Similar presentations:
Sales Management. Lecture 8
1. TEACHING WEEK 8
Sales Management2. Objectives
After finishing this lecture student will be able to answer following questions -:Sales Challenges
Training of Sales Personnel
Skill development
Components of a training programme
Training Programme
Training Methods
Evaluation of training courses
Job Description Factors
What’s in a Signature?
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
2
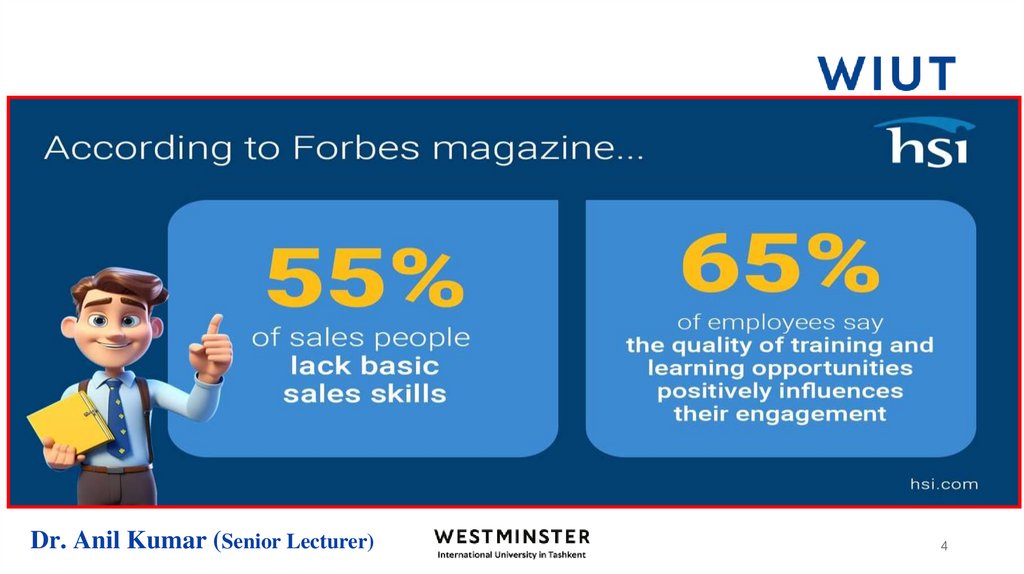
3. Sales challenges
A study for the Learning International Organization revealed seven sales challenges that organisations must meet ifthey are going to survive in the competitive marketplace
Distinguish between similar products and services
Putting together groups of products to form a business solution
Handling the more educated buying population
Mastering the art of consultative selling
Managing a team selling approach
Knowing the customer’s business
Adding value through service
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
3
4.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)4
5. Why Selling Skills are important
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)5
6.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)6
7. Sales Training
Sales training involves the development of a programme which enhances selling skills. Thecomponents of a training programme and methods used were examined before the skills
required for sales management were outlined.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
7
8. Sales Skills examples
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)8
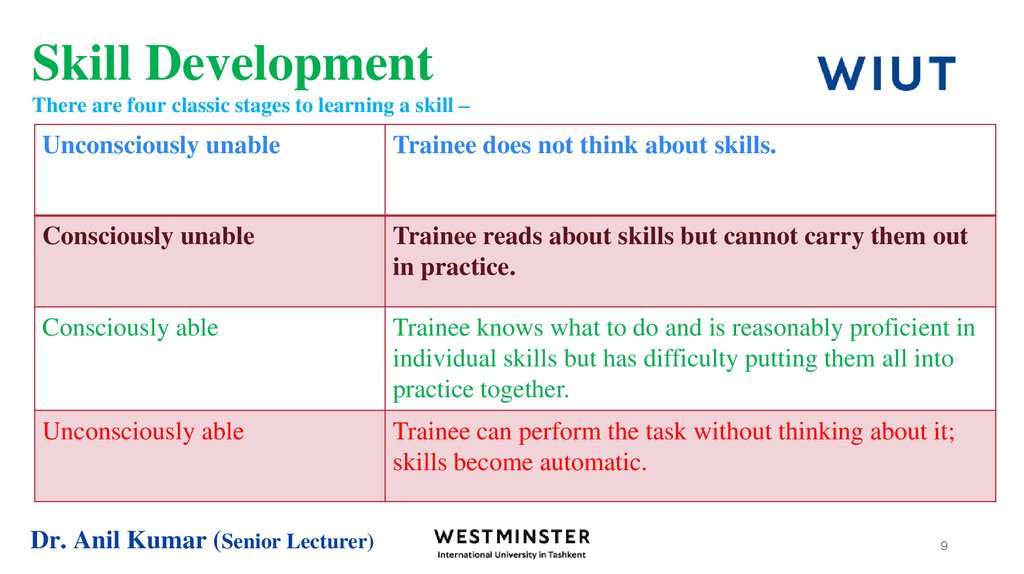
9. Skill Development There are four classic stages to learning a skill –
Unconsciously unableTrainee does not think about skills.
Consciously unable
Trainee reads about skills but cannot carry them out
in practice.
Consciously able
Trainee knows what to do and is reasonably proficient in
individual skills but has difficulty putting them all into
practice together.
Unconsciously able
Trainee can perform the task without thinking about it;
skills become automatic.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
9
10. Components of a training programme
A training programme will attempt to cover a combination of knowledge and skilldevelopment. Five components can be identified:
The company – objectives, policies and organisation.
Its products.
Its competitors and their products.
Selling procedure and techniques.
Work organisation and report preparation.
The first three components are essentially communicating the required level of knowledge to
the salesperson. The first component will probably include a brief history of the company,
how it has grown and where it intends to go in the future.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
10
11. Sales Training Program
Building a sales training programme requires five major decisions – aim, content,method, execution and evaluation. These are referred to as the A-C-M-E-E
decisions. The specific training aims must be defined, content decided, training
methods selected, arrangements made for execution and procedures set up to
evaluate the results.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
11
12.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)12
13. Sales Training Techniques
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)13
14. Training Program
Training varies with the sales person's career cycle Sales persons have variedbackgrounds, experience levels, learning abilities, etc. and therefore have their
own training needs. Another factor deciding the type of training is the stage of the
career of the sales person. Sales person's career cycle is a conceptual framework
which describes the stages through which a sales person passes in his career
cycle. There are four basic stages of this cycle.
Preparation
Development
Maturity
Decline
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
14
15. Four basic stages
Preparation - For the sales person the emphasis should be onorientation and training. He should know about the environment in
which he has to function and given information about the company and
the products he has to sell. Selling instructions and basic selling
techniques are all important at this stage. Sometimes experienced sales
persons new to the company must also be acquainted with the policies
and practices of the company.
Development - This is the second stage when the salesman becomes
productive. He should be supervised and provided field coaching. He
should be able to identify the problems and be kept away from
acquiring bad habits.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
15
16. Four basic stages
Maturity - In maturity stage, the productivity of the sales person levels off. Heworks "smarter than harder". Sometimes refresher training is required to be given
to him to retrain and acquaint him with new concepts and techniques. They can
also be given new challenges and transferred to new areas, new territories or can
be promoted to more responsible positions. Sometimes due to inadequate training
career plateauing takes place. Lack of relevant training hampers growth and
development.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
16
17. Four basic stages
Decline - In this stage the sales person is a problem for themanagement. A lot of motivational retraining is required. The
productivity of the salesman decreases considerably and is difficult to
avert.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
17
18. Training Methods
The training is based on the nature of the job and the products to be sold. There
is a wide variety of training methods. A company has to choose either one or
generally a combination of these methods. The methods chosen should be
consistent with the training needs and the contents of the training program.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
18
19. Group training methods
Lectures or Class Room InstructionsGroup Discussion Method
Sales Conference Method
Case Study Method
Role Playing Method
Simulation or Gaming Method
Brain Storming Method.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
19
20. Individual training methods
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
On the Job Training
Job Rotation
Personal Discussion
Correspondence Courses
Sales Manual
Induction Course
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
20
21. Lectures or Class Room Instructions
(i)Lectures or Class Room Instructions:
They are regarded as one of the simplest ways of imparting knowledge to the trainees,
especially when facts, concepts, attitudes, theories and problem-solving abilities are to
be taught.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
21
22. Lectures or Class Room Instructions Pros and Cons
Lecturesor
Pros and Cons
Class
Room
Instructions
(a) It becomes easier to impart knowledge on
concepts and theories.
(a) The learners are usually of passive
nature and do not participate actively.
(b) A very large groups can be trained within
a short period of time.
(c) Doubts on a particular point can be
cleared on the spot.
(b) Only the theoretical knowledge can
be gained through this type of training
but practical knowledge cannot be
gained. It overlooks the principle of
learning by doing.
(c) One-way communication takes
place and there is no feedback from the
audience.
(d) It is difficult to evaluate the
effectiveness of training.
(d) It reduces the cost of training.
22
23. (ii) Group Discussion Method:
(ii) Group Discussion Method:In this method of training, different groups are formed by limited number
of persons (15-20). Each group seeks guidance under the leadership of a
senior officer. The group discusses the sales problems with the leader and
efforts are made to find out a commonly agreed solution to each problem.
During group discussions, everyone gets an opportunity to learn from the
ideas of others.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
23
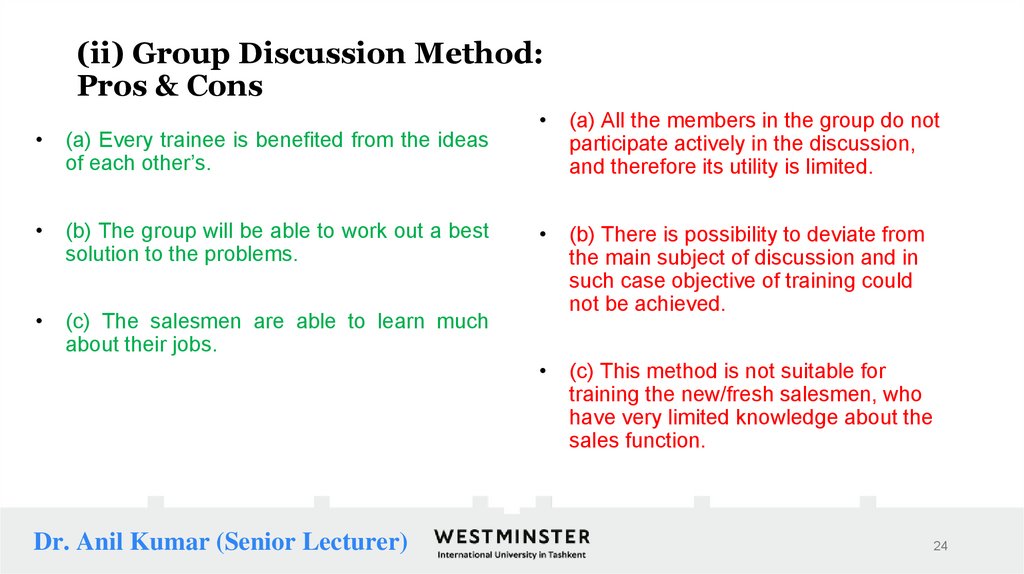
24. (ii) Group Discussion Method: Pros & Cons
(ii) Group Discussion Method:Pros & Cons
(a) Every trainee is benefited from the ideas
of each other’s.
(b) The group will be able to work out a best
solution to the problems.
(c) The salesmen are able to learn much
about their jobs.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)
(a) All the members in the group do not
participate actively in the discussion,
and therefore its utility is limited.
(b) There is possibility to deviate from
the main subject of discussion and in
such case objective of training could
not be achieved.
(c) This method is not suitable for
training the new/fresh salesmen, who
have very limited knowledge about the
sales function.
24
25.
Dr. Anil Kumar (Senior Lecturer)25






















 marketing
marketing








