Similar presentations:
Strategic planning
1. Strategic planning
Introduction2. 1. Planning
Analytický proces, ktorý zahŕňa:• evaluating the future
• determining desirable goals in the context
of the future
• development of alternative courses of
action to achieve goals
• choosing a direction among these
alternatives
3.
Planning includes:• defining goals
• establishing the overall strategy
• development of a comprehensive
hierarchy of plans for integrating and
coordinating activities
4. 1.1. Planning as a process
Planning - projecting the future, i.e. futurestate
determines the goal
the ways to achieve this goal in the
specified time and at the required
level are determined
5.
Planning as a process6. Planning as a process
• Understanding of planning principles• Elaboration of goals
• Creation and implementation of strategic
plans
• Elaboration and implementation of action
plans
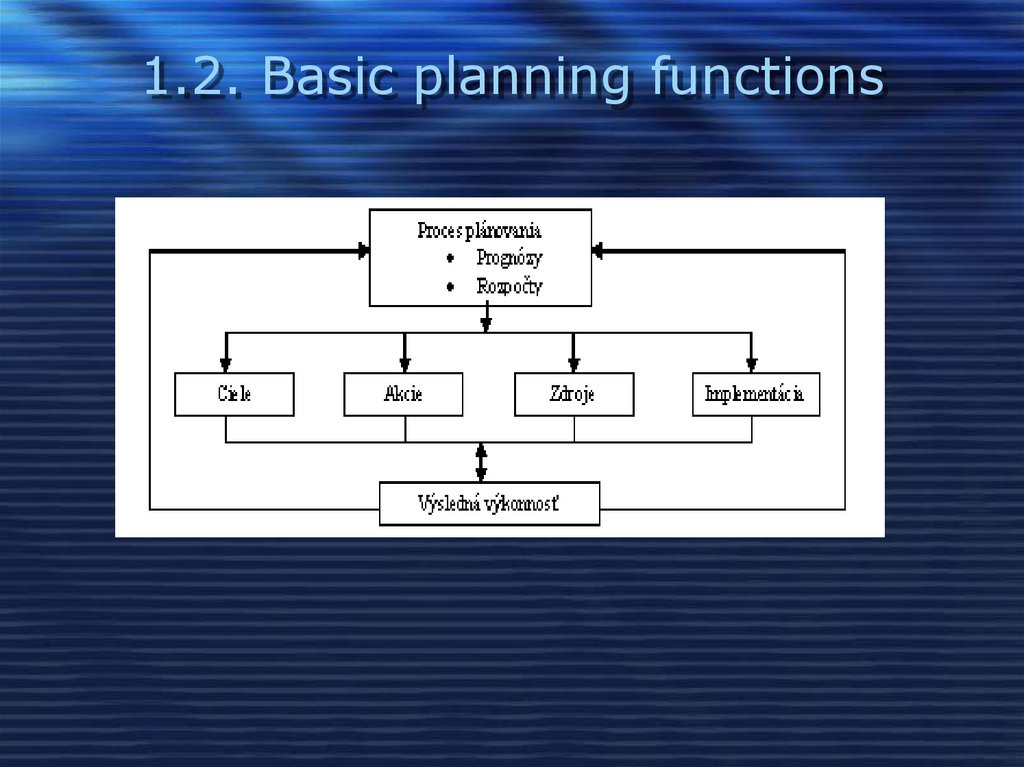
7. 1.2. Basic planning functions
8. Basic planning functions
Planning processPredictions
Budgets
Goals
Actions
Resources
Implementation
Resultant performance
9. 1.3. Specific principles for the implementation of the plan
• Flexibility• Completeness
• Coordination
• Ethics
• Clarity
10. 1.4. Planning classification
1.4.1. According to the planning time horizon• long-term
usually several years (5...7 and more)
• mid-term
• short-term
less than 1 year
11.
1.4.2. According to the nature of theobjectives that the plans contain
• strategic planning
- from the point of view of efficiency the most important basic planning contains decisions conditioning efficiency
- general, containing strategic
objectives as well as the means to achieve
them
- contains decisions regarding priorities
and necessary steps to achieve strategic
objectives (objectives that directly support
the implementation of the mission)
12.
• tactical planning• - determines how to achieve tactical
objectives (they specify the results that are
expected)
• - concretizes and specifies the objectives
set out in the strategic plans as well as the
means for achieving them
Strategic planning - sets objectives (for
several years), tactical planning - starts
from these objectives, concretizes and
specifies them (in shorter time intervals)
and ensures their fulfillment.
13.
operational planning- - specifies how operational objectives
(individuals, lowest departments) will be
achieved
14.
1.4.3. According to the degree of accuracy(details) and concreteness
• detailed planning
- clearly defined and do not leave space for
interpretation
• directional planning
- it is not so detailed, the objectives are given
only as a framework
- they are used if there is a high degree of
uncertainty and if the environment changes very
quickly
15.
1.4.4. According to the frequency of use ofplanning
• one-time use
- solving "unique" problems
- planning research, development and
various other activities
• permanently
- guiding repetitive activities
16.
1.4.5. According to the degree of complexity• aggregated
- it contains interconnected,
coordinated objectives that are
hierarchically aligned with each other
- they are not very detailed, the
objectives are aggregated
• partial
- objectives and means to achieve
them are in individual activities
17.
1.4.6. According to the width of the shot- what breadth of activity the planning
covers
• cross-sectional/collective (comprehensive
development of the municipality, region,
...)
• sectorally (development in a certain area
of the life of the municipality, region, ...)
18. 1.2. The planning process
19. The planning process
• Awareness of opportunities• Setting tasks and objectives
• Development of assumptions
• Determining alternative procedures
• Evaluation of alternative procedures
• Selection of procedures
• Creation of support plans
• Numerical expression using budgets
20. 1.3. Fundamentals of strategic planning
Pearce J.A., Robinson R.B.• Defining the mission and long-term vision of
development
• Setting objectives and performance parameters
• Formulation of the procedure for achieving the set goals
• Elaboration of the procedure for the implementation plan
• Evaluation and strategy changes
Terkel M.
• Formulation of ideas
• Evaluation of external and internal factors
• Setting objectives
• Development of progress programs
• Implementation of programs
• Strategy evaluation
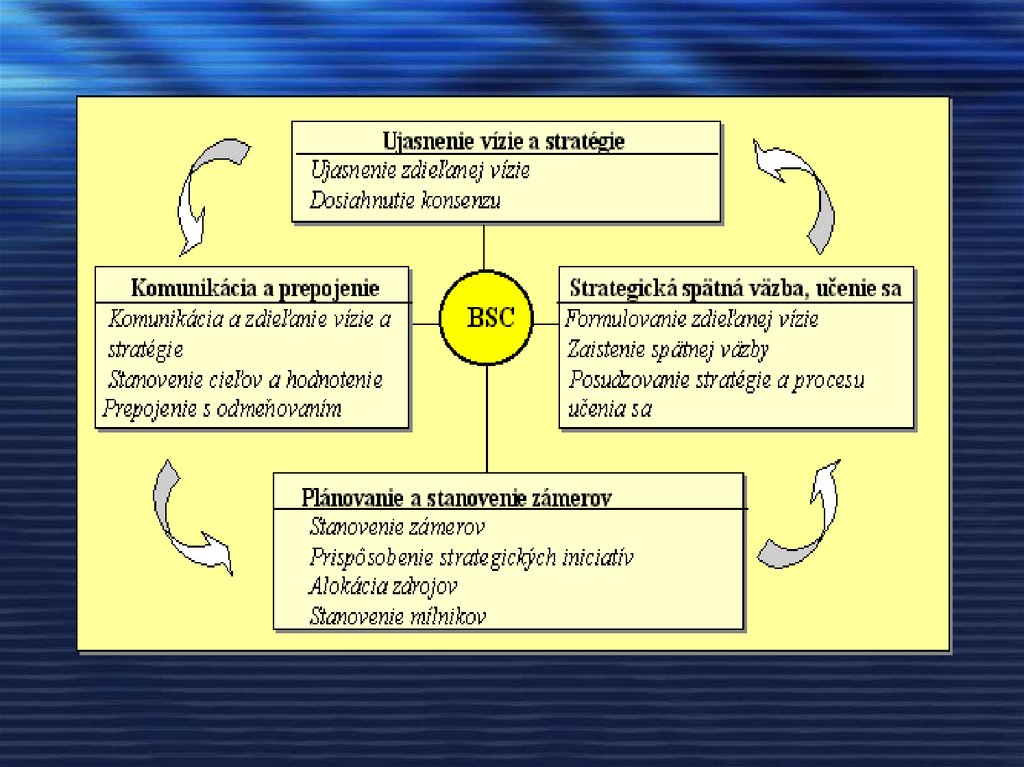
21. 1.3.1. The Balanced Scorecard method
prerequisite for success - understanding theinterrelationships between perspectives (their
intentions, indicators, objectives and initiatives)
and implementing this understanding
work on BSC creation ... strategy development
the BSC approach responds to the demands of the
times ... the integration of strategy into the
decision-making process ... the support of
synergy and the increase of efficiency
22.
23.
BSC- a tool for effective strategic
management
- recognized as the best approach
to transform vision into concrete
measurable activities
- takes into account the factors
creating long-term values
24.
Sila sústredenia, sila synergie získanáimplementáciou BSC
25.
BSC• it does not take the form of a static list of
performance indicators
• it finds its application in the description,
implementation and subsequent
management of strategy at all levels
• emphasis is placed on taking over
objectives, benchmarks and initiatives
(actions and projects) with a mission,
vision and strategy
• translates mission and strategy into
objectives and their metrics (indicators) perspectives
26.
27.
Failed BSC implementation?• vision and strategy are unrealizable
• the strategy is not refined to the objectives
• the strategy is not tied to long-term and
short-term allocations
• absence of feedback, or incorrectly
implemented feedback
28. 2. Strategic planning process
Objectives and mission (visionning)Environmental scanning – prieskumy a rozbory
Strategy formulation (in relation to objectives, to
achieve/realize the vision)
Strategy implementation (plan, program
development, own implementation of individual
steps - interventions)
Evaluation/monitoring and implementation of
feedback


























 economics
economics








