Similar presentations:
Encoding. Decoding. Seven- segment displays (lecture 4)
1.
Digital Logic DesignLecture – 4:
Encoding. Decoding. Seven-segment
displays
Konakbayev Olzhas, senior-lecturer,
2.
Lecture baseDigital Electronics: Principles & Applications, 9th edition by Roger
Tokheim & Patrick E. Hoppe:
• Chapter 6
2
3.
Topics to cover• The 8421 BCD Code
• The Excess-3 Code
• The Gray Code
• The ASCII Code
• Encoders
• Seven-Segment LED Displays
• Decoders
• BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/ Driver
3
4.
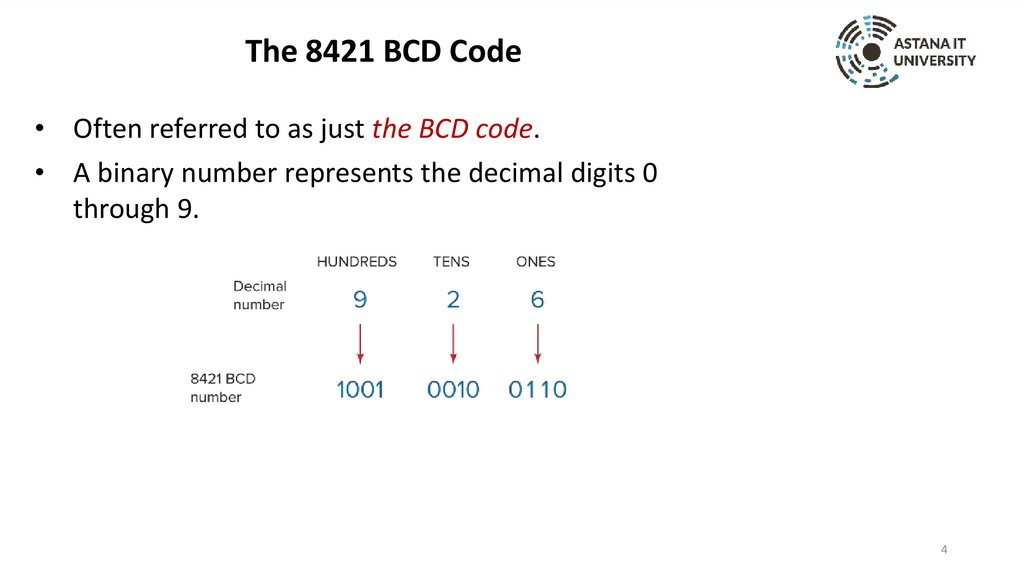
The 8421 BCD Code• Often referred to as just the BCD code.
• A binary number represents the decimal digits 0
through 9.
4
5.
The Excess-3 Code 1• Add 3 to each digit of the decimal number and
convert to binary form.
5
6.
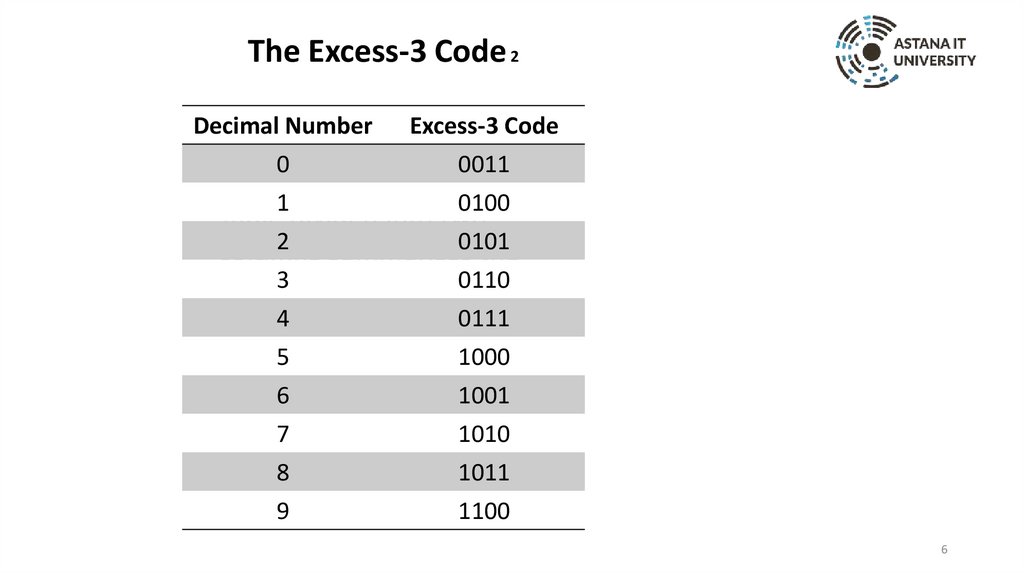
The Excess-3 Code 2Decimal Number
0
1
Excess-3 Code
0011
0100
7
8
9
1010
1011
1100
Table divided into two
2 summarizes
0101
columns
the
3 code. The column
0110
excess-3
4 are marked from
0111
header
5 right as: Decimal
1000
left to
6 and excess-3
1001
number
code.
6
7.
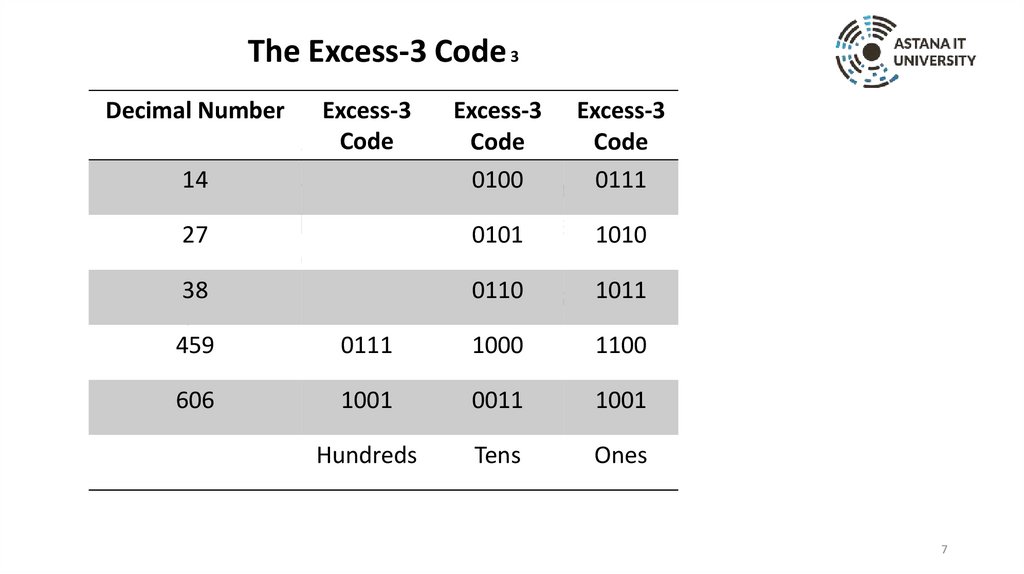
The Excess-3 Code 3Decimal Number
Excess-3
Code
Excess-3 Excess-3
Code
Code
Table divided into four columns
14
0100 The 0111
summarizes
the excess-3 code.
column
from left 1010
27 header are marked0101
to right as: Decimal number and
38
repetition
of three columns0110
excess-3 1011
code.
459
0111
1000
1100
606
1001
0011
1001
Hundreds
Tens
Ones
7
8.
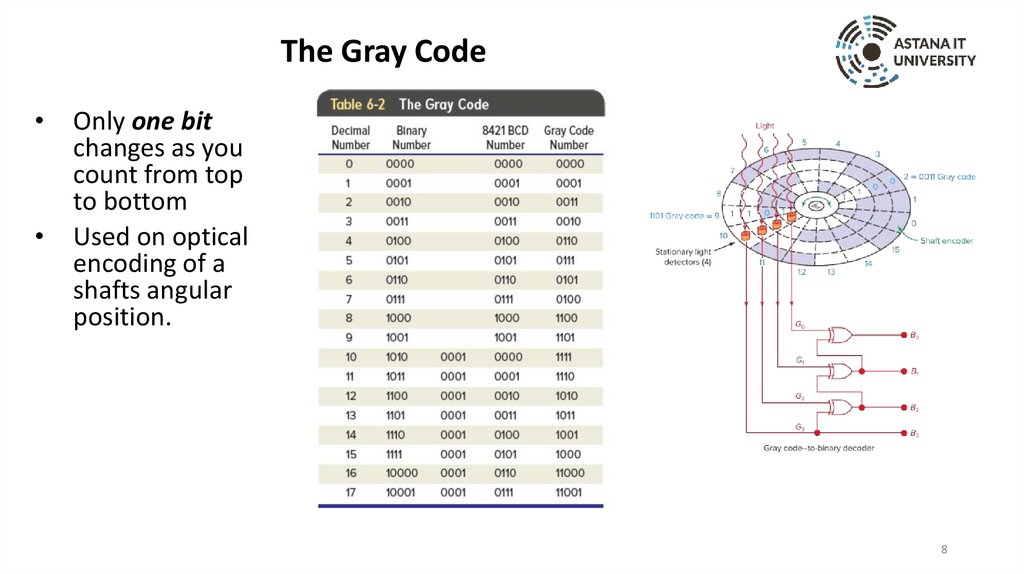
The Gray CodeOnly one bit
changes as you
count from top
to bottom
Used on optical
encoding of a
shafts angular
position.
8
9.
The ASCII Code• ASCII (pronounced “ask-ee”) stands for the American
Standard Code for Information Interchange.
• The standard ASCII code is a 7-bit code used in
transferring coded information from keyboards and to
computer displays and printers.
9
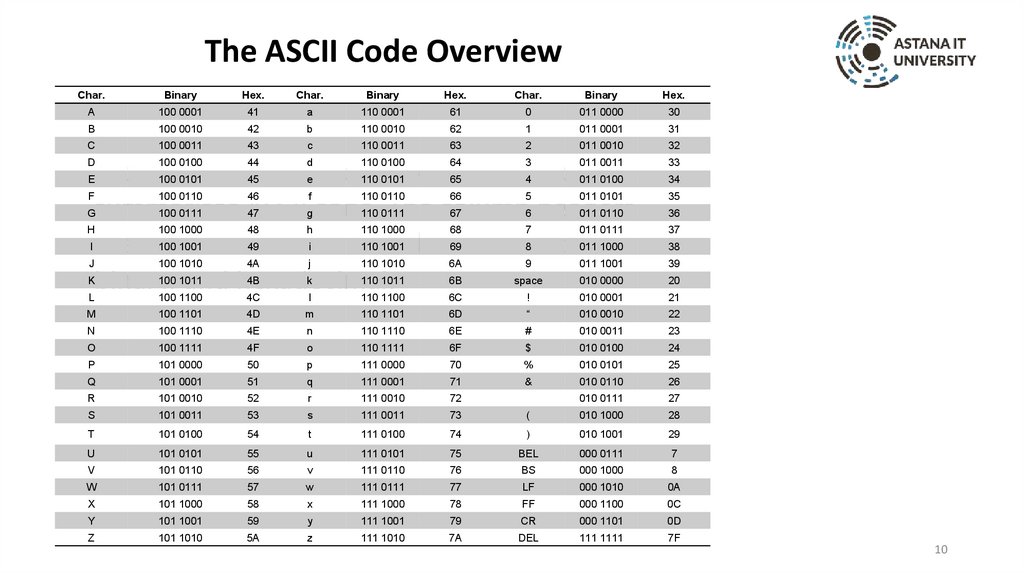
10.
The ASCII Code OverviewChar.
Binary
Hex.
Char.
Binary
Hex.
Char.
Binary
Hex.
A
100 0001
41
a
110 0001
61
0
011 0000
30
B
100 0010
42
b
110 0010
62
1
011 0001
31
C
100 0011
43
c
110 0011
63
2
011 0010
32
D
100 0100
44
d
110 0100
64
3
011 0011
33
E
100 0101
45
e
110 0101
65
4
011 0100
34
F
100 0110
46
f
110 0110
66
5
011 0101
35
G
100 0111
47
g
110 0111
67
6
011 0110
36
H
100 1000
48
h
110 1000
68
7
011 0111
37
I
100 1001
49
i
110 1001
69
8
011 1000
38
100 1010
4A
j
110 1010
6A
9
011 1001
39
K
100 1011
4B
k
110 1011
6B
space
010 0000
20
L
100 1100
4C
l
110 1100
6C
!
010 0001
21
M
100 1101
4D
m
110 1101
6D
“
010 0010
22
N
100 1110
4E
n
110 1110
6E
#
010 0011
23
O
100 1111
4F
o
110 1111
6F
$
010 0100
24
P
101 0000
50
p
111 0000
70
%
010 0101
25
Q
101 0001
51
q
111 0001
71
&
010 0110
26
R
101 0010
52
r
111 0010
72
010 0111
27
S
101 0011
53
s
111 0011
73
(
010 1000
28
T
101 0100
54
t
111 0100
74
)
010 1001
29
U
101 0101
55
u
111 0101
75
BEL
000 0111
7
V
101 0110
56
v
111 0110
76
BS
000 1000
8
W
101 0111
57
w
111 0111
77
LF
000 1010
0A
X
101 1000
58
x
111 1000
78
FF
000 1100
0C
Y
101 1001
59
y
111 1001
79
CR
000 1101
0D
Z
101 1010
5A
z
111 1010
7A
DEL
111 1111
7F
J
Table divided into repetition of three columns
summarizes ASCII code. The column headers
are marked from left to right as: Character,
binary, and hexadecimal.
10
11.
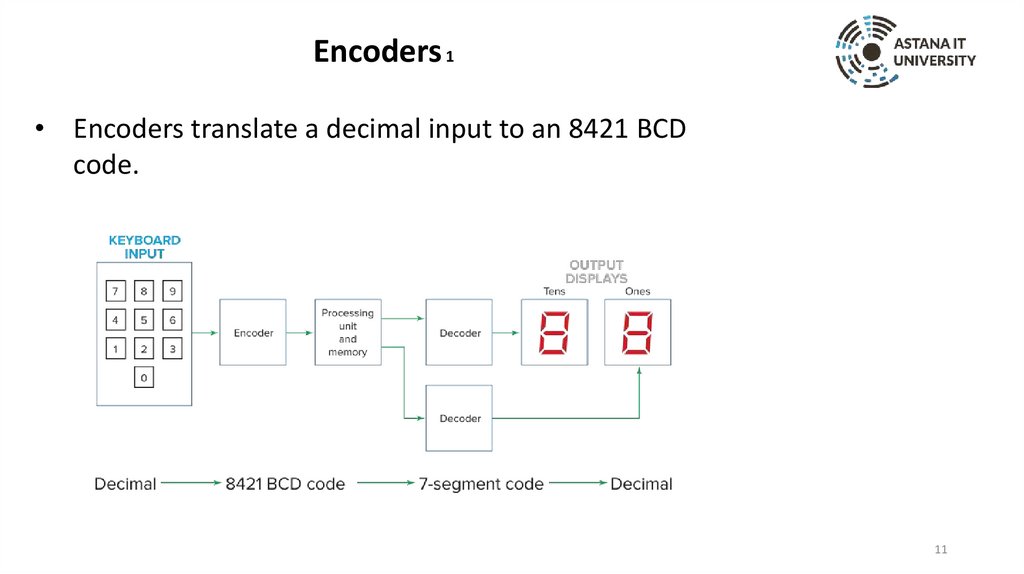
Encoders 1• Encoders translate a decimal input to an 8421 BCD
code.
11
12.
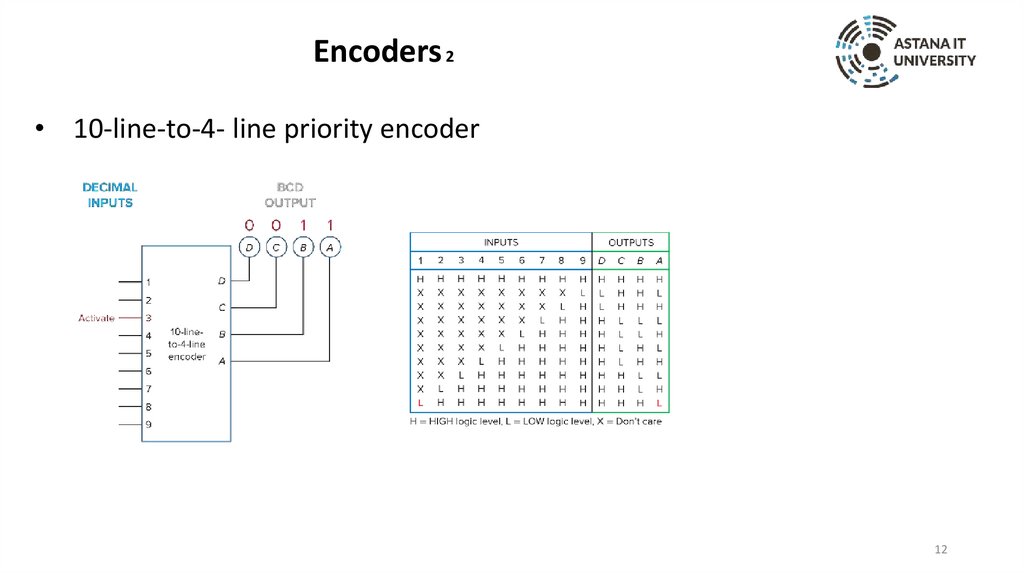
Encoders 2• 10-line-to-4- line priority encoder
12
13.
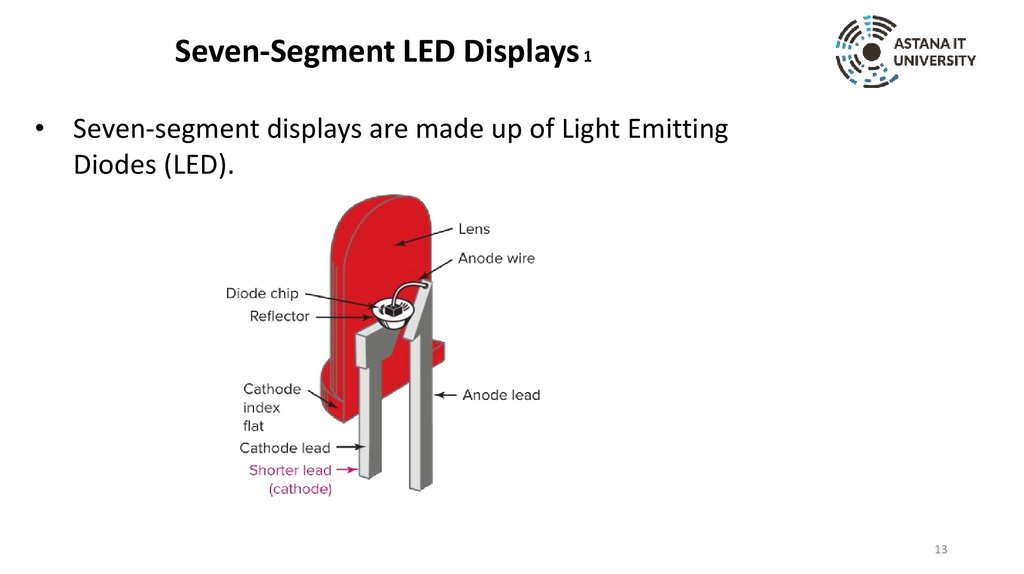
Seven-Segment LED Displays 1• Seven-segment displays are made up of Light Emitting
Diodes (LED).
13
14.
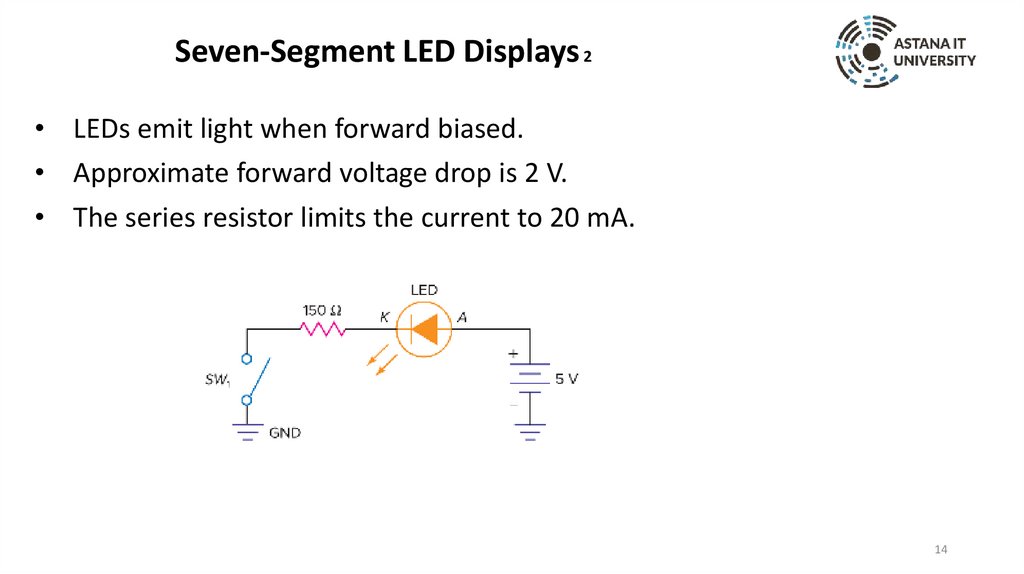
Seven-Segment LED Displays 2• LEDs emit light when forward biased.
• Approximate forward voltage drop is 2 V.
• The series resistor limits the current to 20 mA.
14
15.
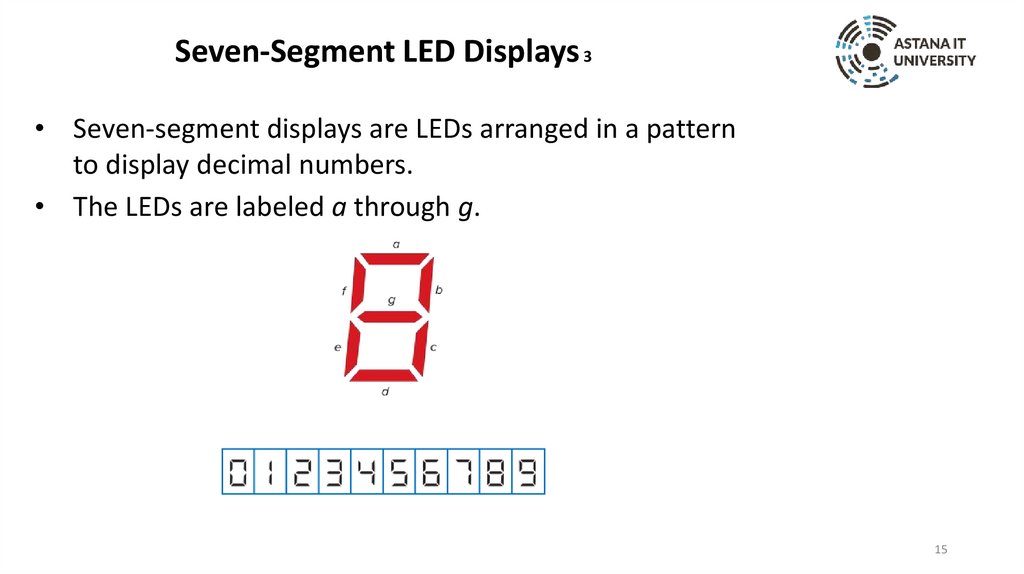
Seven-Segment LED Displays 3• Seven-segment displays are LEDs arranged in a pattern
to display decimal numbers.
• The LEDs are labeled a through g.
15
16.
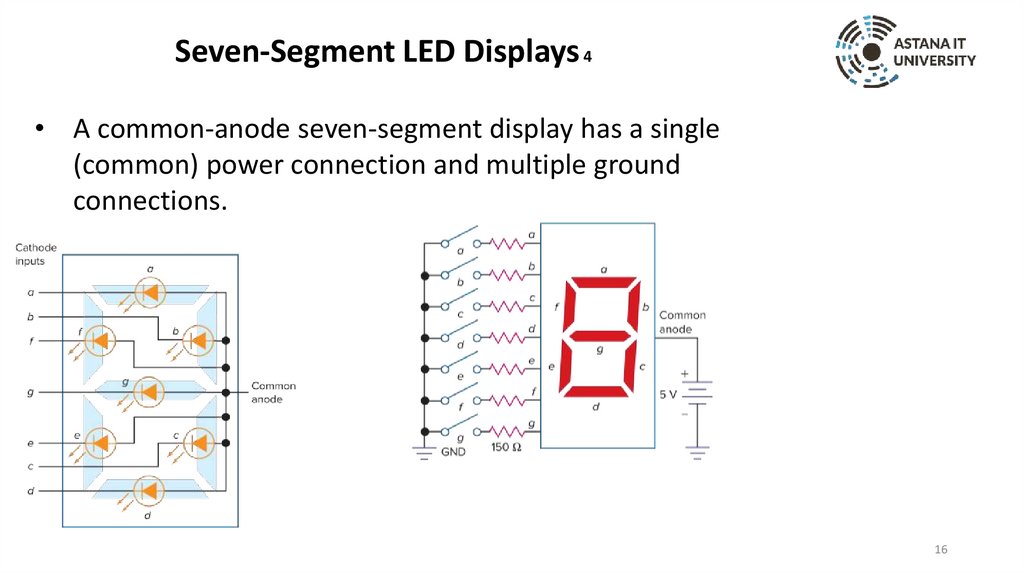
Seven-Segment LED Displays 4• A common-anode seven-segment display has a single
(common) power connection and multiple ground
connections.
16
17.
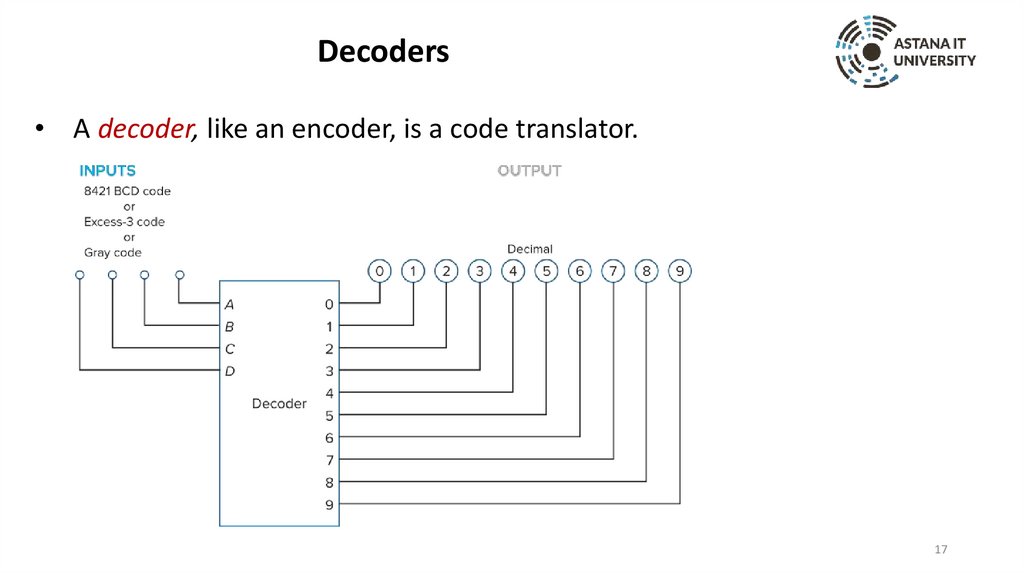
Decoders• A decoder, like an encoder, is a code translator.
17
18.
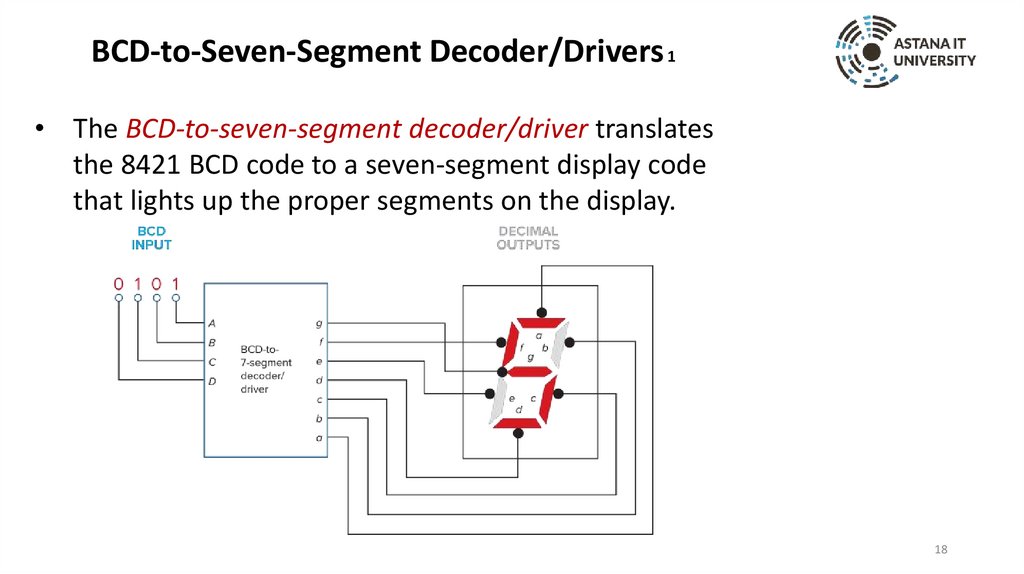
BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/Drivers 1• The BCD-to-seven-segment decoder/driver translates
the 8421 BCD code to a seven-segment display code
that lights up the proper segments on the display.
18
19.
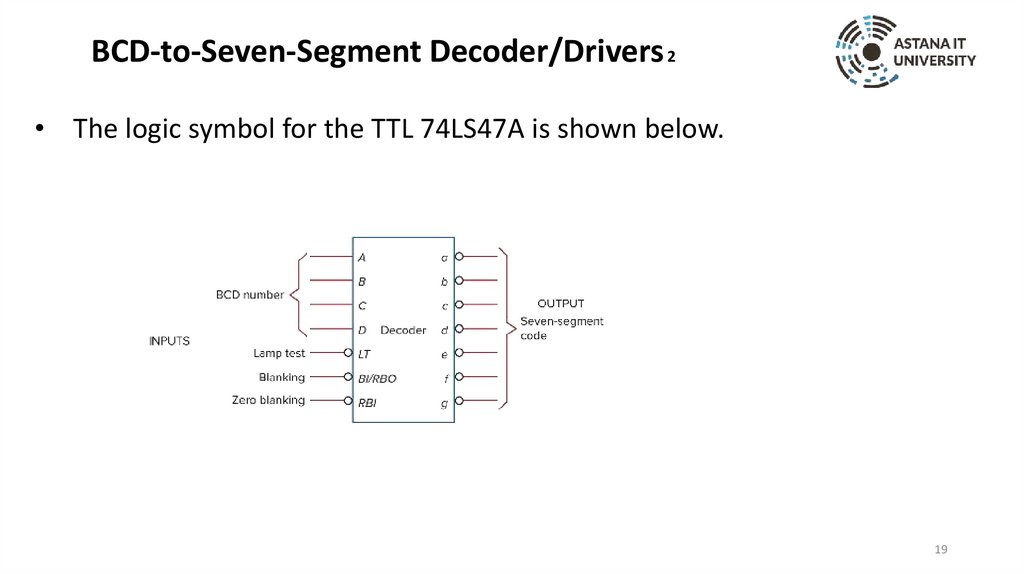
BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/Drivers 2• The logic symbol for the TTL 74LS47A is shown below.
19
20.
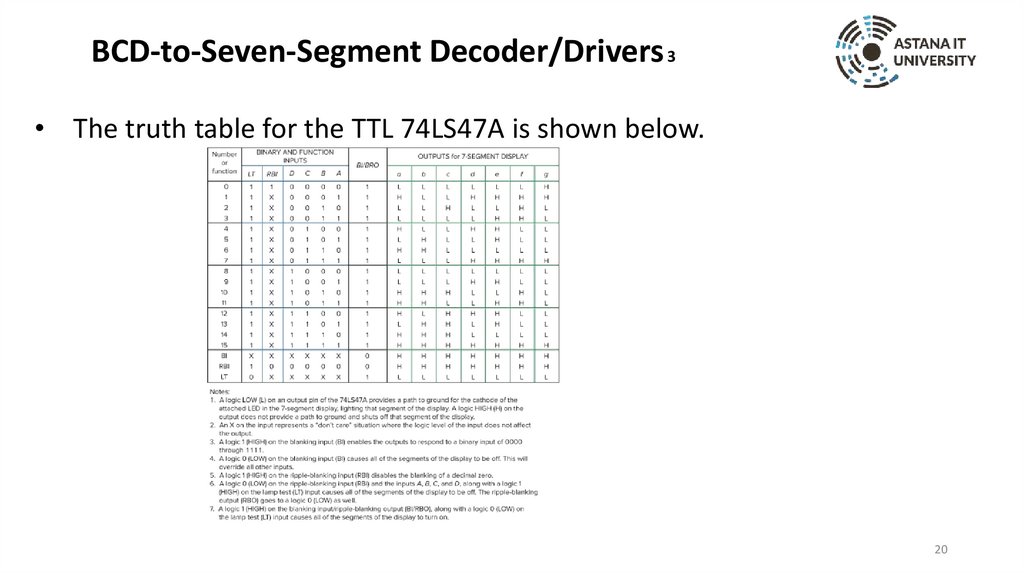
BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/Drivers 3• The truth table for the TTL 74LS47A is shown below.
20
21.
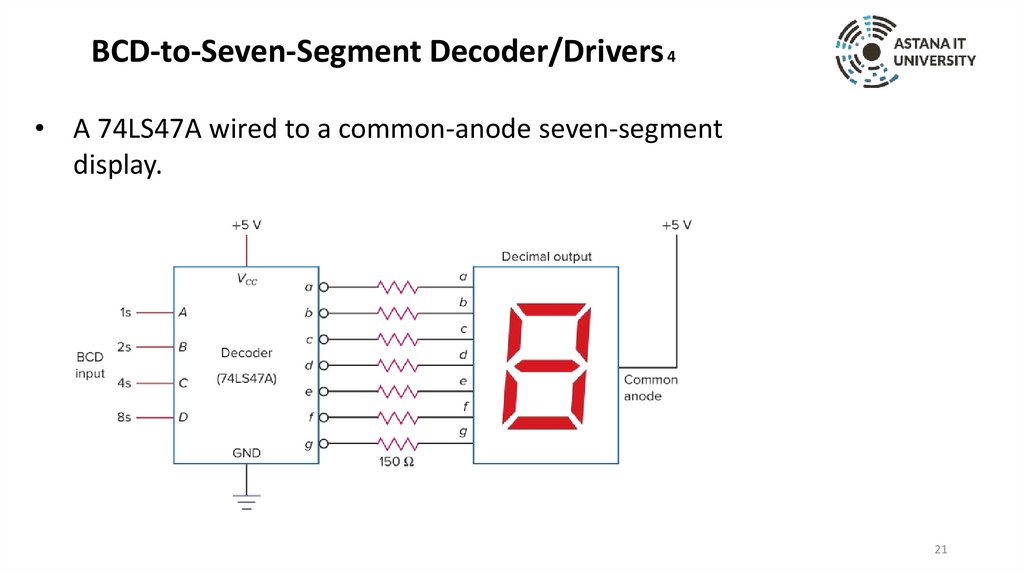
BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/Drivers 4• A 74LS47A wired to a common-anode seven-segment
display.
21
22.
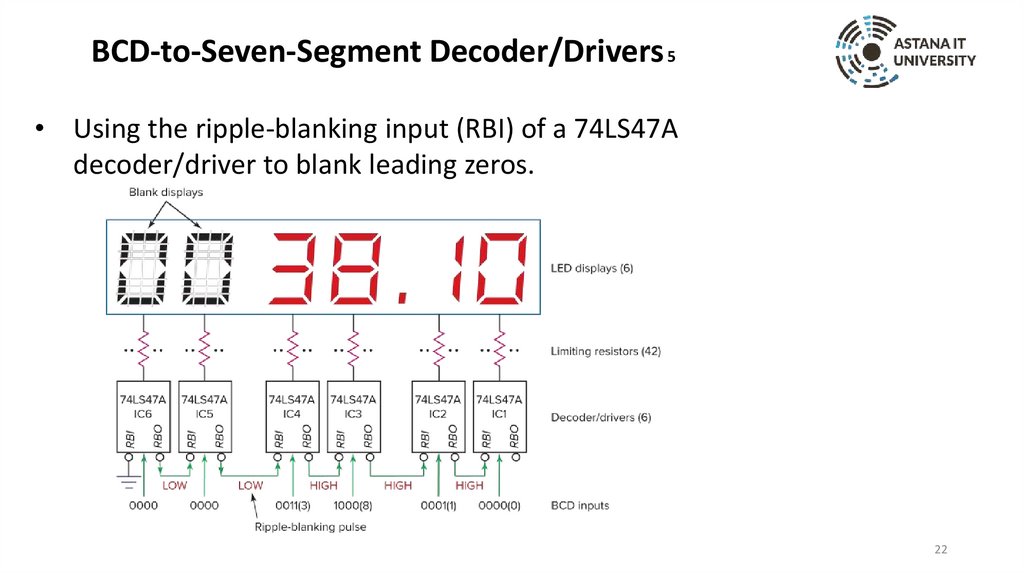
BCD-to-Seven-Segment Decoder/Drivers 5• Using the ripple-blanking input (RBI) of a 74LS47A
decoder/driver to blank leading zeros.
22
23.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) 1• The LCD controls available light.
• Low power consumption.
• Visible in day-light
23
24.
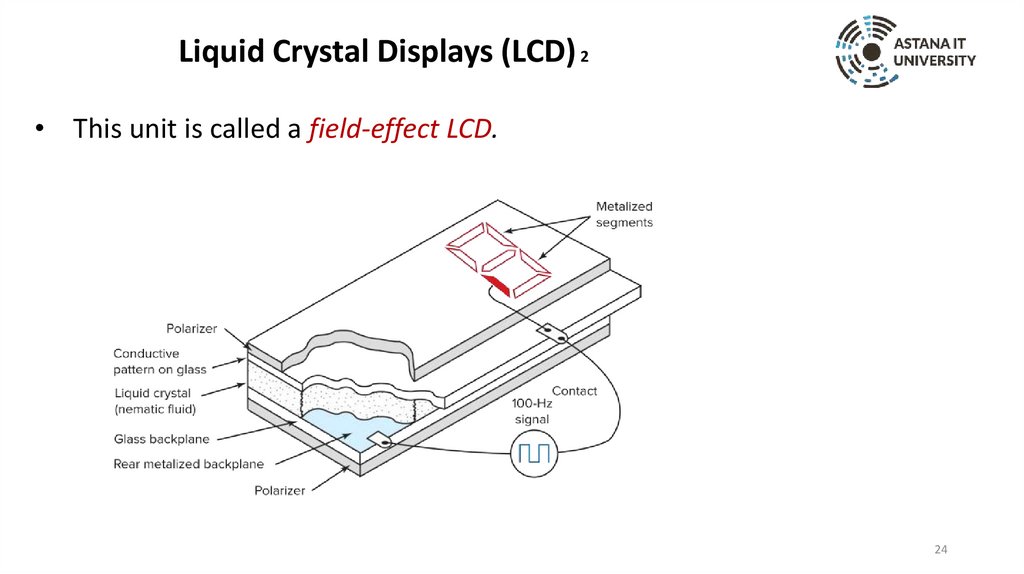
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) 2• This unit is called a field-effect LCD.
24
25.
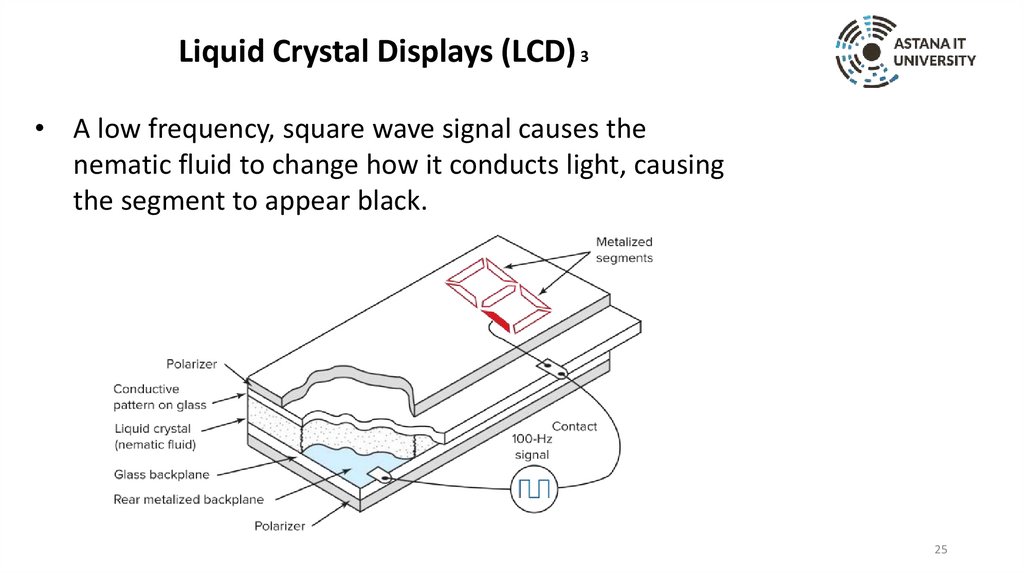
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) 3• A low frequency, square wave signal causes the
nematic fluid to change how it conducts light, causing
the segment to appear black.
25
26.
Driving Liquid Crystal Display 1• A BCD input of 0111 activates (HIGH) the a, b,
and c outputs. The remaining outputs are LOW.
• The 100 Hz square-wave is applied to the
backplane and two each of the CMOS XOR
gates.
• The XOR gates produce an inverted signal when
activated.
• The 180° out-of-phase signals to the backplane
and segments a, b, and c cause the segments to
turn black.
26
27.
Driving Liquid Crystal Display 227
28.
Review 1• The decimal number 31 is the same as _______ in
binary.
• The decimal number 31 is the same as _______ in
the 8421 BCD code.
• The 8421 BCD code 1000 1100 0011 0001 equals
_______ in decimal.
28
29.
Review 2• The decimal number 31 is the same as 00011111 in
binary.
• The decimal number 31 is the same as 0011 0001 in
the 8421 BCD code.
• The 8421 BCD code 1000 1001 0011 0001 equals 8931
in decimal.
29
30.
Review 3• The decimal number 7 equals _______ in excess-3
code.
• The excess-3 code 0100 0111 equals ________ in
decimal.
30
31.
Review 4• The decimal number 7 equals 1010 in excess-3 code.
• The excess-3 code 0100 0111 equals 14 in decimal.
31
31
32.
Review 5• The Gray code is commonly used for __________.
• The most important characteristic of the Gray code is
________________________.
32
33.
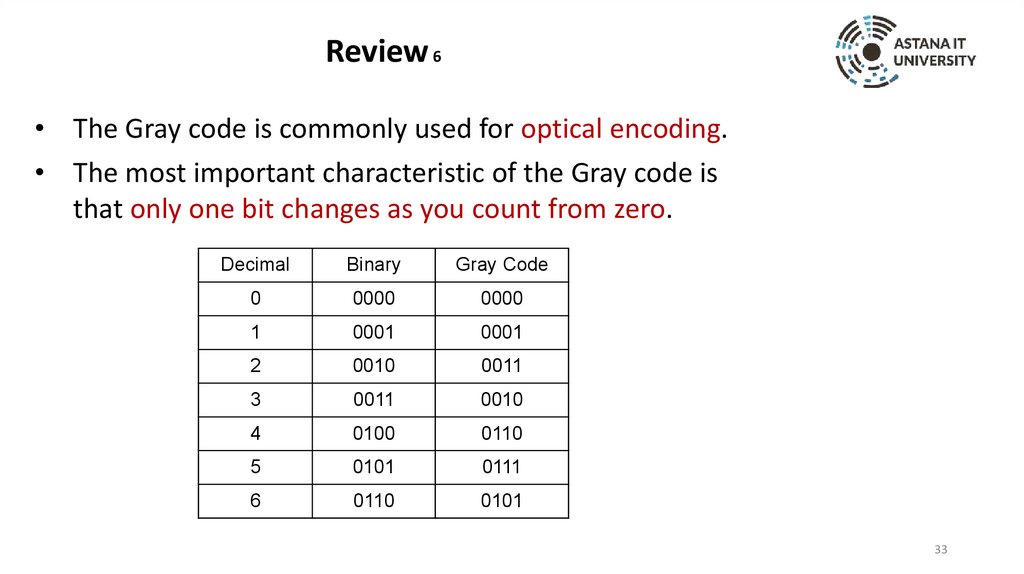
Review 6• The Gray code is commonly used for optical encoding.
• The most important characteristic of the Gray code is
that only one bit changes as you count from zero.
Decimal
Binary
Gray Code
0
0000
0000
1
0001
0001
2
0010
0011
3
0011
0010
4
0100
0110
5
0101
0111
6
0110
0101
33
34.
Review 7• The letters ASCII stands for _________________.
• What is the difference in hexidecimal, between the
letters a and A in ASCII?
• Why was ASCII developed?
34
35.
Review 8• The letters ASCII stands for American Standard Code
for Information Interchange.
• There is a 20H difference between the letters a and A
in ASCII. A 41H , a 61H
• ASCII was developed to send information from
keyboards to computers and from computers to
monitors and printers.
35
36.
Review 9• Encoders translate a ______ input to an 8421 BCD
code.
• When a decoder has a priority feature and two inputs
are activated at the same time, the ________ number
will be encoded.
36
37.
Review 10• Encoders translate a decimal input to an 8421 BCD
code.
• When a decoder has a priority feature and two inputs
are activated at the same time, the larger number will
be encoded.
37
38.
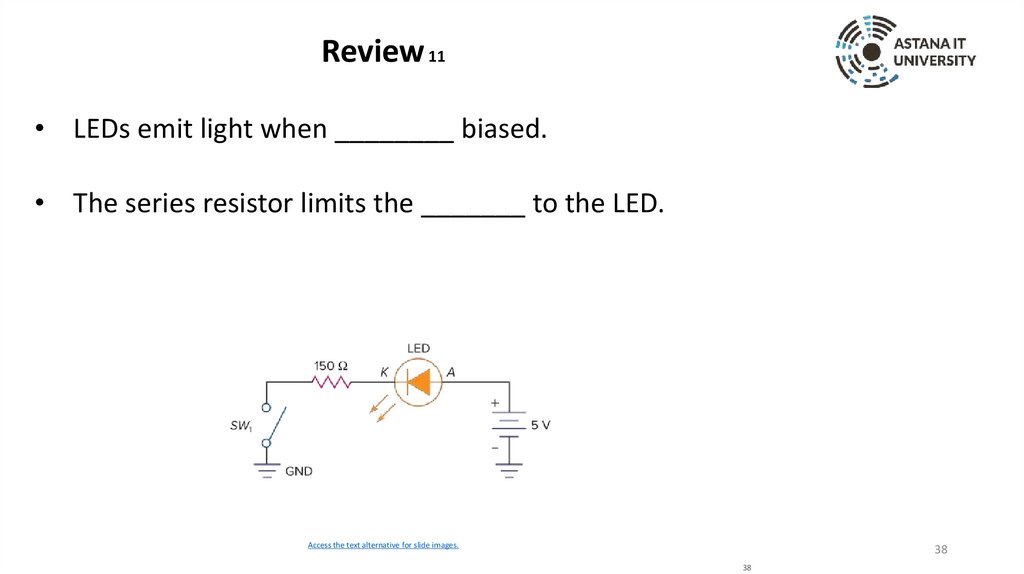
Review 11• LEDs emit light when ________ biased.
• The series resistor limits the _______ to the LED.
Access the text alternative for slide images.
38
38
39.
Review 12• LEDs emit light when forward biased.
• The series resistor limits the current to the LED.
Access the text alternative for slide images.
39
39
40.
4041.
4142.
4243.
4344.
Thank you!44























 informatics
informatics








