Similar presentations:
Intercultural Communication Theories
1. Intercultural Communication Theories
Lecture 22. Learning outcomes
• understand such terms as cultural dimensions and culturalorientation.
• recognize how communication barriers affect intercultural
communication.
• understand the concepts of globalization, glocalization, grobalization.
• understand the dimensions of culture and cultural iceberg concept
• dimensions of culture by Hall, Hofstede, Schwartz, Maslow hierarchy
of needs.
• Understand such terms as stereotype, enculturation, acculturation,
ethnocentrism.
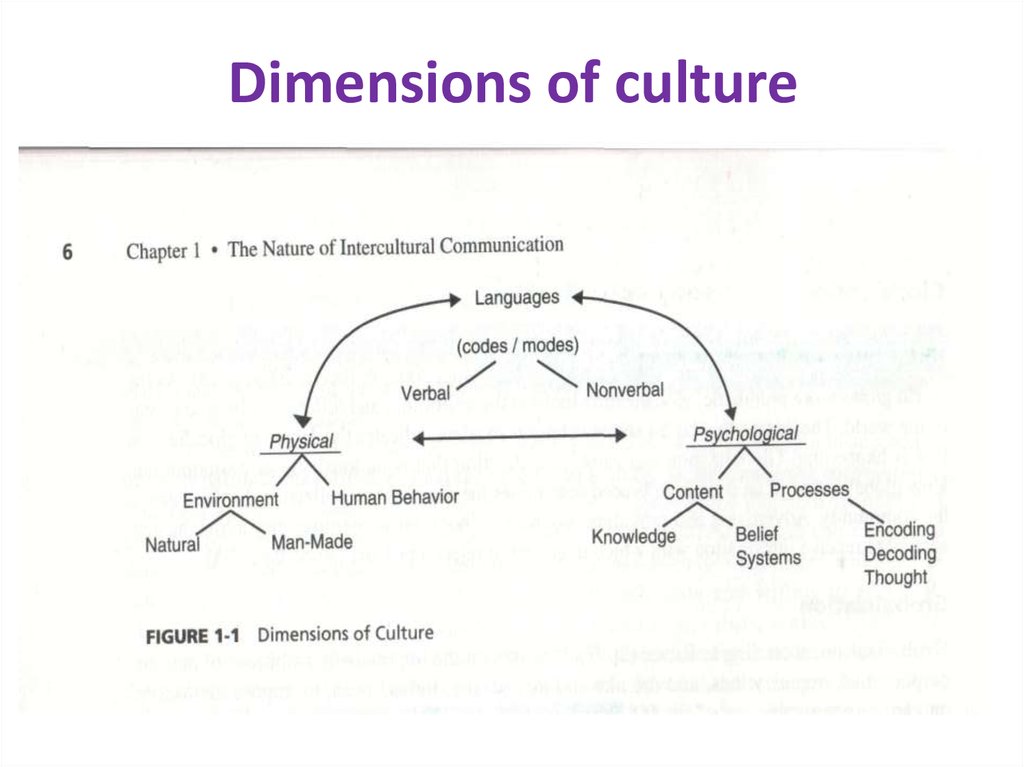
3. Dimensions of culture
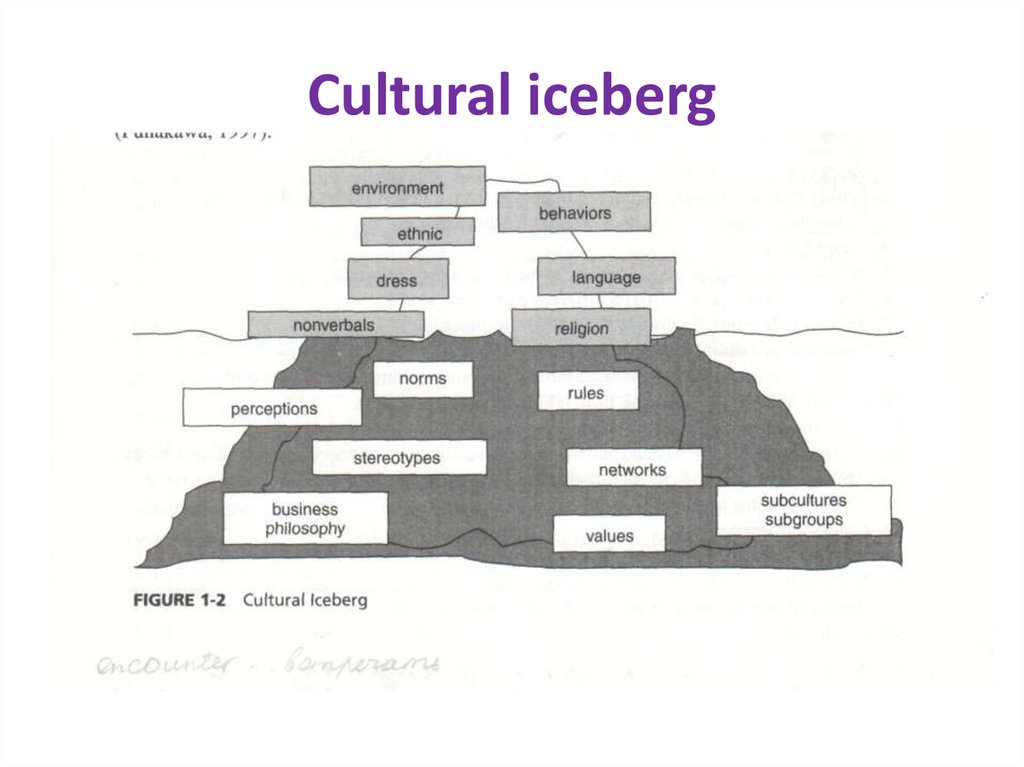
4. Cultural iceberg
5. Edward Hall
High context culture
Low context culture
Polychronic time
Monochronic time
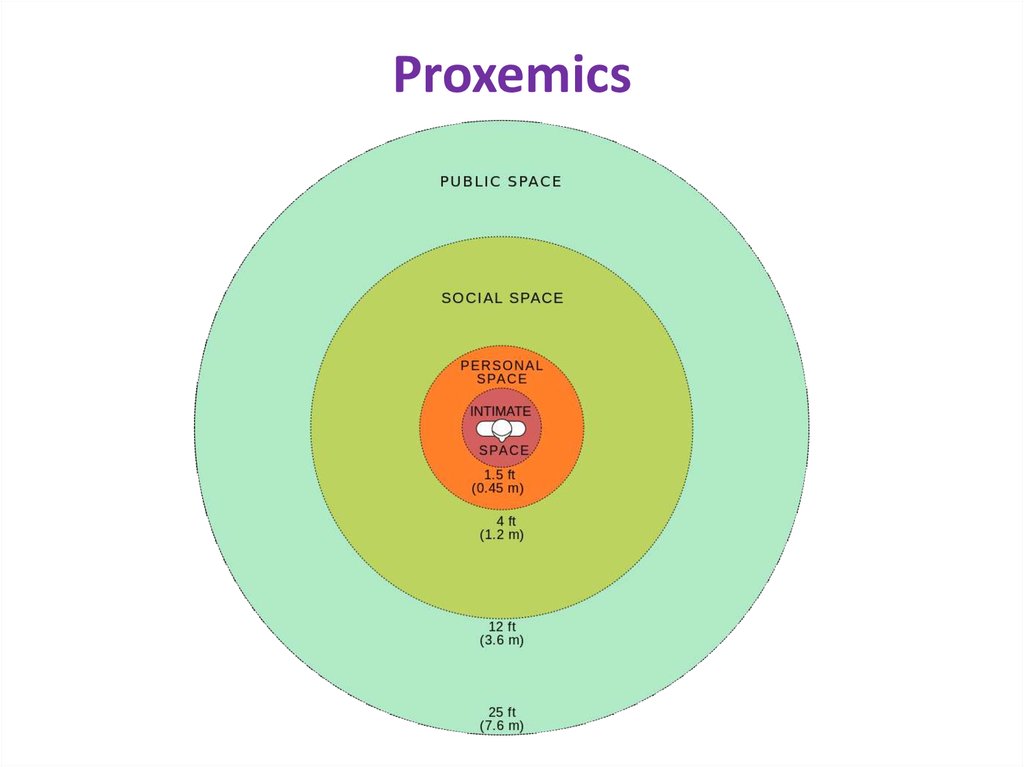
Proxemics
6. Proxemics
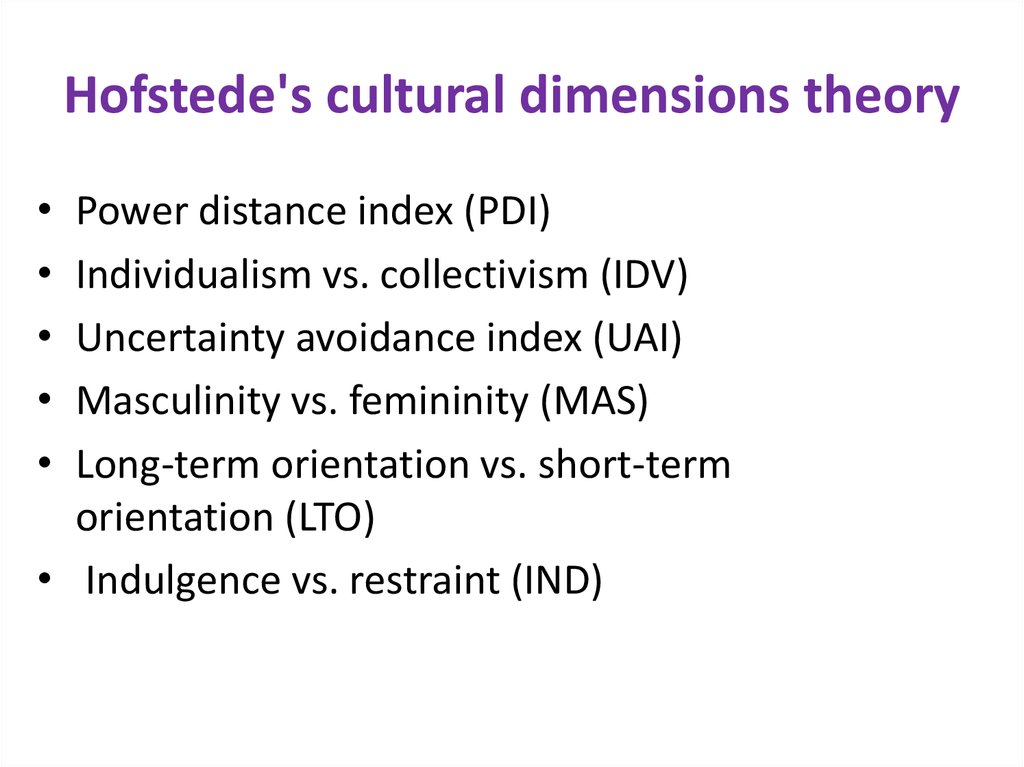
7. Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory
Power distance index (PDI)
Individualism vs. collectivism (IDV)
Uncertainty avoidance index (UAI)
Masculinity vs. femininity (MAS)
Long-term orientation vs. short-term
orientation (LTO)
• Indulgence vs. restraint (IND)
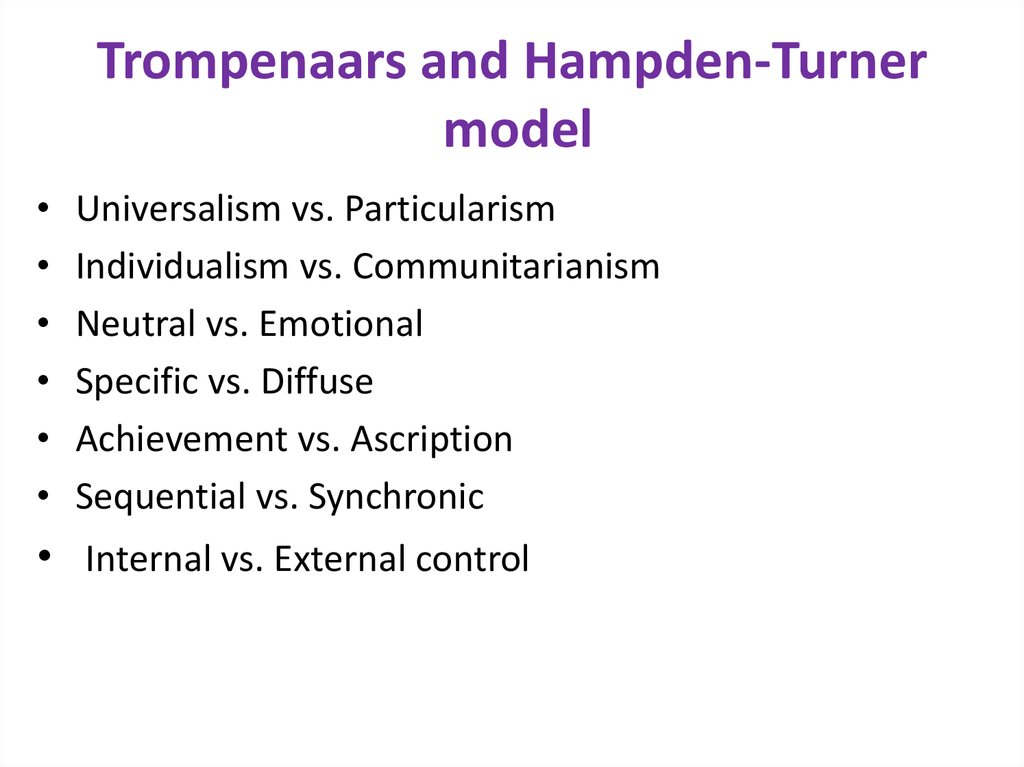
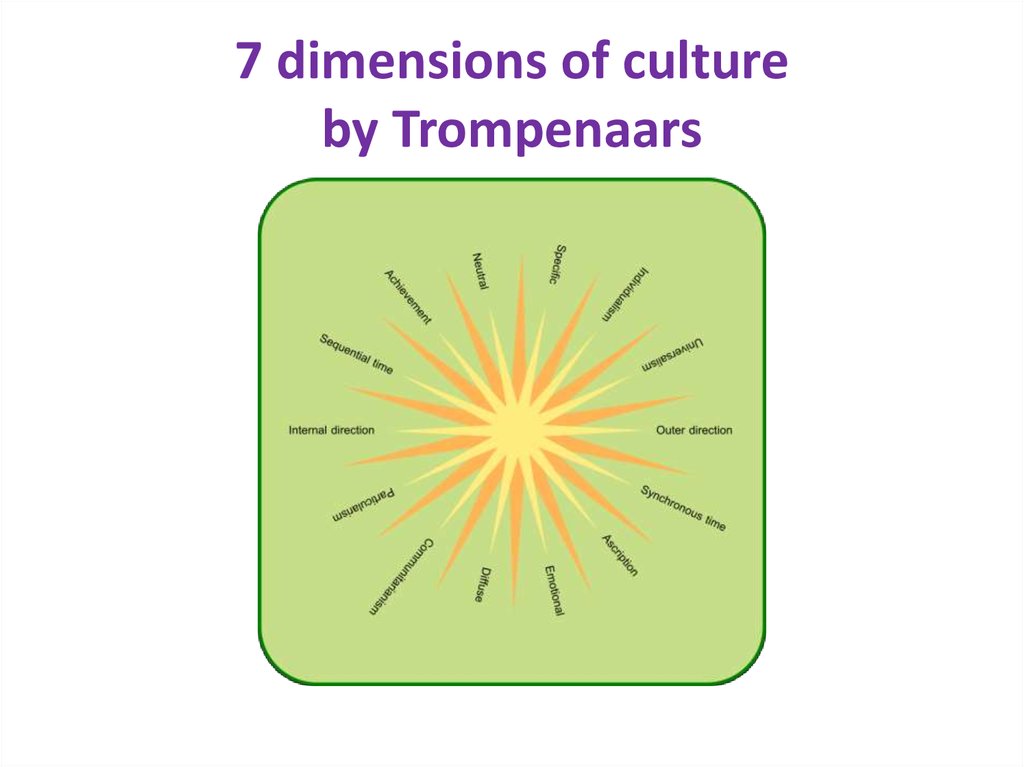
8. Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner model
Universalism vs. Particularism
Individualism vs. Communitarianism
Neutral vs. Emotional
Specific vs. Diffuse
Achievement vs. Ascription
Sequential vs. Synchronic
• Internal vs. External control
9. 7 dimensions of culture by Trompenaars
10. The GLOBE Study
Power Distance
Uncertainty Avoidance
Humane Orientation
Collectivism I: (Institutional)
Collectivism II: (In-Group)
Assertiveness
Gender Egalitarianism
Future Orientation
Performance Orientation
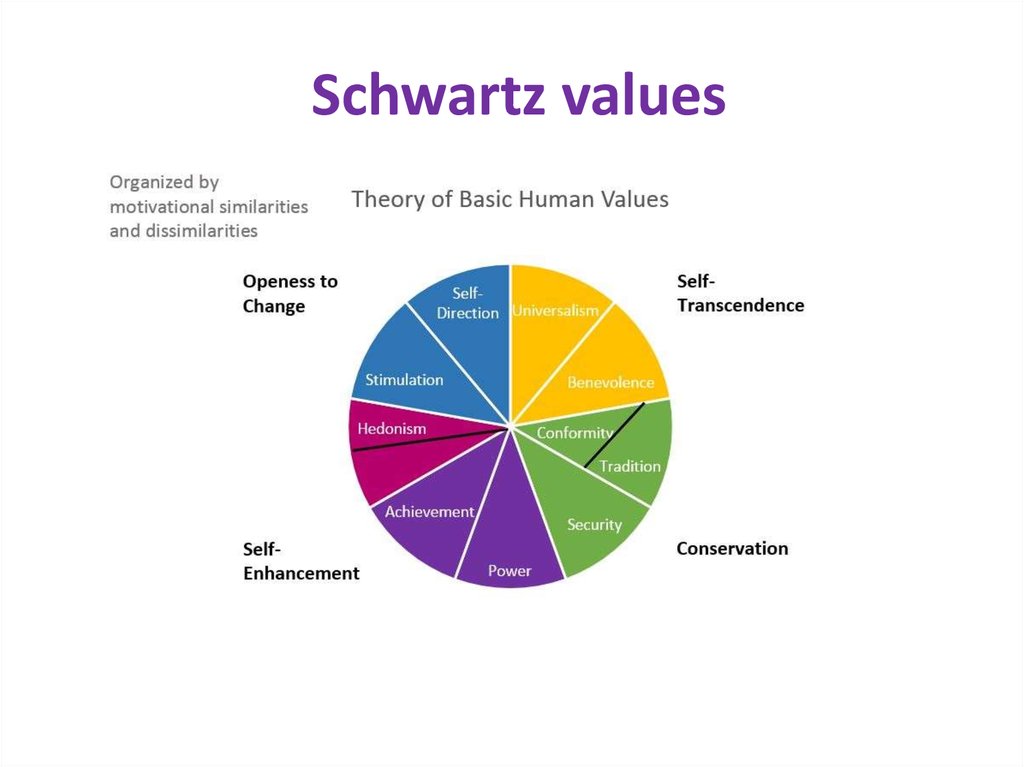
11. Schwartz values
12. Steven Reiss values
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Recognition
Curiosity
Food
Family
Honour
Idealism
Independence
Order
Physical activity
Power
Romance
Frugality
Communication
Status
Peace
Revenge
13. Maslow hierarchy of needs
14. Cultural Orientations Model by Hofstede, Hall & Hall, Mole
Cultural Orientations Modelby Hofstede, Hall & Hall, Mole
• Лекция 1
Source: tmcorp.com







 english
english








