Similar presentations:
Toyota Motor Corporation
1.
Toyota Motor CorporationLeading the way to the future of mobility
2.
Content• 1. History of brand development
• 2. Strategies of Toyota Motor Corporation
• 3. Toyota Business Principles
• 4. IT Governance Framework Matrix
• 5. SWOT analysis1
3.
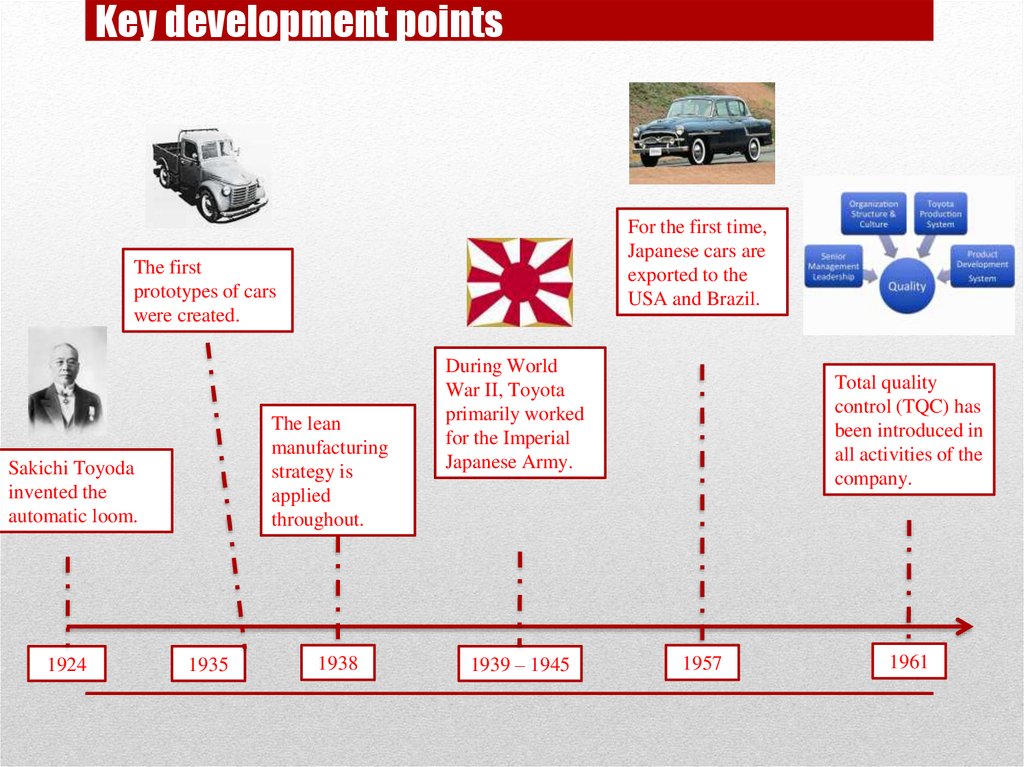
Key development pointsFor the first time,
Japanese cars are
exported to the
USA and Brazil.
The first
prototypes of cars
were created.
The lean
manufacturing
strategy is
applied
throughout.
Sakichi Toyoda
invented the
automatic loom.
1924
1935
1938
During World
War II, Toyota
primarily worked
for the Imperial
Japanese Army.
1939 – 1945
Total quality
control (TQC) has
been introduced in
all activities of the
company.
1957
1961
4.
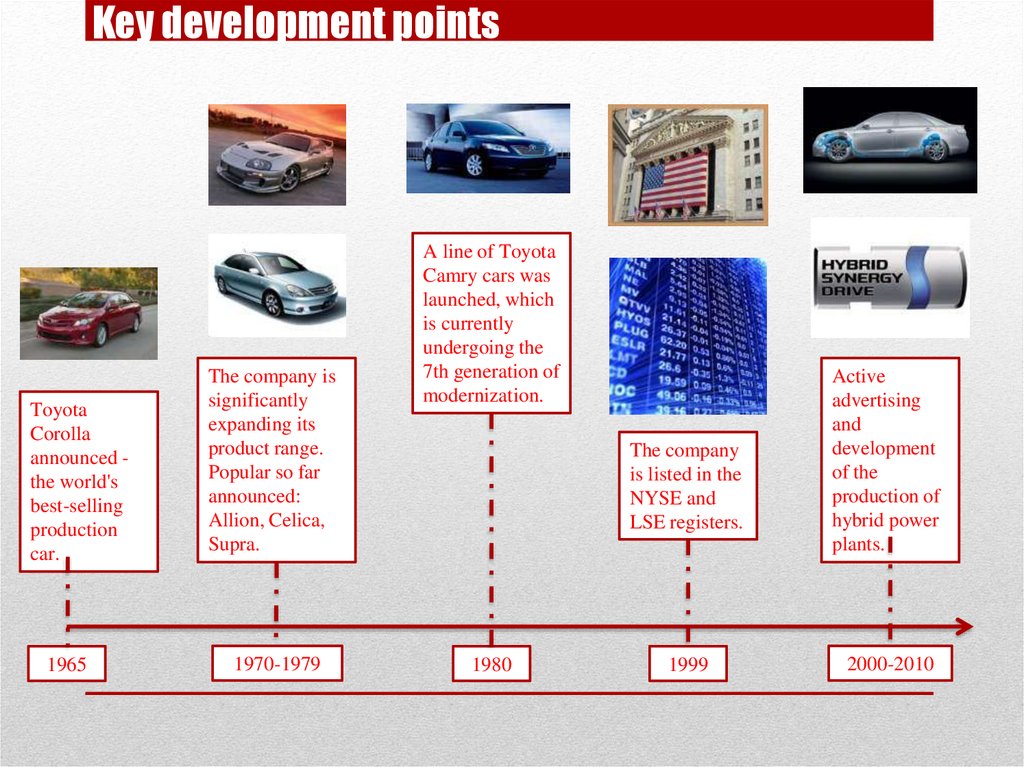
Key development pointsToyota
Corolla
announced the world's
best-selling
production
car.
The company is
significantly
expanding its
product range.
Popular so far
announced:
Allion, Celica,
Supra.
1965
1970-1979
A line of Toyota
Camry cars was
launched, which
is currently
undergoing the
7th generation of
modernization.
The company
is listed in the
NYSE and
LSE registers.
1980
1999
Active
advertising
and
development
of the
production of
hybrid power
plants.
2000-2010
5.
Leading the way to the future of mobility…Toyota will pave the way for humanity to a mobile future by
improving the conditions of life around the world, providing
people with the safest and most reliable means of transportation..
6.
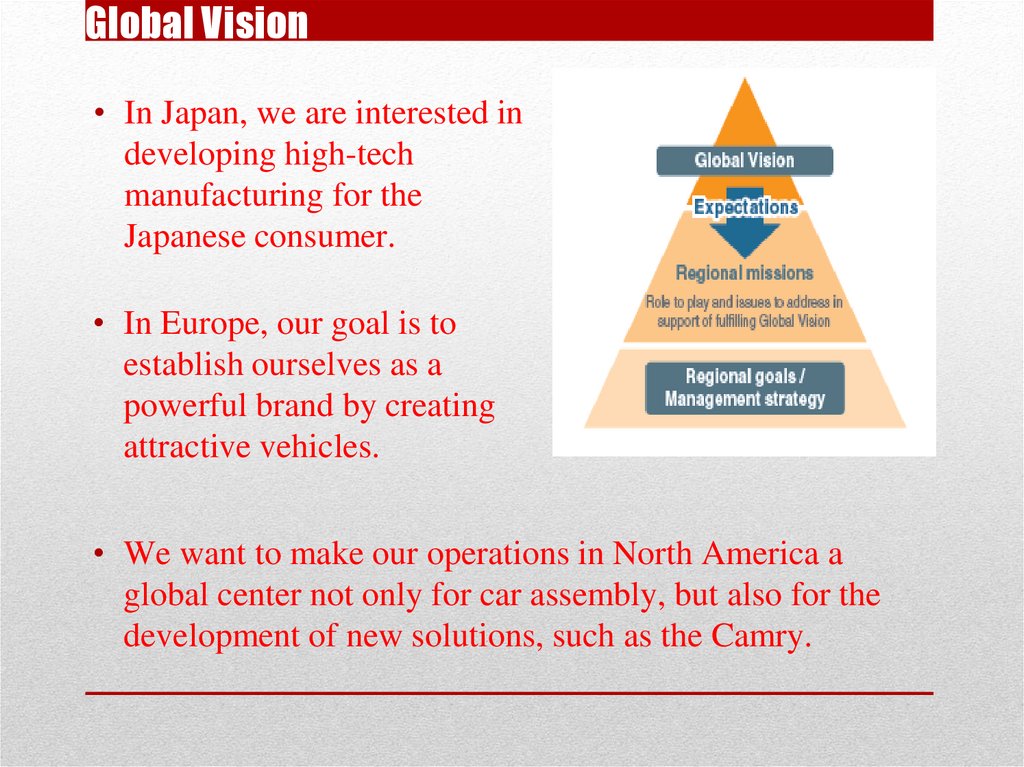
Global Vision• In Japan, we are interested in
developing high-tech
manufacturing for the
Japanese consumer.
• In Europe, our goal is to
establish ourselves as a
powerful brand by creating
attractive vehicles.
• We want to make our operations in North America a
global center not only for car assembly, but also for the
development of new solutions, such as the Camry.
7.
Global Vision• Our work in China and other emerging markets is aimed at
enhancing our brand image as a technology that helps to
save a healthy environment.
8.
Pursuit of Security• The goal is zero deaths as a result
of traffic accidents.Ensuring
traffic safety:work with people participants in the
movement;work on car models
for the safety of both passengers
and pedestrians;work to provide
road infrastructure.Special
quality control department for
traffic safety. A new position of
CSTO, Chief Safety Technology
Officer, has been established on
the Board of Directors.
9.
TТoyota Business PrinciplesMake management decisions with a long-term perspective, even if it hurts shortterm financial goals.
Continuous flow process helps identify problems.
The organization of the work of production requires that the consumer receive
what he needs, at the right time and in the right quantity.
Balance out the workload. To improve the quality of service, not always strictly
following the order of receipt of orders.
Stop production if quality requires it.
Standard tasks and delegation of authority to employees are the basis of
continuous improvementия.
10.
Toyota Business PrinciplesUse visual control so that no problem goes unnoticed.
Use only reliable, proven technology.
Cultivate leaders who know their business thoroughly and can teach it to others.
Raise extraordinary people and form teams
Respect your partners and suppliers, challenge them and help them improve.
If you want to understand the situation - look at everything with your own
eyes.
Make a decision slowly, weighing all possible optionsты.
Make your company a learning organization through relentless reflection and
continuous improvementания.
11.
SWOT. StrengthsыGlobal international corporation, products are represented in 170
countries around the world.
Stable financial performance and advanced financial management system.
Excellent positions in the key markets of the world - USA, China,.
A strong brand image, quality, respect for the environment and a wide range
of models..
The largest automaker in the world. The company took the lead from the
auto giant General Motors, which held this place for 76 years.
Toyota owns the technology behind the best Hybrid Synergy Drive to date.
12.
SWOT. Weak sidesJapanese automaker seen as an importer in key markets.
Concentration of production volumes. The company produces the
majority of vehicles in Japan and the US, while competitors are more
conveniently located in relation to a potential consumer in other
countries..
The main office and most of the production are located in a seismically
active zone.
13.
SWOT. PossibilitiesInnovation. First of all, increasing the production of cars, based on
technologies and the capabilities of our own R&D.
More aggressive conquest of new market segments.
Production of cars that will generate more power, at lower fuel costs and at
the same time have a weaker impact on the environment.
Development of vehicles that clearly meet the social and industrial needs of a
particular region.
Continued expansion into emerging markets with growing demand such
as China, India and Russia.
14.
SWOT. RisksGrowing competition, intensive marketing programs increase the pressure
of competitors.
An increase in stock indices will lead to a decrease in profits and an increase in
the cost of consumables.
Economic instability in Europe and the US will lead to a decrease in
demand for new cars.
Дdemographic risks. The number of large families is declining, the demand
for large family cars will fall.
Business aims to reduce the number of trips by introducing information
technology for communication (teleconferencing). Demand for business
vehicles is falling.
Oil prices and car maintenance are rising. Many people may refuse to buy a
car.
15.
Thank you for your attention!TOYOTA MOTOR
CORPORATION












 business
business industry
industry








