinion about something. The weather is the favourite topic
of conversation in the UK. As the weather changes with the
wind, and Britain is visited by winds from different parts of
the world, the most characteristic feature of Britain's
weather is its variability.
The English also say that they have three variants of
weather: when it rains in the morning, when it rains in the
afternoon, or when it rains all day long. Sometimes it rains
so heavily that they say "It's raining cats and dogs".
5.
Vegetation and WildlifeThe humid and mild climate of Great Britain is good for plants and flowers.
Some of them have become symbols in the UK.
The UK was originally a land of vast forests, mainly oak and beech in the
Lowlands and pine and birch, in the Highlands, with great stretches of
marshland and smaller areas of moors.
Extensive forests remain in eastern and northern Scotland and in
southeastern and western England. Oak, elm, ash, and beech are the
commonest trees in England, while Scotland has much pine and birch. The
Highlands with their thin soil are largely moorland with heather and grasses.
In the cultivated areas that make up most of Britain there are many wild
flowers, flowering plants and grasses.
The fauna, or animal life of the UK is much like that of northwestern
Europe.
Some 230 kinds of birds live in the UK, and another 200 are regular visitors,
many are songbirds. The most numerous are blackbirds, sparrows and
starlings. Robin Redbreast is the national bird of the UK. The number of
ducks, geese and other water fowl has diminished during recent years.
Partridges, pheasants and other large and rare birds are protected by law.
Gulls, geese and other sea birds nest near the coast.
6.
3. The state systemThe Administrative division of the Kingdom is as the follows:
it consists of four administrative-political units (historical
provinces): England (39 counties, 6 Metropolitan counties and
London), Wales (9 counties, 3 cities, 10 towns-counties),
Scotland (32 regions) and Ireland (26 districts).
The official language is English. Although they speak another
4 languages: Welsh, Irish, Gaelic and Cornish.
There is a hierarchy of cities. The main cities are: Edinburgh,
Cardiff and Belfast (the capital cities of Scotland, Wales and
Northern Ireland); Glasgow, Newcastle, Leeds and Bradford,
Birmingham, Manchester, Sheffield and Liverpool.
7.
4. IndustryThe UK has proved itself as a
highly developed industrial
country in the world which acts as
a supplier of industrial products.
The largest industrial monopolies
are Imperial chemical industries,
or ICI, Unilever, British Leyland
and General electric company.
8.
5. The main parts of the countryThe national flag of England is
white with red upright cross of St
George, the patron saint of
England.
The national symbol of England is rose,
the national colour is white.
9.
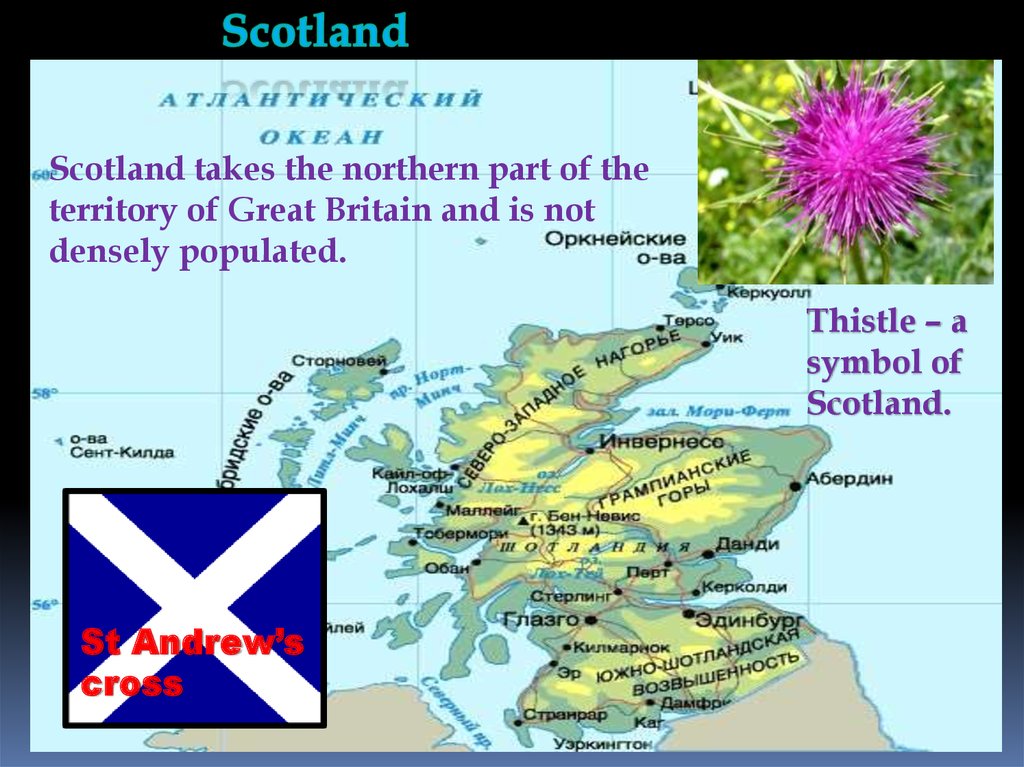
Scotland takes the northern part of theterritory of Great Britain and is not
densely populated.
Thistle – a
symbol of
Scotland.
St Andrew’s
cross
10.
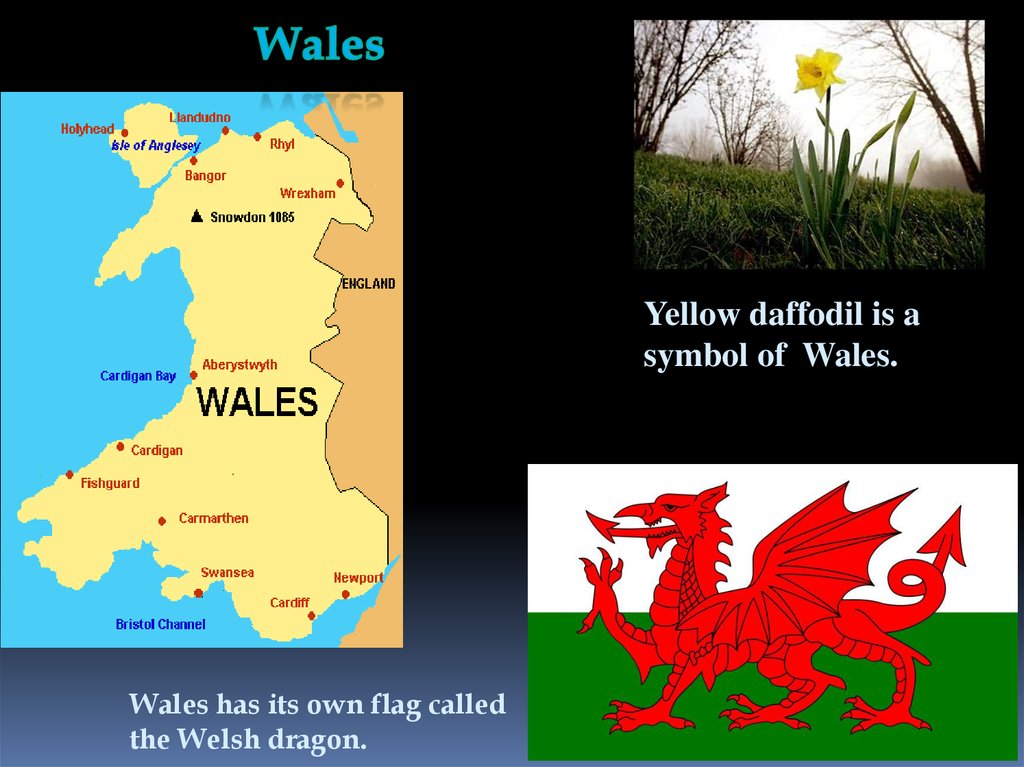
Yellow daffodil is asymbol of Wales.
Wales has its own flag called
the Welsh dragon.
11.
Northern Ireland is thesmallest component of the
United Kingdom.
It occupies the northeast of
the island of Ireland, only
one-sixth of its territorry.
The national symbol of Northern
Ireland is shamrock.









 geography
geography








