Similar presentations:
Chernobyl disaster. The worst man-made disaster in human history
1.
Chernobyl disasterThe worst man-made disaster
in human history
2. The nuclear power station
3.
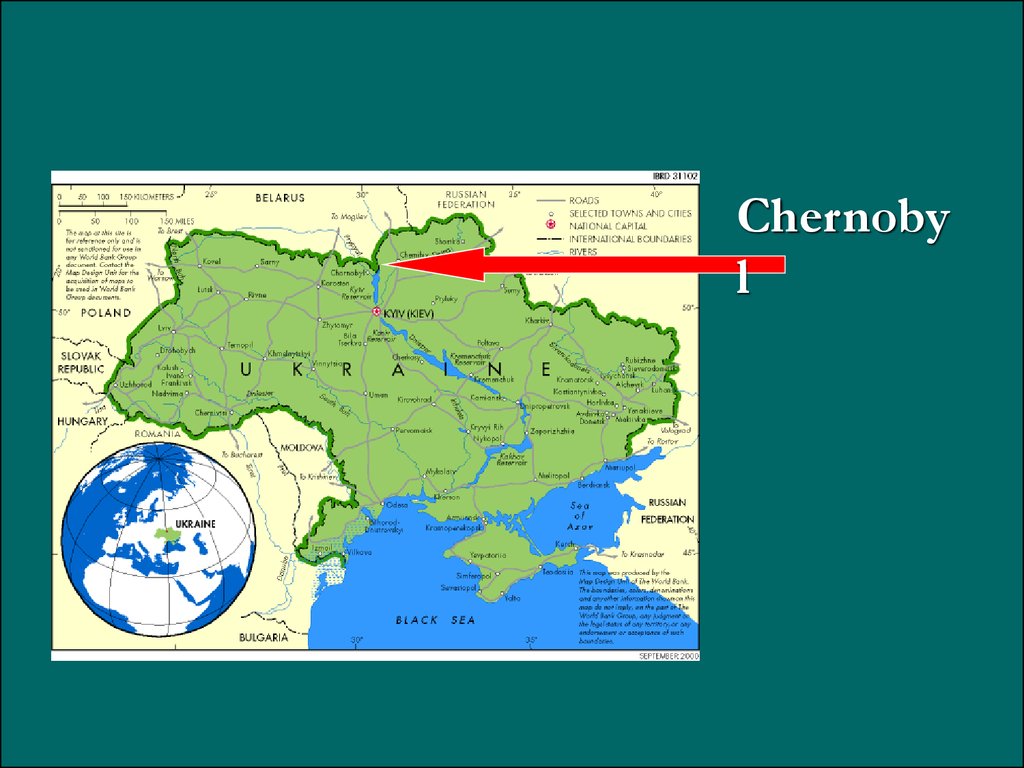
Chernobyl is located on the borderarea between Ukraine and
Belarus.
4.
Chernobyl
5. The Chornobyl nuclear power station was built in 1978-1979.
6.
7.
8. The Explosion
9.
In the early morning hours of26 April 1986, a testing error
caused an explosion at the
Chernobyl nuclear power
station.
10.
11.
12.
13. Radioactive fallout
14.
The explosion released 190 tonsof radioactive gases into the
atmosphere.
15.
16.
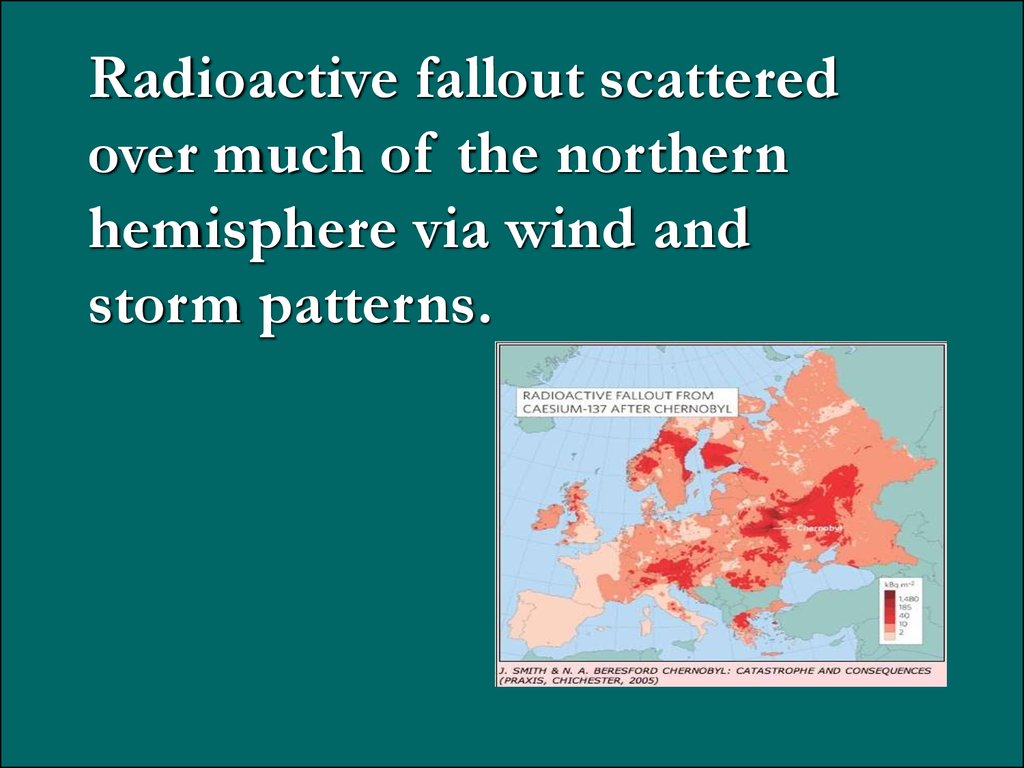
Radioactive fallout scatteredover much of the northern
hemisphere via wind and
storm patterns.
17.
70% of the radioactive materialwas blown into the neighboring
country of Belarus.
18.
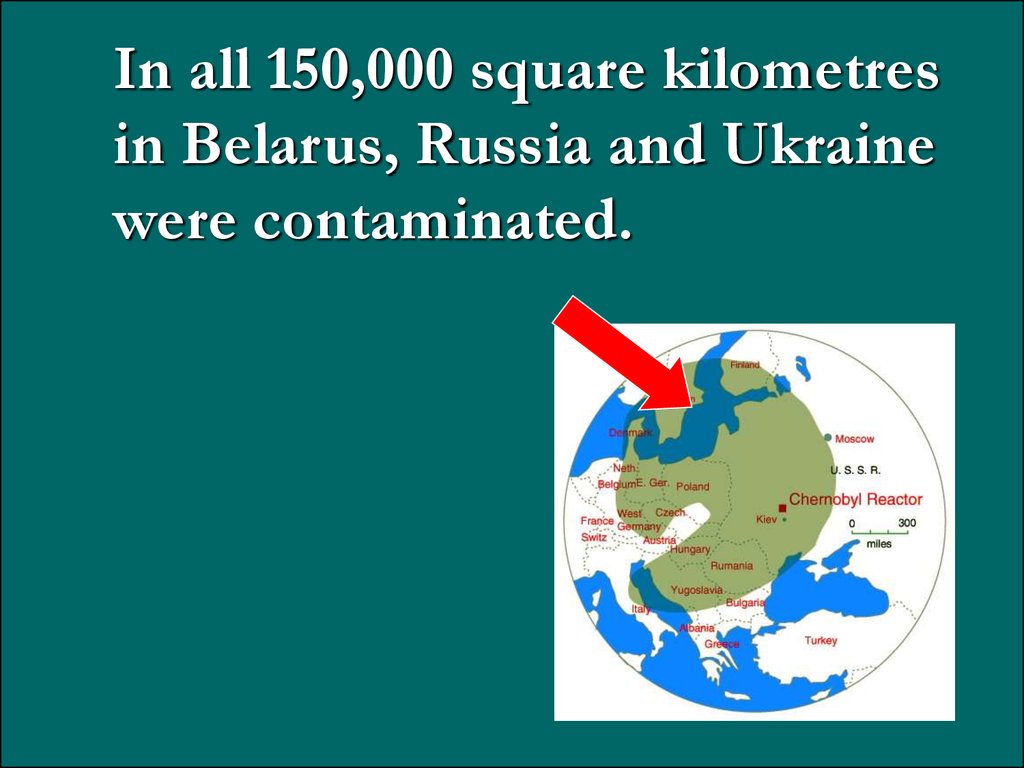
In all 150,000 square kilometresin Belarus, Russia and Ukraine
were contaminated.
19.
7 million people living in theseareas were exposed to the
radiation fallout.
20. The evacuation
21. The morning after the explosion, there was no hint of a disaster.
22.
Children went to school andplayed outside.
23.
Gardeners worked on their plotsoutdoors.
24.
Even weddings took place thatSaturday night.
25.
Only on the second day after thedisaster (after 36 hours) did the
Soviet authorities start
evacuating people from the area
around Chernobyl.
26. In total some 200,0000 people are believed to have been relocated as a result of the accident.
27. 3 million of those evacuated were children.
28.
29.
The Human Casualties30.
The immediate impact31. The immediate casualties were operators, rescue workers, firefighters and soldiers involved in the clean up operations.
32.
31 emergency clean-up peopleworkers died in 3 months of
radiation poisoning.
33. 134 emergency workers suffered from acute radiation sickness.
34. 25,000 of the rescue workers later died from diseases caused by radiation.
35.
Diseases caused by radiationincluded:
- lung cancer,
- leukemia,
- cardiovascular disease.
36.
Long term exposure37.
Eight years after the accident8,000 people had died from
diseases due to radiation.
38.
To date medical statisticsreported 270,000 cancers (mostly
thyroid) caused by the Chernobyl
disaster.
39. Of these 93,000 of these cancer cases were fatal.
40. There have been at least 1800 documented cases of thyroid cancer in children.
41.
In region of Belarus, incidence ofleukemia has increased 50% in
children and adults.
42.
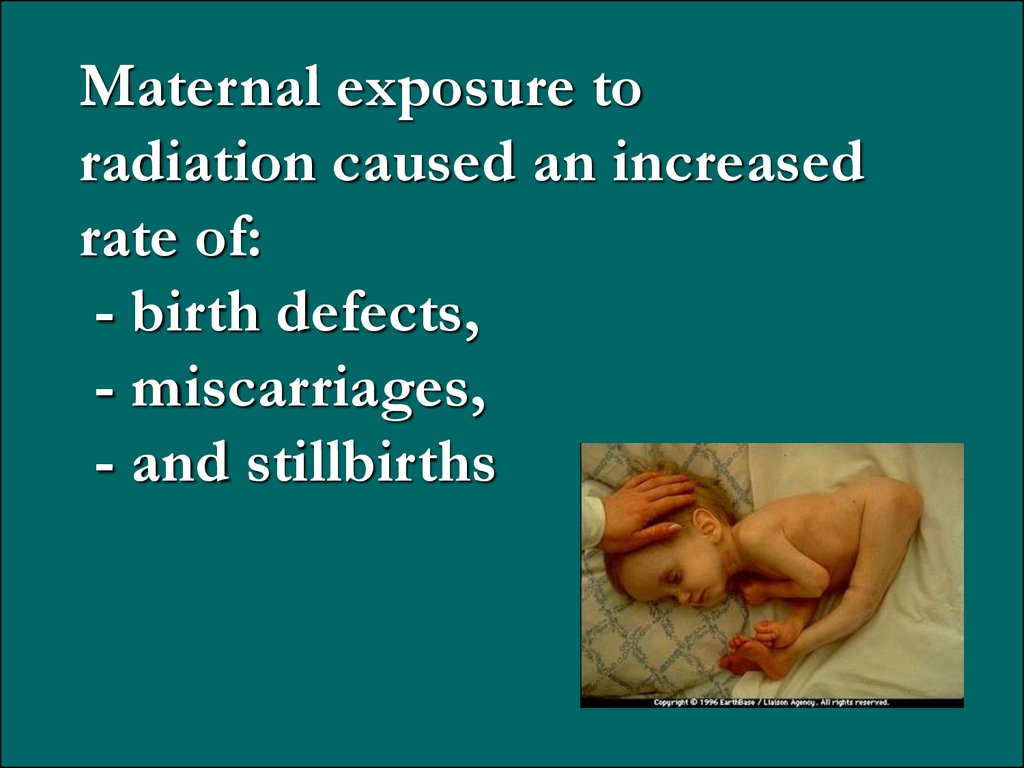
Maternal exposure toradiation caused an increased
rate of:
- birth defects,
- miscarriages,
- and stillbirths
43. Environmental Impact
44.
Areas still impacted today:- soil
- water
- air
- crops and food
- livestock
45.
20% of prime farmland inBelarus
remains contaminated from the
decaying components of
plutonium.
46.
Radiation is concentrated insediments at the bottoms of lakes
and ponds.
47.
Still the population continuesto contaminate itself by fishing
there.
48.
Livestock such as cattle andgoats accumulate radioactivity
in their meat and milk.
49.
The food and water supply iscontinuously contaminated by
rainfall and by the movement of
radioactive dust.
50. Problems Today
51.
After the disaster, a huge cementbox (sarcophagus) was hastily
built around the radioactive
material.
52.
According to a 2003 report by theRussian Atomic Energy Ministry,
"the concrete shell surrounding
the Chernobyl nuclear reactor
was in real danger of collapsing
at any time."
53.
A new shelter - a 1.3 million europroject was completed in 2009.
54.
It is hoped to safely contain thenuclear material for the next 100
years.
55.
97% of the radioactive materialsfrom the Chernobyl plant still
remains inside this sarcophagus.
56.
Even if the people are aware ofthe danger many have returned
to live in their old homes.
57.
Today 5.5 million people still livein contaminated areas.
58.
They continue to be exposed tolow doses of radiation for
decades to come.






















































 ecology
ecology








