Similar presentations:
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
1. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM)
Fawzy Elbarbry, PhD, RPh, BCPS2. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
• Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) refers to adjustmentof drug doses based on measured plasma
concentrations to attain values within a therapeutic
range.
• Clinical pharmacists play a key role in ensuring safe and
effective administration of medications via performing
TDM of selected medications
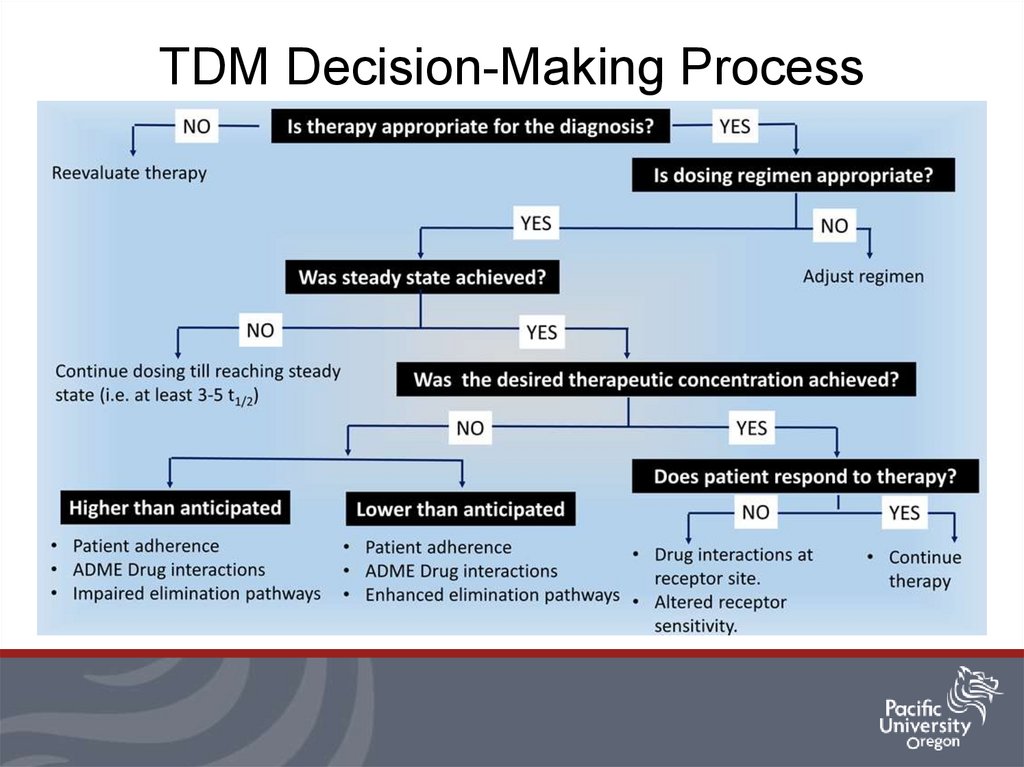
3. TDM Decision-Making Process
4. When Should we Perform TDM?
• Good correlation between pharmacologic response and drugconcentrations
• Wide inter-patient variation
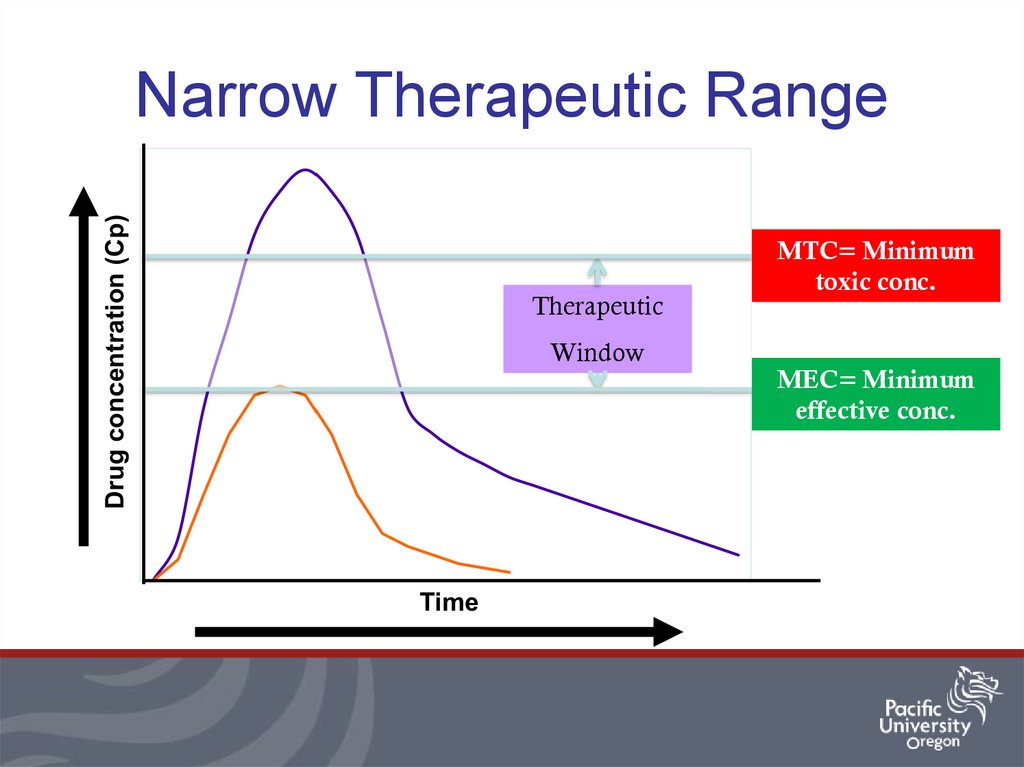
• Drug has narrow therapeutic index (range)
• Absence of good clinical markers of effect
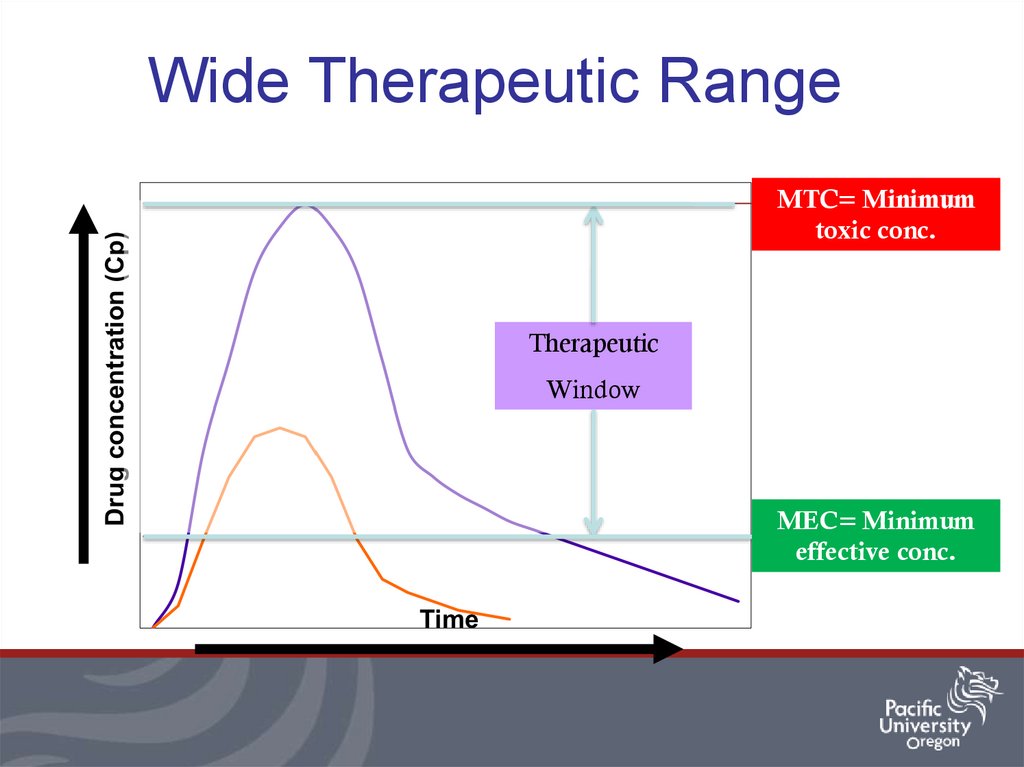
5. Therapeutic Range
MTC= Minimumtoxic conc.
Therapeutic
Window
MEC= Minimum
effective conc.
6. Wide Therapeutic Range
MTC= Minimumtoxic conc.
Therapeutic
Window
MEC= Minimum
effective conc.
7. Narrow Therapeutic Range
TherapeuticMTC= Minimum
toxic conc.
Window
MEC= Minimum
effective conc.
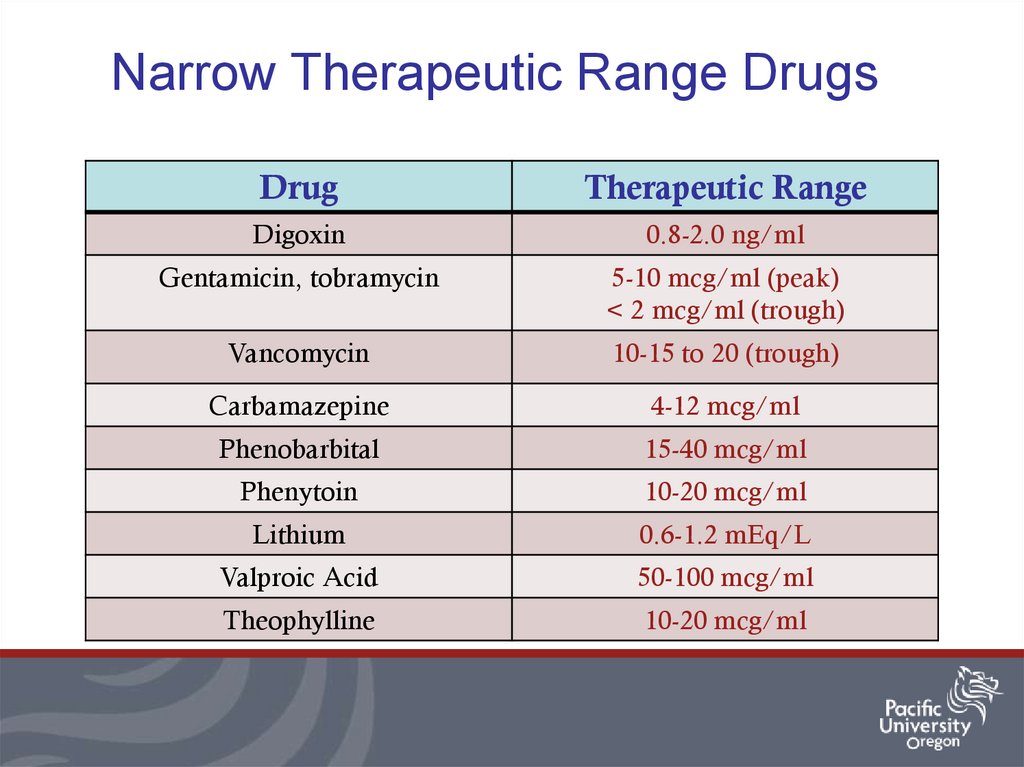
8. Narrow Therapeutic Range Drugs
DrugTherapeutic Range
Digoxin
0.8-2.0 ng/ml
Gentamicin, tobramycin
5-10 mcg/ml (peak)
< 2 mcg/ml (trough)
Vancomycin
10-15 to 20 (trough)
Carbamazepine
4-12 mcg/ml
Phenobarbital
15-40 mcg/ml
Phenytoin
10-20 mcg/ml
Lithium
0.6-1.2 mEq/L
Valproic Acid
50-100 mcg/ml
Theophylline
10-20 mcg/ml
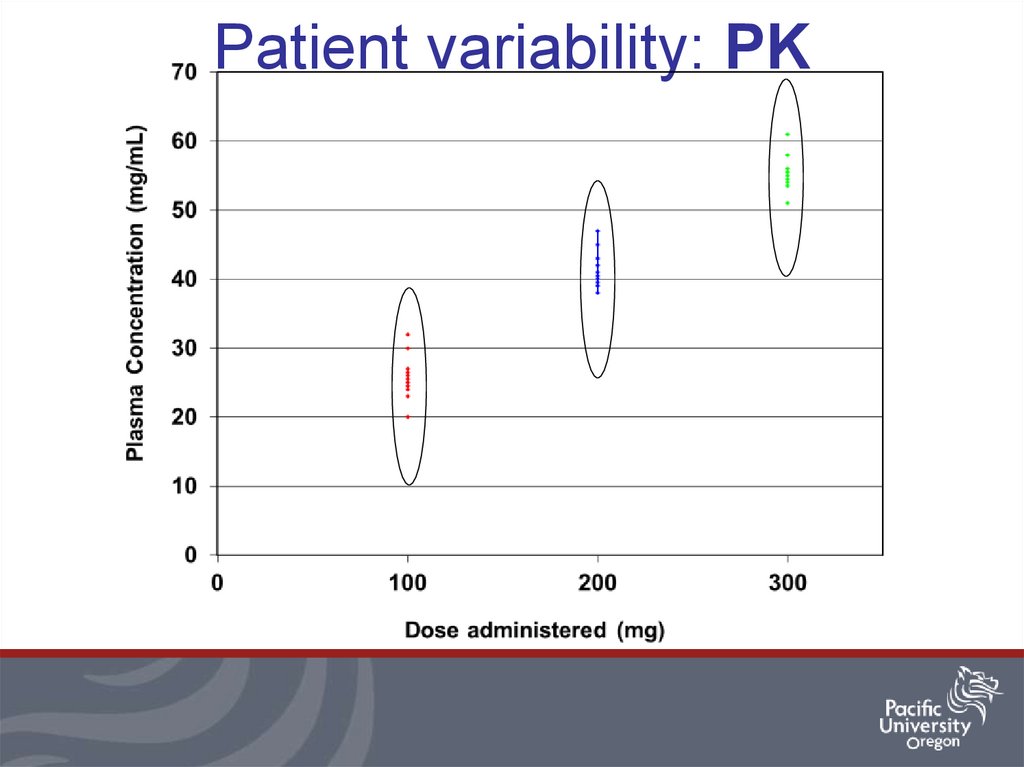
9. Patient variability: PK
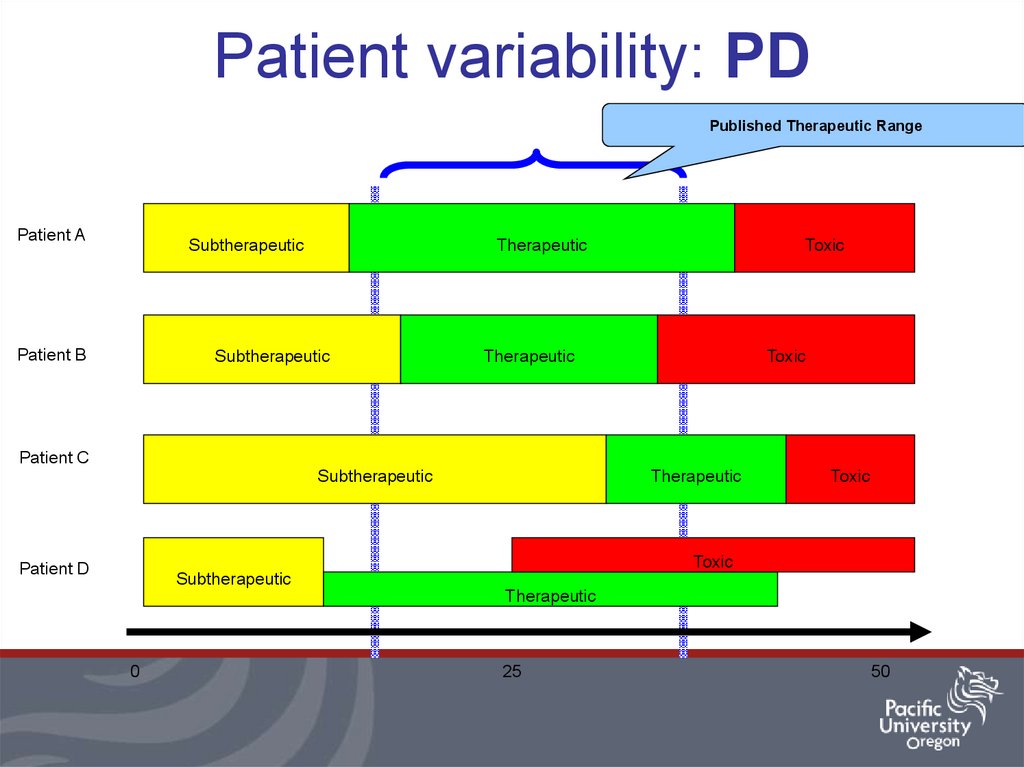
10. Patient variability: PD
Published Therapeutic RangePatient A
Subtherapeutic
Patient B
Therapeutic
Subtherapeutic
Toxic
Therapeutic
Toxic
Patient C
Subtherapeutic
Therapeutic
Toxic
Toxic
Patient D
Subtherapeutic
Therapeutic
0
25
50
11. Patient variability: Reasons
• Physiologic states that alter ADME:– Age
– Genetic polymorphisms
– Pregnancy
• Disease/physiologic states that alter ADME:
– Organ dysfunction (hepatic and renal function)
– Genetic polymorphisms
– Variations in drug absorption (gastric motility)
• Drug interactions
• Variability can be Inter-patient, or Intra-patient.
12. Measuring Drugs Concentration:
Indications1. Drugs used for prophylaxis
use of cyclosporine to prevent transplant rejection
2. Early diagnosis of toxicity
aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity
3. Detection of drug Interactions
Addition of rifampicin to a cyclosporine regimen
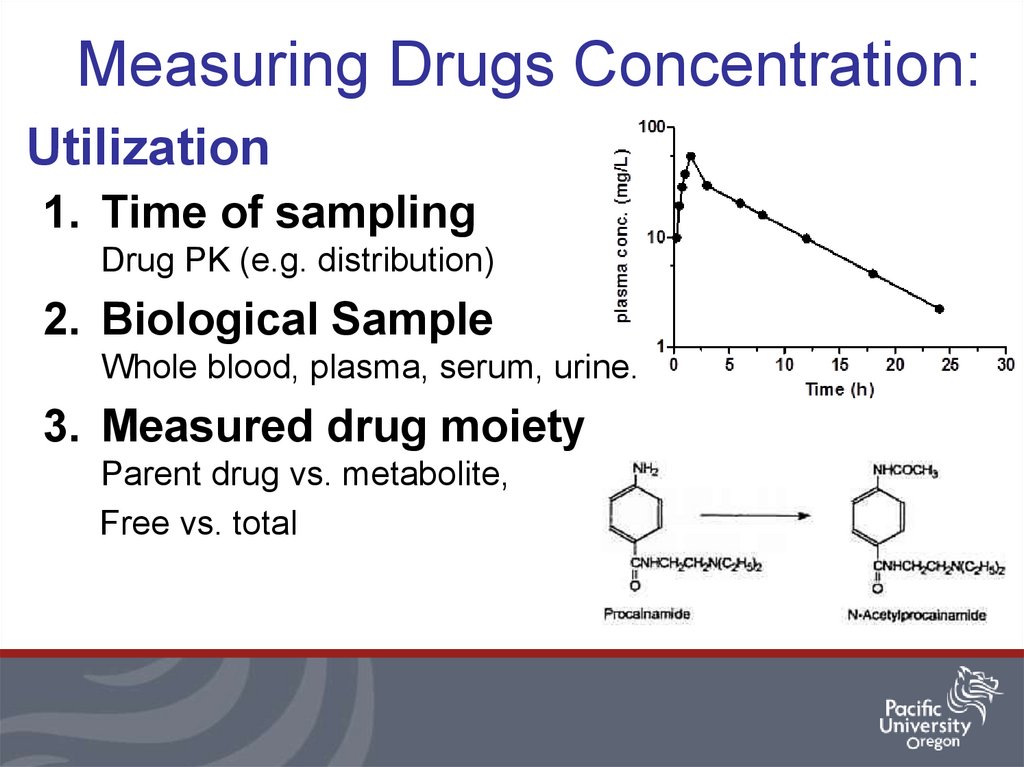
13. Measuring Drugs Concentration:
Utilization1. Time of sampling
Drug PK (e.g. distribution)
2. Biological Sample
Whole blood, plasma, serum, urine.
3. Measured drug moiety
Parent drug vs. metabolite,
Free vs. total
14. Measuring Drugs Concentration:
“Should I get a drug level for my patient?”– Is the patient already responding appropriately to the drug
therapy?
– Is the patient having any toxicity from the drug therapy?
– Are the efficacy and toxicity of this drug better predicted by
measuring drug concentrations or evaluating clinical
response?
– How will obtaining a drug concentration change the clinical
management of the patient?
– What is the expected duration of therapy?
$$$$$$$$$
15.
16.
17. Clinical Apps/Calculators
• https://globalrph.com/medical-calculatorsinternal-medicine/• https://clincalc.com/
18.
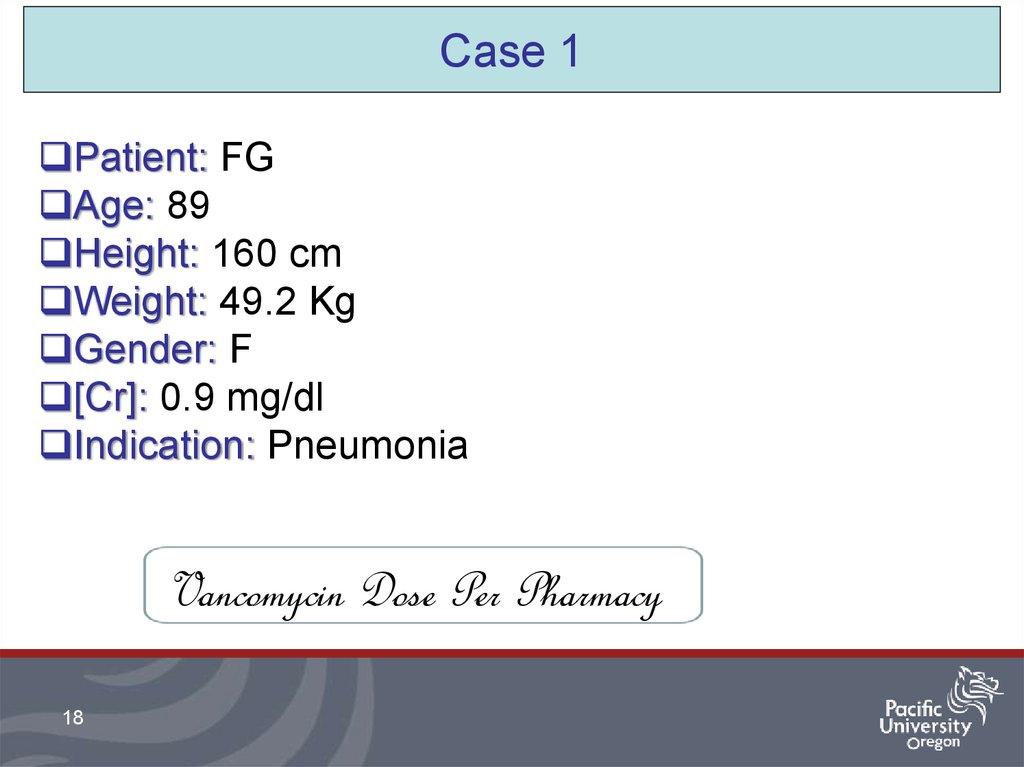
Case 1Patient: FG
Age: 89
Height: 160 cm
Weight: 49.2 Kg
Gender: F
[Cr]: 0.9 mg/dl
Indication: Pneumonia
Vancomycin Dose Per Pharmacy
18
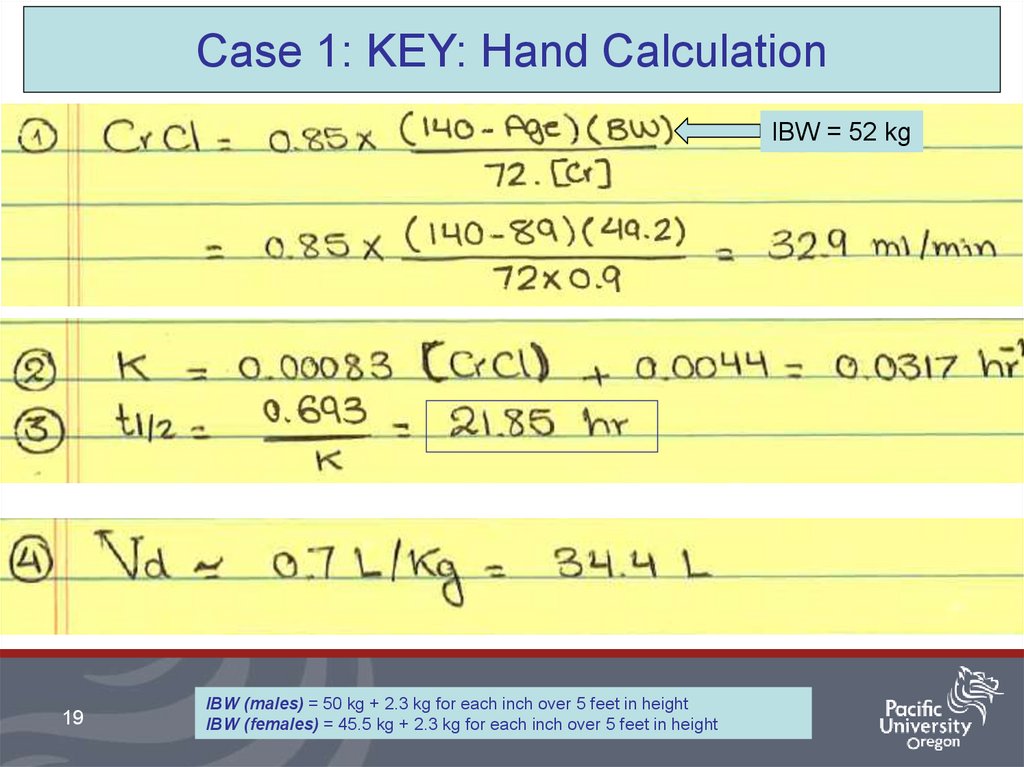
19.
Case 1: KEY: Hand CalculationIBW = 52 kg
19
IBW (males) = 50 kg + 2.3 kg for each inch over 5 feet in height
IBW (females) = 45.5 kg + 2.3 kg for each inch over 5 feet in height
20.
Case 1: KEY, Hand Calculation20
21.
Case 1: KEY, Hand CalculationLoading Dose: 25-30 mg/kg
= 25-30 mg/kg X 49.2 kg ~ 1250-1500 mg, Infuse over 75-90 min
Final Recommendation:
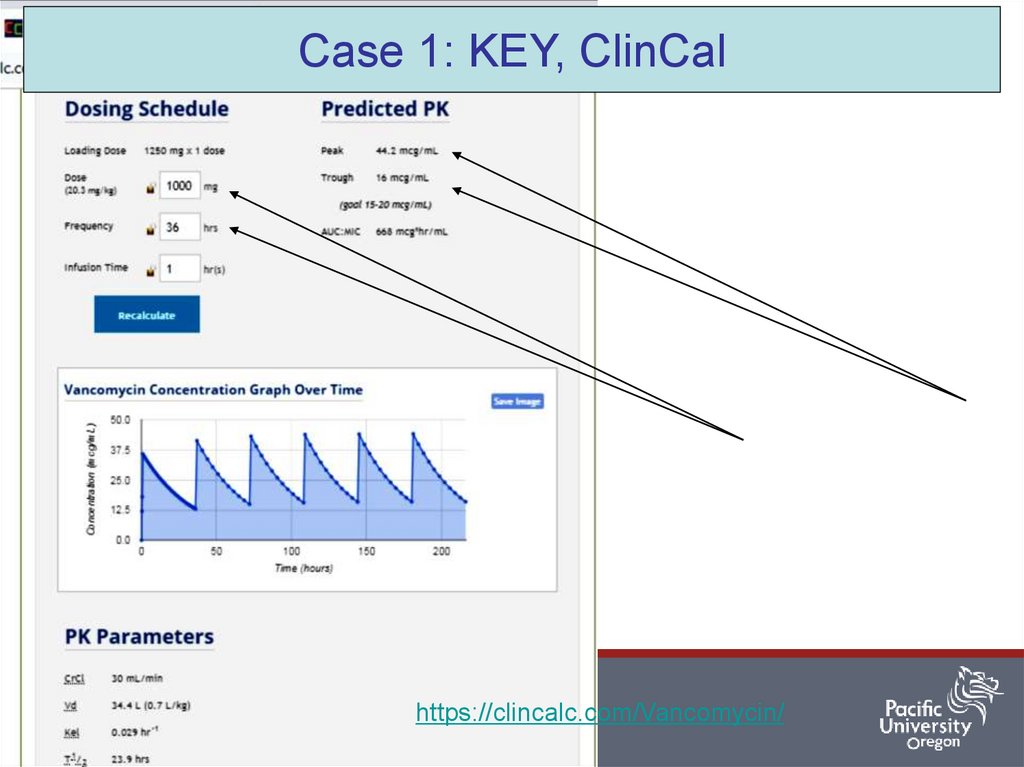
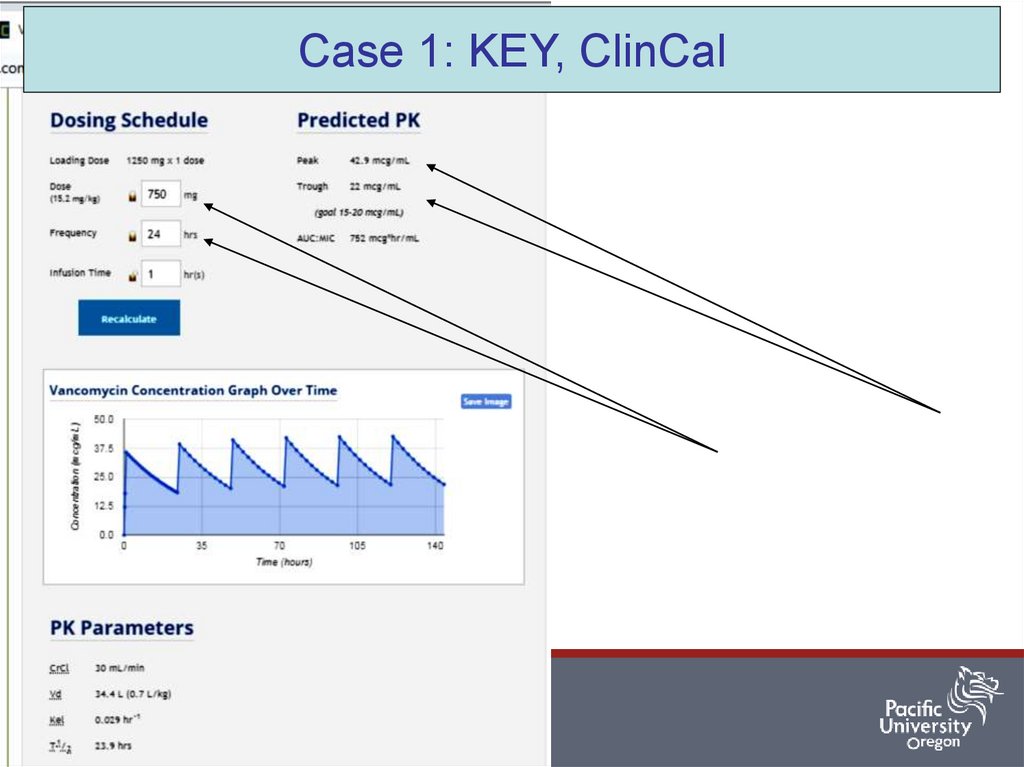
Administer 1250 mg over 75 min now, followed by 750 mg Q24 hr. infused over 60 min
after 24 hr.
21
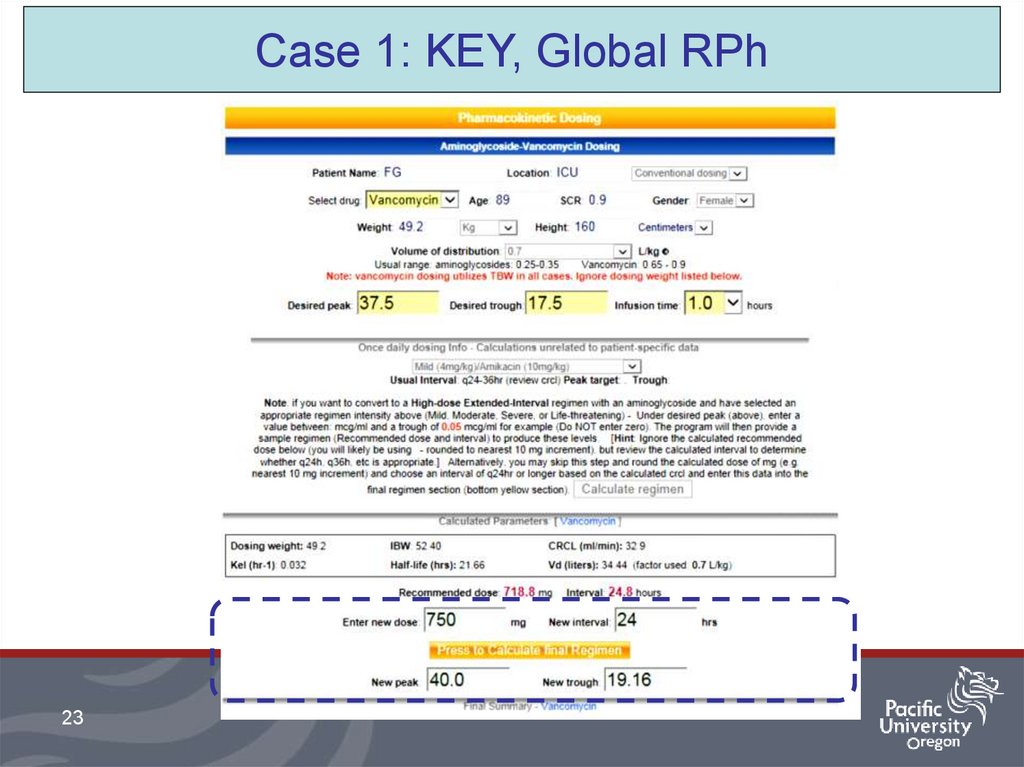
22.
Case 1: KEY, Global RPh22
http://www.globalrph.com/aminoglycosides.htm
23.
Case 1: KEY, Global RPh23
24.
Case 1: KEY, ClinCal24
https://clincalc.com/Vancomycin/
25.
Case 1: KEY, ClinCal25
26. Learning Objectives
• Describe the different components of therapeutic drugmonitoring (TDM).
• List drug properties that make them candidates for TDM.
• Discuss factors to be considered when utilizing
measured drug concentration.
• Describe and list possible reasons for patient variability
within pharmacokinetics
• Distinguish the role of the pharmacist in providing
optimal patient care via performing clinical PK and TDM.
• Utilize Clinical Apps in drug therapy and monitoring












 informatics
informatics
