Similar presentations:
Jemaah Islamiayh (JI)
1. Jemaah Islamiayh (JI)
Pak Anastasiia2. History of the organization
• was founded in 1993 by Abu Bakar Baasyir and Abdullah Sungkar in Malaysia• in 1998 JI moved to Indonesia
• has been conducting terrorist attacks since 1999
• has since expanded to Malaysia, Singapore, the Philippines, Australia,
Thailand, and Pakistan
• After the bombing in Bali in 2002, was listed by the UN on the list of terrorist
organizations associated with Al Qaeda and the Taliban.
3.
4. Ideology and Doctrine
• Ideology- Salafism• Doctrine is based on five founding
principles:
1. iman (belief),
2. hijrah (emigration),
3. i’dad (preparation to struggle in the way
of God),
4. jihad (struggle in the way of Allah),
5. al wala wal bara (division of the world
into friends and enemies).
• JI’s ideology is influenced by al-Qaeda’s
political theology
5. Social, national, age, gender analysis of the participants
JI’s current membership isn’t known publicly, but was estimated in2007 to range between 900 and several thousand members
6. “Myth”- story that cements the creation of this organization
• JI’s roots can be traced to Darul Islam, a radical anti-colonialist movementin 1940s Indonesia.
• In 1985 small factions fled to Malaysia to eventually regroup and rebrand as
Jemaah Islamiyah
• JI leaders adopted principles of Darul Islam to maintain a low profile in order
to avoid government retaliation.
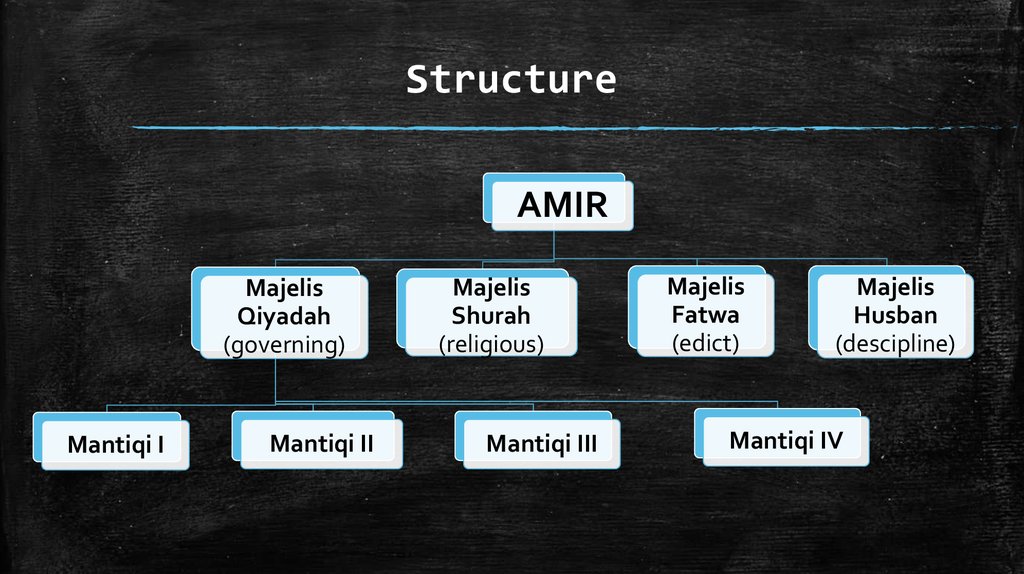
7. Structure
AMIRMajelis
Qiyadah
(governing)
Mantiqi I
Mantiqi II
Majelis
Shurah
(religious)
Mantiqi III
Majelis
Fatwa
(edict)
Majelis
Husban
(descipline)
Mantiqi IV
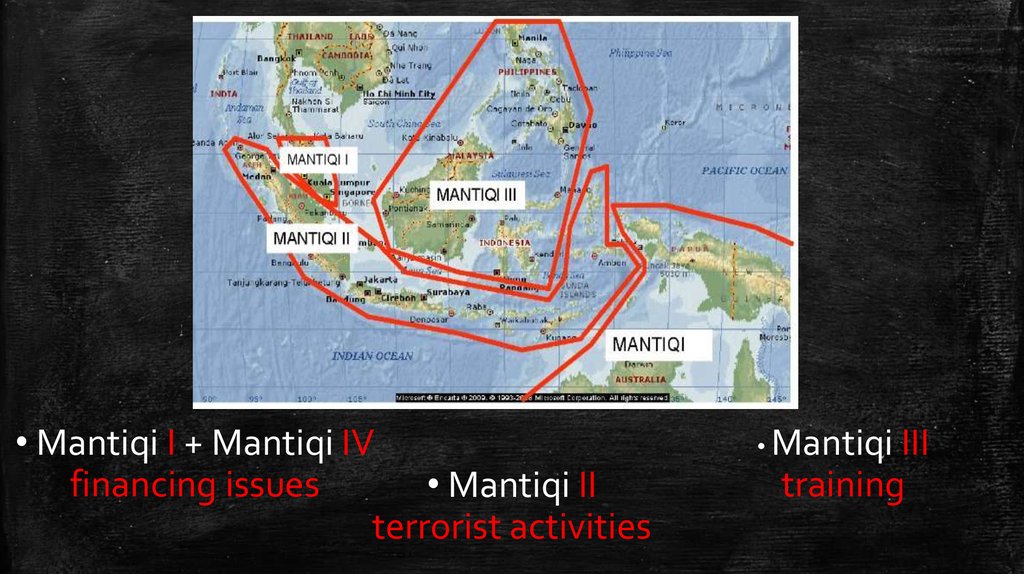
8.
• Mantiqi I + Mantiqi IVfinancing issues
• Mantiqi II
terrorist activities
• Mantiqi
III
training
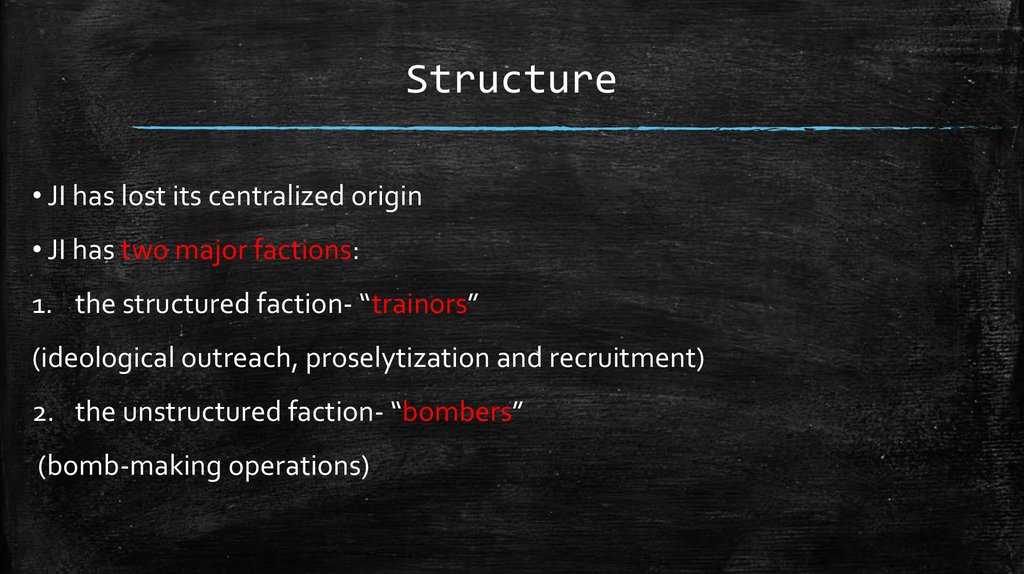
9. Structure
• JI has lost its centralized origin• JI has two major factions:
1. the structured faction- “trainors”
(ideological outreach, proselytization and recruitment)
2. the unstructured faction- “bombers”
(bomb-making operations)
10. International support
JI support contacts with both:• international terrorist organizations
Al-Qaida
• and those in the region:
Abu Sayyaf
the Islamic Front for the Liberation of Moro
the Misuari Renegade Group (MRG / MBG)
the Philippine Movement Rajah Sulaiman ( RSM) and etc.
11. Financial sourses
• islamic charities• contributions from JI’s own members, outside supporters,
• Al Qaeda investments and accounts already established in
the region
• proceeds from:
petty crime
extortion
racketeering
gun-running
kidnapping
12. Goals and aims
The main goal has two stages:1. The first stage is the continuation of the goal of Darul Islam- the creation
of an Islamic state in Indonesia.
2. The second stage is to create an Islamic state that covers the whole of
South East Asia and include the countries of Singapore, Indonesia,
Malaysia, Brunei, southern Thailand and southern Philippines.
This Islamic state would be ruled by Shari’ah law (Muslim religious law).
13. Methods
• crime• racketeering
• extortion
• gun-running
• kidnapping
14. Activities
Major attacks:2000- several Christian churches across Indonesia
2002- a nightclub in Bali
2003- near a ferry terminal in the southern Philippines,
the JW Marriot in Jakarta
2004- near the Australian embassy in Jakarta
2005- Jimbaran Bay and Kuta, tourist destinations in Bali, Indonesia
2009- the JW Marriot and the Ritz-Carlton hotels in Jakarta’s business district
15. A degree to be discussed in Mass media
CNN PhilippinesVoice of America
Manila Bulletin
Free Malaysia Today
Asian Correspondent
etc.













 policy
policy


