Similar presentations:
Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks
1.
Astana IT UniversityDepartment of General Education Disciplines
Academic Writing
Week 5
Lecture 1: Theoretical and Conceptual
Frameworks
Lecture 2: Concept Definition.
Extended Definitions of Terms
Seminars 1-2: Language
focus: Extended definitions
Seminar 3: Midterm: Test 1 on language
focus and academic article evaluation
2.
Learning outcomes:By the end of the lessons, students will be able to:
analyze the teacher's comments;
modify the definitions according to the teacher's comments;
formulate the definition for their research.
3.
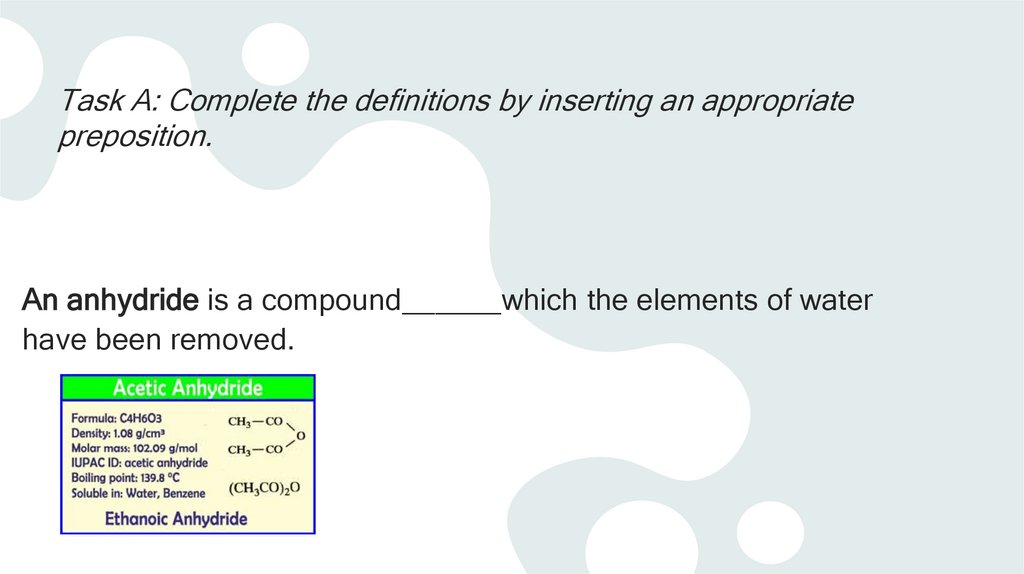
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
An anhydride is a compound______which the elements of water
have been removed.
4.
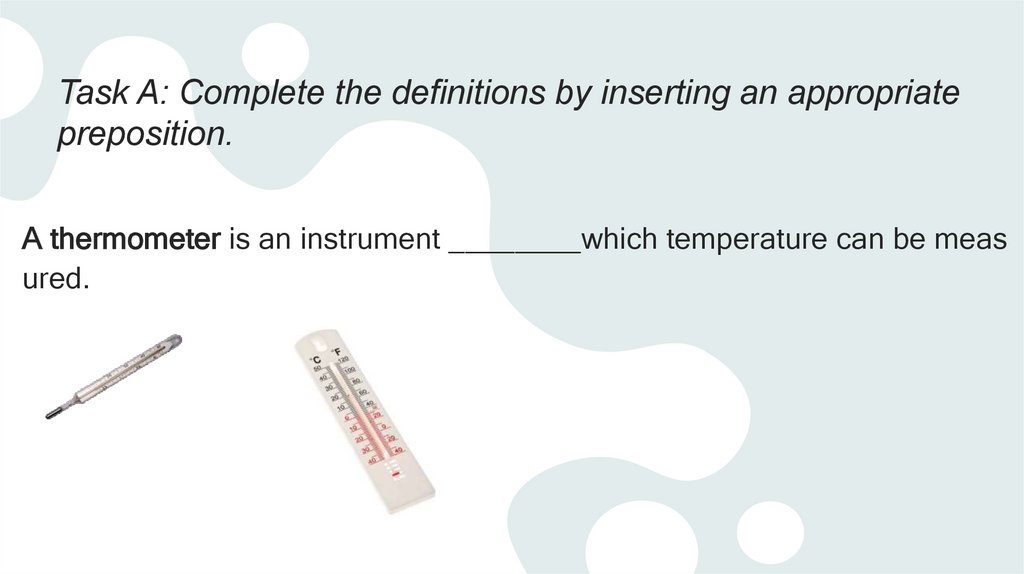
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
A thermometer is an instrument ________which temperature can be meas
ured.
5.
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
An eclipse is a celestial event________which one body, such as a star, is covered by a
nother, such as a planet.
6.
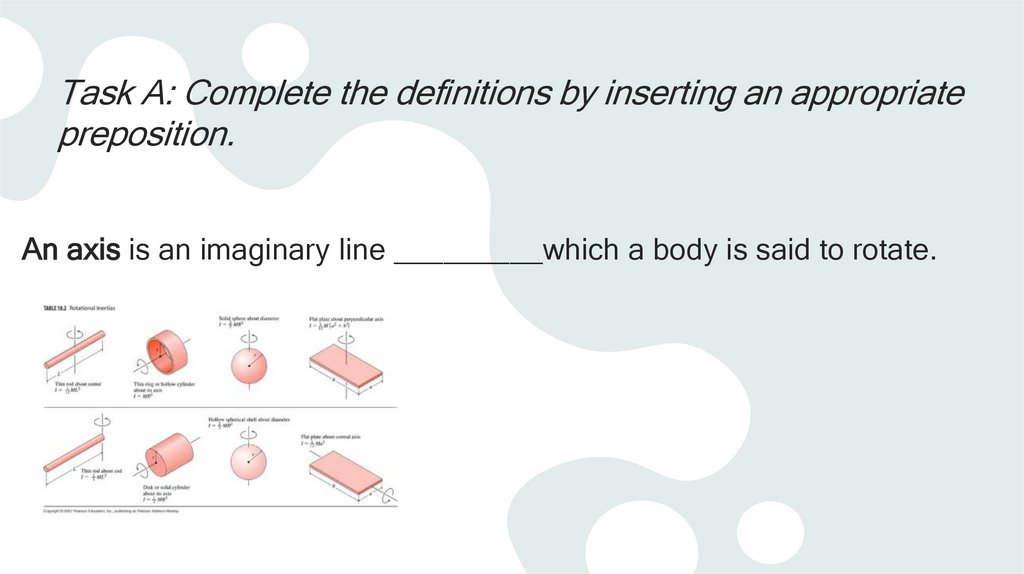
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
An axis is an imaginary line _________which a body is said to rotate.
7.
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
Demography is a discipline that is concerned with changes in population size and the d
egree _____ which fertility (i.e., births), mortality (i.e., deaths), and migration
(i.e., movement into and out of an area) contribute to these changes.
8.
Task A: Complete the definitions by inserting an appropriatepreposition.
Energy balance is a state___________which the number of calories eaten equals the n
umber of calories used.
9.
Task B. 10 minPut the sentences in the correct order.
Palindromes
____a. The term itself comes from the Ancient Greek word palindromes meaning "running back
again."
____b. Another good and more recent example is "draw pupil's lip upward".
____c. Now, however, computers have allowed word puzzlers to construct palindromes that are
thousands of words long, but these are simply lists of unrelated words that do not have meaning
when taken together.
____d. A palindrome is a word or phrase that results in the same sequence of letters no matter
whether it is read from left to right or from right to left.
____e. One of the classic long palindromes is "A man, a plan, a canal, Panama."
____f. Before we had computers, long palindromes used to be very hard to construct, and some
word puzzlers spent immense amounts of time trying to produce good examples.
____g. Some common English words are palindromes, such as pop, dad, noon, and race car.
10.
Task C. 20 minThis task presents a draft of a definition along with
some instructor comments.
Revise the text after reading the comments.
Rewrite the entire passage to reflect the changes
that you think are reasonable
1.Automotive airbag is occupant restraint system. 2.It provides protection for
occupant of vehicle in crash. 3.Although airbags may seem to be somewhat
recent innovation, rapidly inflating air cushions designed to prevent crash injuries
existed for quite some time. 4.Before being used in the automobiles. 5.In fact
researchers filed very first patents for inflatable safety cushion to be used in
airplanes during World War II. 6.A recent study by the National Highway Traffic
Safety Administration concluded that airbags save nearly 1,000 lives annually.
7.In the future even more lives will be saved as new airbag technologies are
developed. 8.Currently, for example, research is being done on as many as six
different types of airbags that will offer protection in a wider range of accidents
beyond front-end and side-impact collisions. 9.Automotive airbag technology
developed between 1940 and 1960 was quite similar to that of airbags currently
in use. 10.Those early airbag systems were very difficult to implement and costly.
11.The main concern for design engineers at the time centered on storage.
12.And the efficient release of compressed air . 13.The housing of the system
had to be large enough for a gas canister. 14.The canister had to keep the gas at
high pressure for a long period of time. 15.The bag itself had to have a special
design. 16.It would deploy reliably and inflate within 40 milliseconds. 17.The
solution to these problems came in the early 1970s with the development of small
inflators. 18.Inflators used hot nitro- gen instead of air to deploy the bag. 19.It
allowed the widespread installation of airbags in vehicles beginning in the 1980s.
11.
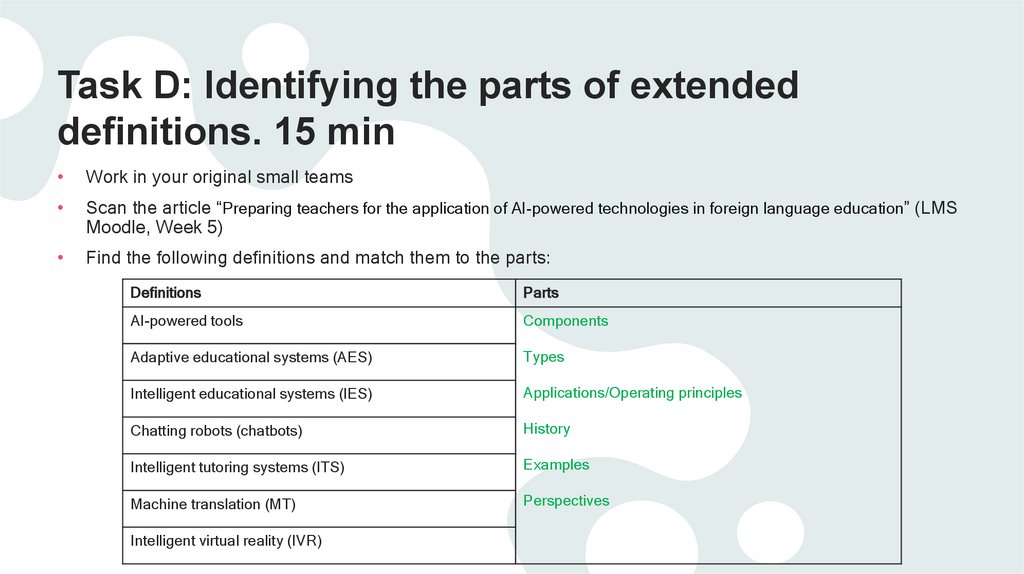
Task D: Identifying the parts of extendeddefinitions. 15 min
Work in your original small teams
Scan the article “Preparing teachers for the application of AI-powered technologies in foreign language education” (LMS
Moodle, Week 5)
Find the following definitions and match them to the parts:
Definitions
Parts
AI-powered tools
Components
Adaptive educational systems (AES)
Types
Intelligent educational systems (IES)
Applications/Operating principles
Chatting robots (chatbots)
History
Intelligent tutoring systems (ITS)
Examples
Machine translation (MT)
Perspectives
Intelligent virtual reality (IVR)
12.
DefinitionsAI-powered tools
Baker and Smith (2019) divide AI tools used in education into three groups: a) learner-facing, b) teacher-facing, and c) system-facing ones. a. Learner-facing
AI tools are software that students use to learn a subject matter. b. Teacher-facing systems are used by teachers with the purpose to reduce their workload
and make their output more effective in specific automating tasks, such as administration, assessment, feedback and plagiarism detection. c. System-facing
AI tools provide information for administrators and managers on the institutional level, for example, they help monitor attrition patterns across faculties or
colleges.
Adaptive
educational
systems
(AES)
Adaptive educational systems (AES) are designed to adapt some of the key functional characteristics (e.g. content, sequence of activities or navigation
support) to the learner needs. This may happen thanks to “building a model of the goals, preferences and knowledge of each individual student and using
this model throughout the interaction with the student in order to adapt to the needs of that student” (Brusilovsky & Peylo, 2003, p. 156). An adaptive system
thus “operates differently for different learners, taking into account information accumulated in the individual or group learner models” (Magnisalis et al.,
2011).
Intelligent
educational
systems
(IES)
Intelligent educational systems (IES) incorporate and perform “some activities traditionally executed by a human teacher - such as coaching students or
diagnosing their misconceptions“ (Brusilovsky & Peylo, 2003, p. 156). They aim to provide learner-tailored support through implementing “extensive
modelling of the problem-solving process in the specific domain of application” (Magnisalis et al., 2011). Brusilovsky & Peylo (2003) list as major Intelligent
Tutoring technologies the following: curriculum sequencing (providing the student with the most suitable individually planned sequence of topics and learning
tasks to help find an “optimal path” through the learning material), intelligent solution analysis, and problem solving support.
Chatting robots
(chatbots)
Chatting robots (chatbots) are groups of computer programs that are meant to simulate intelligent human language interaction. A human user and a
computer (robot) are engaged in informal chat (in a written or spoken form) using a natural language. Chatbots are most frequently utilized in marketing
communication; however, they may be used effectively in foreign language classrooms as well (Dargan, 2019; Jia, 2004a, 2004b; Jia, 2008; Kerly et al.,
2007).
Intelligent
tutoring
systems (ITS)
ITS are computer-based learning systems designed to simulate one-to-one personal tutoring. They consist of four basic components: the domain model, the
student model, the tutoring model, and the interface model. “Based on learner models, algorithms and neural networks, they can make decisions about the
learning path of an individual student and the content to select, provide cognitive scaffolding and help, to engage the student in dialogue. ITS have enormous
potential, especially in large-scale distance teaching institutions, which run modules with thousands of students, where human one-to-one tutoring is
impossible” (Zawacki-Richter et al., 2018, p. 5).
Machine
translation (MT)
Machine translation (MT) is the process when computer software is employed to translate a text (written or spoken) from one natural language to another.
For a long time, using MT tools for language learning purposes has been limited due to a questionable quality of their outputs. Artificial intelligence
technologies like neural machine translation have improved the quality of machine translation considerably and free-access web-based MT services resulted
in millions of users using services such as Google Translator, Translator Online, Foreign Word, Web Trance for their work or study every day.
Intelligent
virtual reality
(IVR)
Intelligent virtual reality (IVR) is a complex system integrating conversational AI tools, spatial context awareness technologies, and gesture and facial
landmark recognition systems, NLP, speech recognition and natural language understanding technologies. Learners can practice speaking with AIbased
avatars that simulate realistic conversations with native speakers, which enable learners to gain fluency and build confidence through highly personalized
practice.
13.
Develop a Theoretical FrameworkAsking yourself the following questions, should help you to develop an effective theoretical
framework, tailored to your own data analysis needs:
Are there theories that have been developed in the field of my research topic, or in similar topics that
might inform an understanding of my research question, my research problem and data analysis?
What do experts in the field of my proposed research say about the problem I want to investigate?
What do they say about the research questions I want to investigate, from theoretical perspectives?
Which assumptions, definitions, and propositions are in these leading scholars’ theories, and how
can I make them explicitly relevant to my research question, research problem, and data analysis?
Have I defined the key concepts in my theoretical framework?
Does the theoretical framework I am developing address the research questions of my research?
Is my theoretical framework easily applicable to my data analysis?
14.
Task E. 10 minWriting a definition
Write an extended definition for a key innovation or discovery related to your chosen research
topic. For example, this could be a process, an approach to doing something, or a device.
Include the following information: a sentence definition of the innovation, when the innovation
came about, the importance of the innovation, the problem that the innovation addressed, and
some discussion of how the innovation changed your field.
There may be a need to focus on aspects such as:
o Components
o Types
o Examples
o or Perspectives etc.
15.
Language chunks recommended to usehttps://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk/writing-definitions/
16.
Assessment criteria rubricConcepts submission 5%
Deadline – Week 6, Sunday 23:59
Criteria
Score
Content: One key concept is identified in relation to the topic of the research paper.
The description of the concept is based on a minimum of at least 2 academic sources and has these features:
1. Two definitions of one key concept , e.g., from a dictionary or an expert in the field (from at least two different sources)
20
2.
An extended definition of one key concept with expansion to components/types/applications/operating principles/history/examples
35
3.
A comment on the definition and its relation to the research paper written by the students
20
Formatting and citations:
Both, in-text citation and the references are correctly formatted following the APA 7 th style conventions
10
Paper submitted:
1. is free of grammar, punctuation and spelling mistakes
2. is flexible and accurate use of a wide range of vocabulary and has language chunks provided in lectures (use and highlight at least
3 chunks)
4.
15
is 100-150 words long
Total
100
Score
given
17.
Variations in DefinitionsSometimes a definition of a term or concept is not fixed.
There may be a lack of agreement as to a precise definition, or perhaps there are competing perspectives.
While not as common in the hard sciences, this is something that students in other fields may encounter.
If competing definitions exist for a term that you will be using, a good strategy is to acknowledge some of the different
definitions, but then make clear to your reader the definition you will adopt.
Notice how the authors of the examples express the lack of agreement surrounding a term.
• Here are some skeletal phrases that you could use to present the definition that you have chosen.
• While debate exists regarding a precise definition of ... , the stance adopted in this paper is that ....
• For the purposes of this paper, ... refers to/is defined as/is considered to be .... Here we define ... as ...
• In this paper I have adopted [author's] definition of ... . This paper follows [author's] definition of ....
18.
Draft your assignment• See the template in Week 5, LMS Moodle














 education
education








