Similar presentations:
This lesson is being recorded
1.
This lesson isbeing recorded
2.
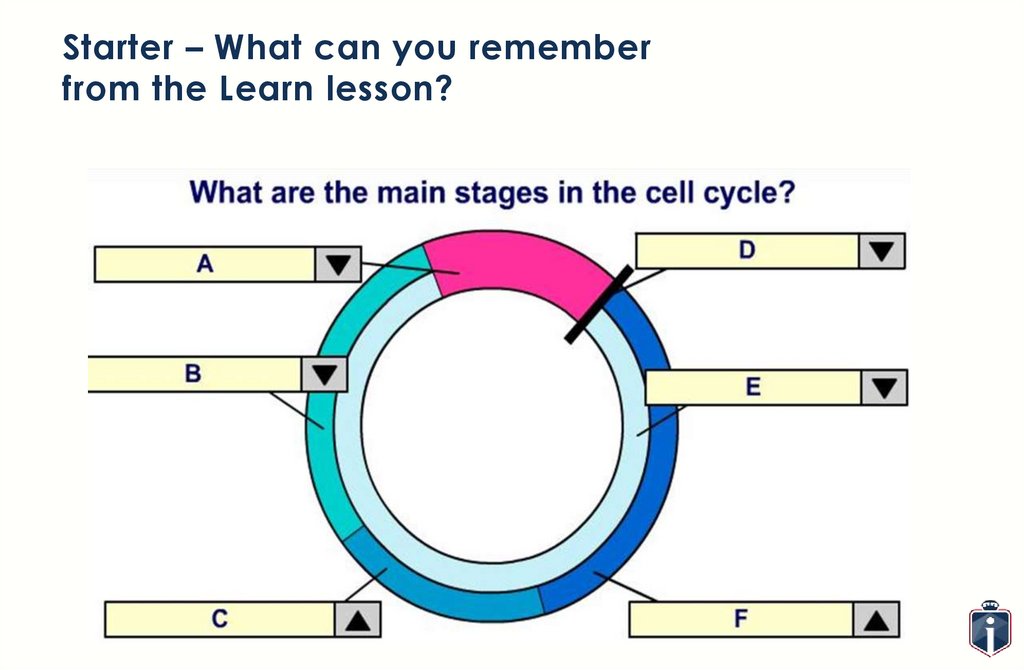
Starter – What can you rememberfrom the Learn lesson?
3.
For today’s biology lesson, you need to be:Ready to think
Ready to discuss
thoughts and ideas
Ready to complete
activities
This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY
This Photo by Uknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
ALWAYS have the tools you may need:
writing equipment i.e. pens, pencils, ruler etc; lined, plain and
graph paper and a calculator
4.
5.
Previous knowledgeto build on
• Mitosis
• Meiosis
• Chromosomes
• Gamete
• Alleles
6.
Useful wordsfor this week
• Mitosis
• Meiosis
• Independent assortment
• Gametes
• Alleles
• Metaphase
• Prophase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
• Asexual
7.
8.
Week 15 BIO UK EXPLORE – Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis& Sexual Reproduction
Textbook Ref: page 112 – 114, 120 – 125
9.
Learning Objectives3.10 understand the role of mitosis and the cell cycle in producing
genetically identical daughter cells for growth and asexual
reproduction
3.9 Understand the role of meiosis in ensuring genetic variation
through the production of non-identical gametes as a consequence
of independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over of
alleles between chromatids(details of the stages of meiosis are not
required).
CORE PRACTICAL 5 Prepare and stain a root tip squash to observe the
stages of mitosis
10.
Question:How does the cell make sure that the daughter cells are genetically identical?
[2]
1.
DNA replication before division
2.
Separation of one chromatid from the pair to each pole of the cell
11.
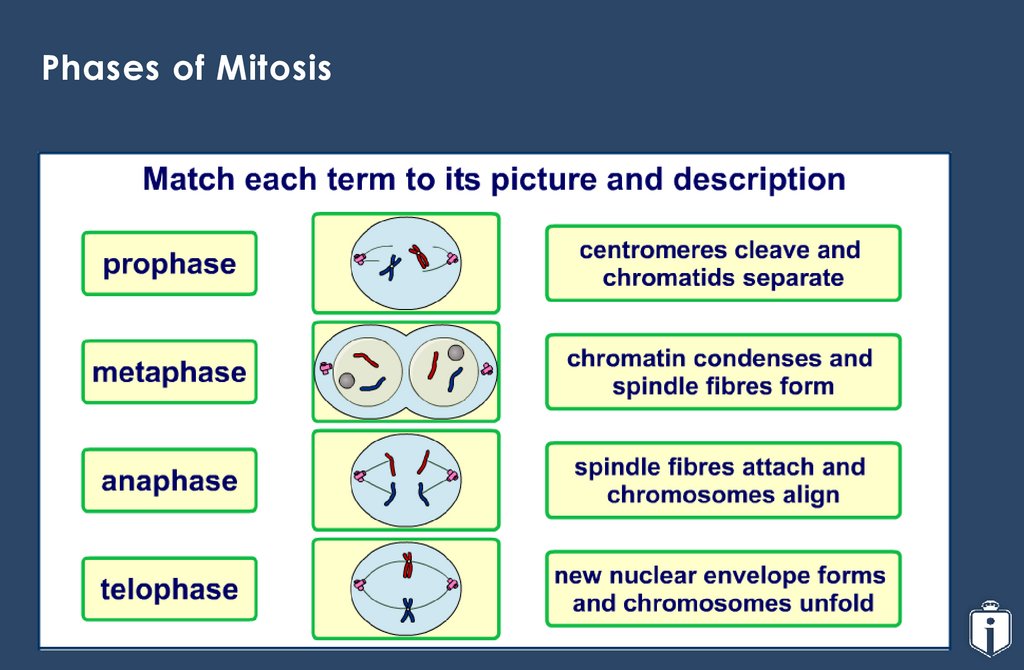
Phases of Mitosis12.
Click the globe to watch(up to 6m 13s)
13.
Questions1.
How many cells are in interphase and
telophase?
2.
What does this suggest about the length of
time that the cell spends in each phase?
14.
NarrativeUse the animation in this link (https://vcell.science/project/mitosis) to write a narrative on
what happens in each stage of mitosis
15.
Mitosis Essay QuestionDescribe the events that occur during one complete cell cycle including mitosis in an animal
cell. (10)
There are actually 15 points on the mark scheme – can you get them all?
16.
The Mark SchemeI Centromere divides at anaphase;
J Chromatids/chromosomes to opposite poles at
anaphase;
A Interphase, replication of DNA; (not: DNA doubles)
B Also replication of organelles;
C Synthesis of rRNA/proteins/ATP; (not: metabolic
activity)
D Prophase chromosomes appear as two chromatids/
ref, condensation;
E Joined at centromere;
F Nuclear membrane disappears;
G Chromosomes line up at equator during metaphase;
H Spindle formation;
K Contraction/shortening of spindle fibres;
L Nuclear membrane reforms during telophase;
M Cytokinesis/cell division occurs by furrowing of
membrane/cleavage;
N Cytoplasm splits/divides;
O Centrioles replicate / move to poles.
Note: ref. to each event must take place in correct
stage
10
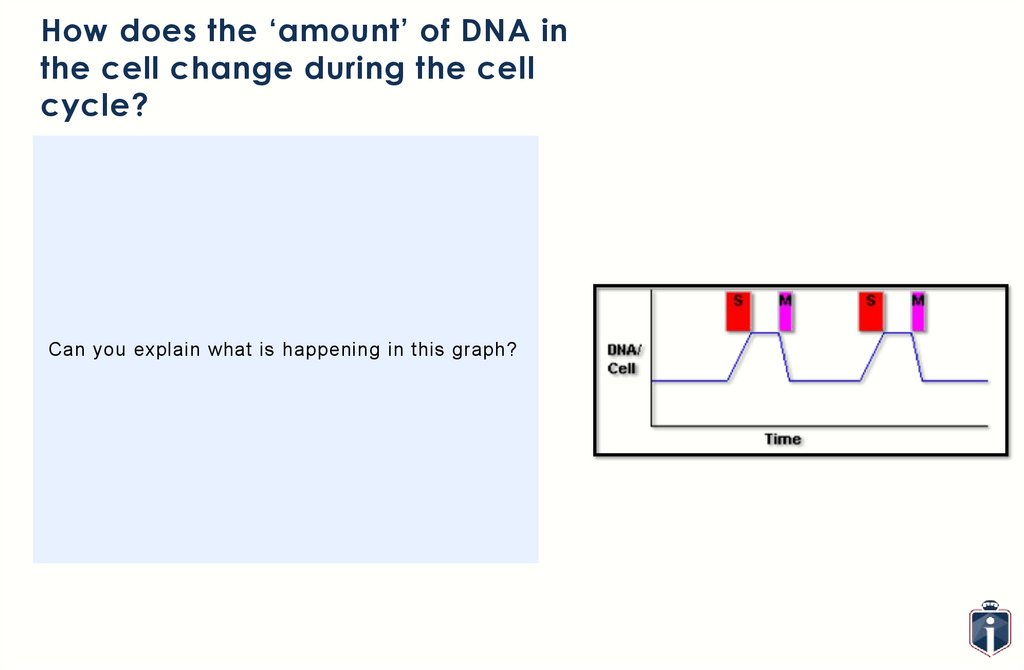
17.
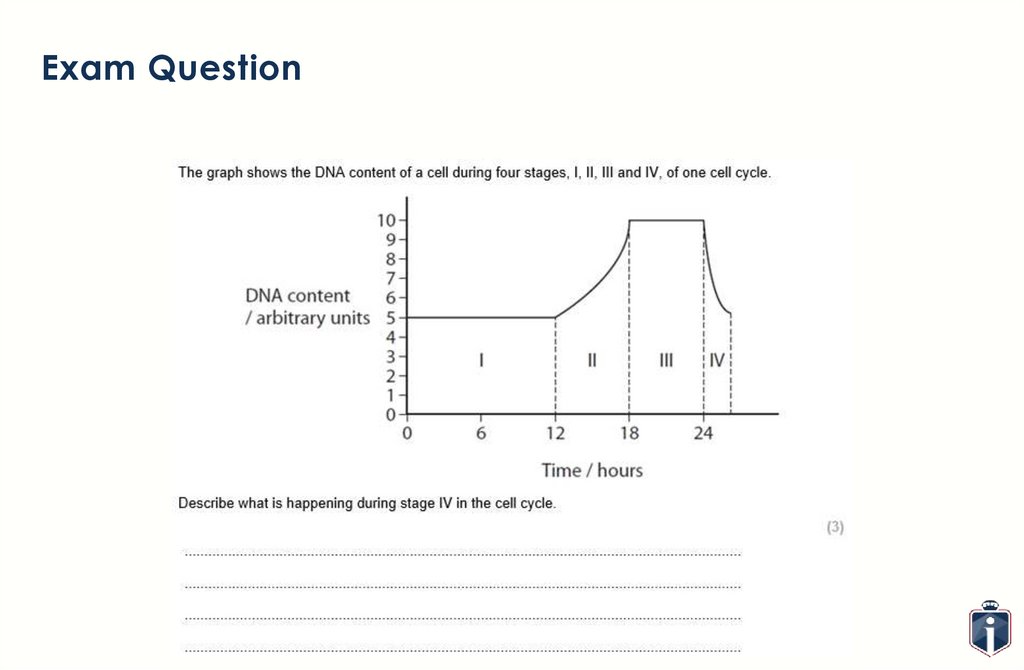
How does the ‘amount’ of DNA inthe cell change during the cell
cycle?
Can you explain what is happening in this graph?
18.
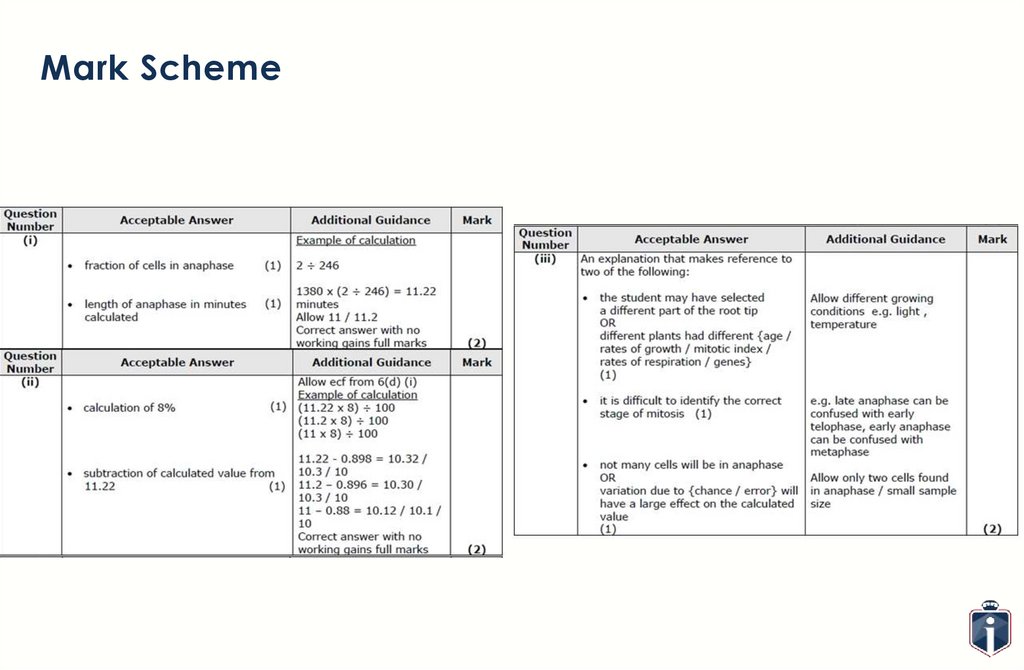
Exam Question19.
Mark Scheme20.
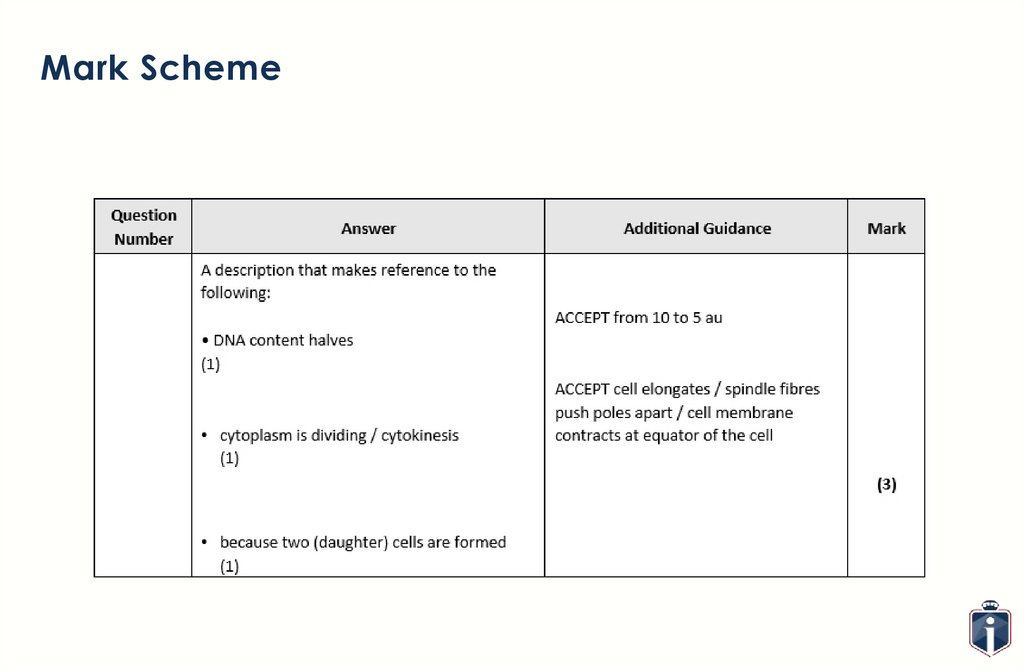
Exam Question21.
Mark Scheme22.
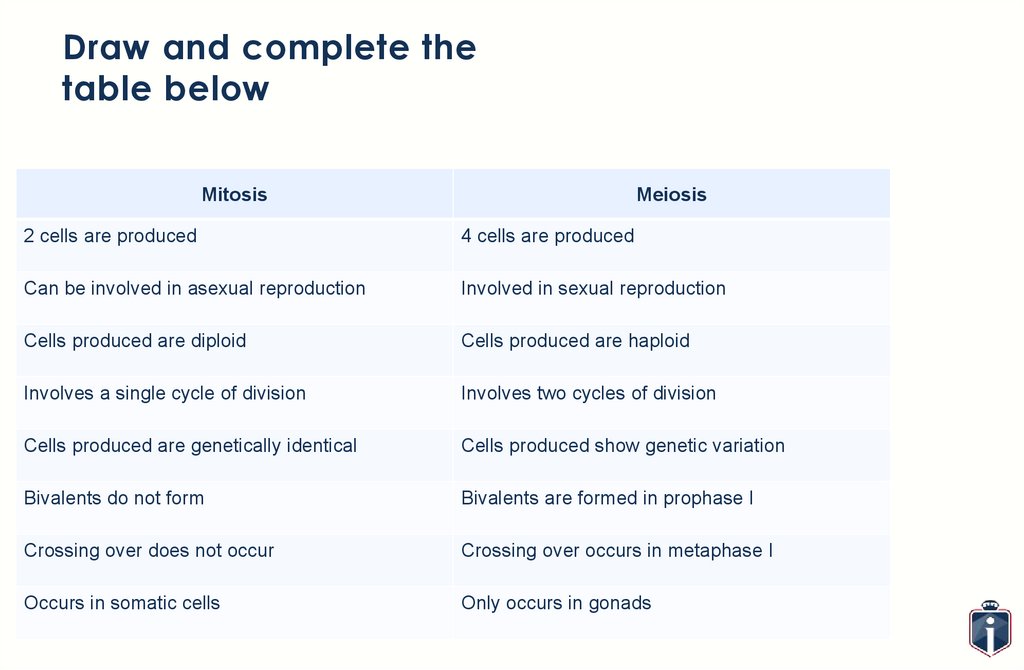
Draw and complete thetable below
Compare and Contrast Meiosis & Mitosis – one has been done for you (you may need to
add more rows!)
Mitosis
2 cells are produced
Meiosis
4 cells are produced
23.
Draw and complete thetable below
Mitosis
Meiosis
2 cells are produced
4 cells are produced
Can be involved in asexual reproduction
Involved in sexual reproduction
Cells produced are diploid
Cells produced are haploid
Involves a single cycle of division
Involves two cycles of division
Cells produced are genetically identical
Cells produced show genetic variation
Bivalents do not form
Bivalents are formed in prophase I
Crossing over does not occur
Crossing over occurs in metaphase I
Occurs in somatic cells
Only occurs in gonads
24.
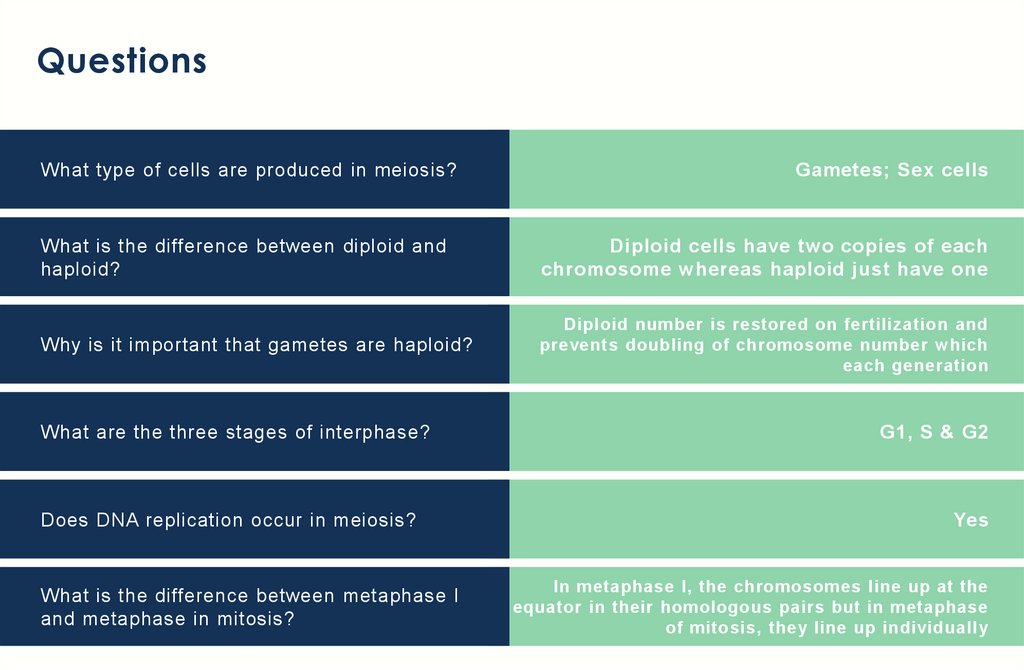
QuestionsWhat type of cells are produced in meiosis?
Gametes; Sex cells
What is the difference between diploid and
haploid?
Diploid cells have two copies of each
chromosome whereas haploid just have one
Why is it important that gametes are haploid?
Diploid number is restored on fertilization and
prevents doubling of chromosome number which
each generation
What are the three stages of interphase?
Does DNA replication occur in meiosis?
What is the difference between metaphase I
and metaphase in mitosis?
G1, S & G2
Yes
In metaphase I, the chromosomes line up at the
equator in their homologous pairs but in metaphase
of mitosis, they line up individually
25.
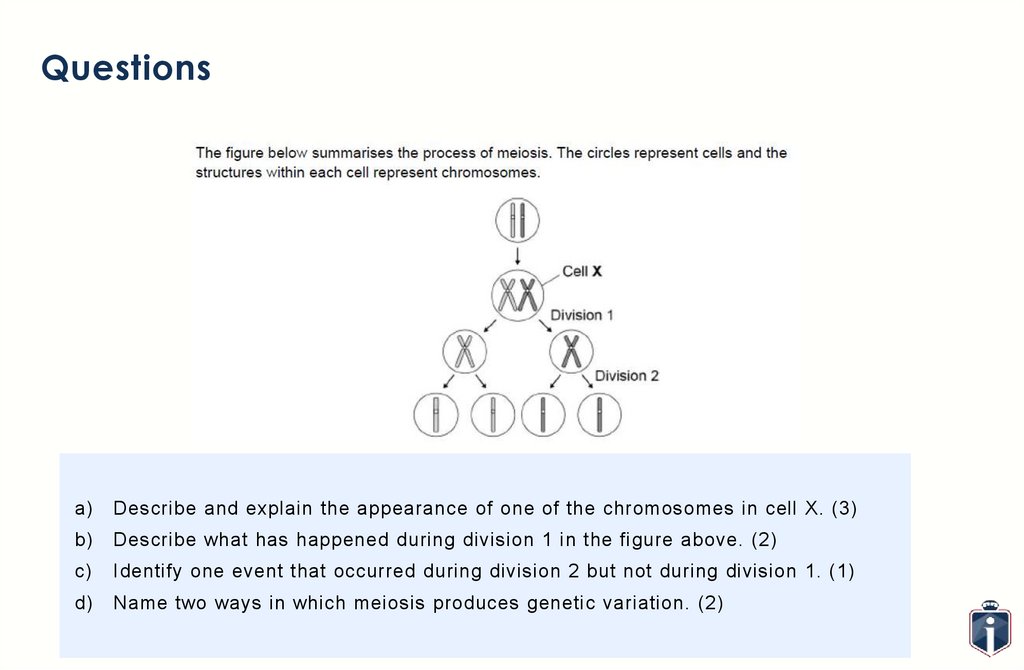
Questionsa)
Describe and explain the appearance of one of the chromosomes in cell X. (3)
b)
Describe what has happened during division 1 in the figure above. (2)
c)
Identify one event that occurred during division 2 but not during division 1. (1)
d)
Name two ways in which meiosis produces genetic variation. (2)
26.
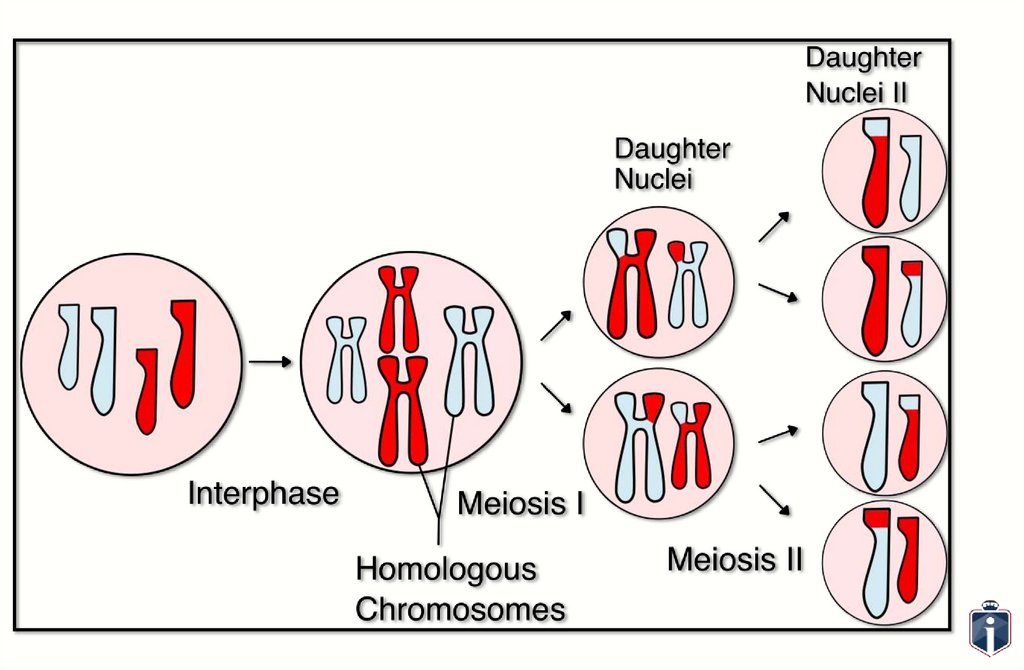
Mark Scheme27.
Answer in the pollDuring which division in meiosis in the chromosome number halved?
a)
Meiosis I
b)
Meiosis II
28.
29.
Recap the events of meiosisand be prepared to answer
questions
30.
Give one other piece ofinformation on meiosis from
that animation
31.
Explore Activity: Week 15 BIO UKExplore Activity Discussion
What happens when mitosis goes wrong?
What is the difference between a chromosome and a chromatid?
How does meiosis lead to variation between offspring?
Why is meiosis important for gamete formation?
32.
Explore ActivityWeek 15 BIO UK Resource – The Cell/The Cell Poster
• Study this material and find out all the points about cell division
you can
• Share on the next slide
33.
Explore ActivityWeek 15 BIO UK Resource – Mitosis Exam Questions
Work on these but ask if you don’t understand something.
34.
Explore ActivityWeek 15 BIO UK Resource – Meiosis Questions
The examiners report and mark scheme is also included
35.
If you need more clarification,watch this independently……
36.
If time…Week 15 BIO UK Resource – 076 – The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle & Mitosis
Read and have a go at the questions
37.
ApplyWeek 15 BIO UK Apply – Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
38.
Poll Time!Add two things you have learned in today’s
lesson
39.
What were theuseful words
for this week?
• Mitosis
• Meiosis
• Independent assortment
• Gametes
• Alleles
• Metaphase
• Prophase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
• Asexual
40.
How confident do you feel about todaysobjectives?
3.10 understand the role of mitosis and the cell cycle in producing
genetically identical daughter cells for growth and asexual
reproduction
3.9 Understand the role of meiosis in ensuring genetic variation
through the production of non-identical gametes as a consequence
of independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over of
alleles between chromatids(details of the stages of meiosis are not
required).
CORE PRACTICAL 5 Prepare and stain a root tip squash to observe the
stages of mitosis
41.
In week 16 you will study:• Text book page: 110 – 112 & 118
Gametes and fertilization
• Inspired AI
The structure of mammalian
gametes
• Gametes and fertilization
Fertilization in plants
• Weblink: here
• Video: here
42.
Lesson complete!See you next lesson



























 biology
biology