Similar presentations:
International Organizations. Week 10. Regional and Other IOs
1. International Organizations
Week 10: Regional and OtherIOs
2. Attendance Sheet 1, Week 10 Please scan the QR code below:
Kaskelen 20233. Office Hour: Wednesdays at 16:00-17:00 D 211
Kaskelen 20234.
Kaskelen 20235. By the end of this week, you should be able to:
Comprehendregional and other IOs
Recognise and identify
major functions of such IOs by studying WTO through
reading the text, having
listened to the lecture
Discuss
main issues and critical
questions around the
regional and other IOs
Kaskelen 2023
by having read an
academic text (book
chapter), having listened to
the lecture
through class discussions
6. States pursue their national interests in international organizations, and sometimes those interests can be better achieved
through smaller or morelocalized organizations established along geographical, regional, cultural,
linguistic, or economic lines.
NATO vs. Warsaw Pact
Brussels Treaty Organization (1948: Belgium, France, Luxembourg, the
Netherlands, and Britain)
Article 5 of the Treaty, that “an armed attack against one or more of them in
Europe or North America shall be considered an attack against them all”.
Kaskelen 2023
7. In the developing world, it often made more sense to establish regional organizations — free trade movements, cultural
organizations, development organizations — to pursue interests thatwere not or could not be met by the universal institutions.
“Neighbors are not always impartial” (Nye, Peace in Parts, 130).
Kaskelen 2023
8. What constitutes a region is unclear. Political decisions allow Turkey into the North Atlantic region as a member of NATO but
keep Israel out of Middle Eastern IGOs.The purpose — and lifespan — of these organizations varies as well.
NATO, SEATO, CENTO, Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe,
OSCE, G8, G20, Commonwealth of Independent States, Shanghai Five,
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO), etc.
Kaskelen 2023
9.
Kaskelen 202310. The Pan American Union was the first and the largest regional organization in the world, whose history and development was
concurrent with that of the League ofNations and the UN.
The Pan American Union was integrated into a new and larger Organization of
American States (OAS).
On 2 September 1947 the Inter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance (or Rio
Treaty) was signed, establishing a collective defence pact for the Western Hemisphere
in which an attack on one member was to be considered an attack on all members
(although the pact was not technically binding).
Organization of Central American States (1951), the Latin American Free Trade
Association (1960), and the Caribbean Free Trade Area (1968), the Caribbean
Community (CARICOM 1973)
Kaskelen 2023
11.
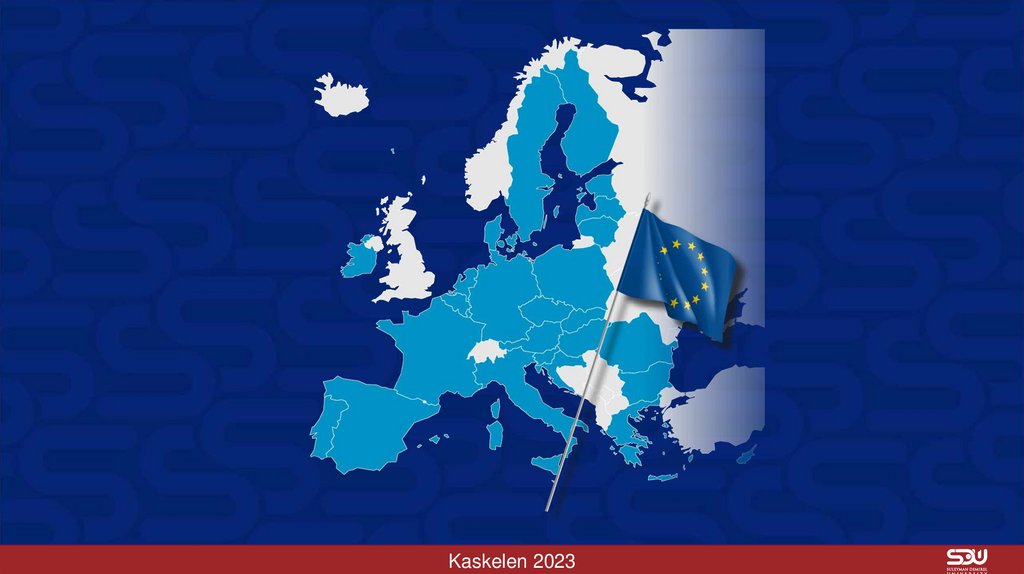
Kaskelen 202312. The European states were major contributors to the evolution of international organizations. Pan-European groups,
“sub-regional” organizations such as the NordicCouncil, which deals only with European issues; the Arctic Council.
Council of Europe, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
The most important European organization is the European Union (EU). The EU
began as the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), created in 1952 by Belgium,
France, West Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands.
Kaskelen 2023
13.
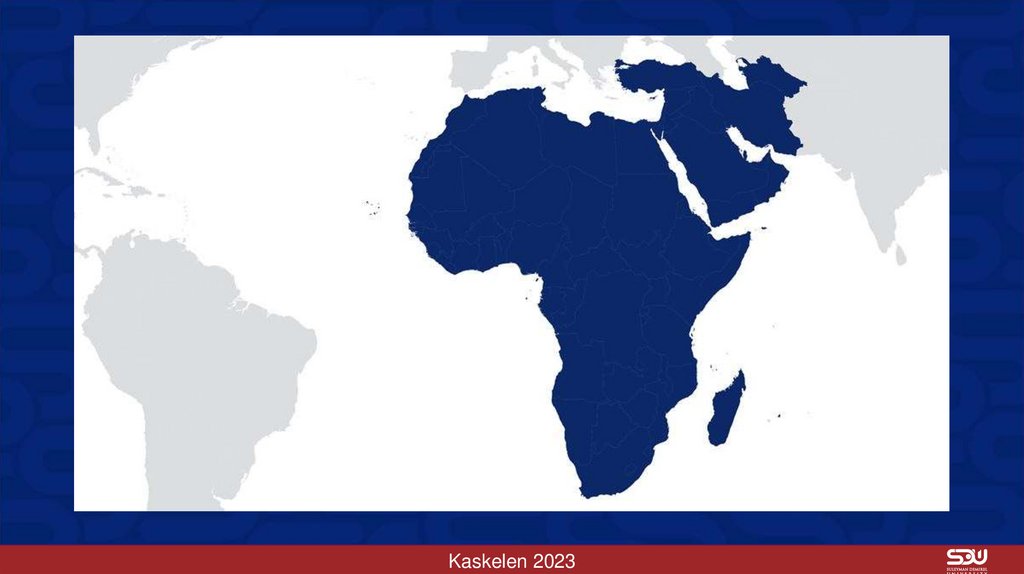
Kaskelen 202314. Regional organizations in Africa and the Middle East came with a somewhat different set of problems and concerns compared to
those in Europe.The first of the postwar organizations was the League of Arab States, known as the
Arab League (Cairo, 1945).
Gulf Cooperation Council, Greater Arab Free Trade Area, Organization of Petroleum
Exporting Countries (OPEC).
There was no lack of international organizations in Africa in the postwar era:
The East African Community, Southern African Customs Union, Central African Customs
and Economic Union (1964) and the Economic Community of West African States
(1975), Arab Maghreb Union.
Kaskelen 2023
15. Organization of African Unity (OAU, 1963). In the end the OAU never achieved the kind of internal unity hoped for in 1963, and
in July 2002 it was replaced by a new organization — the African. Union(AU) — at a conference in Durban, South Africa.
Kaskelen 2023
16.
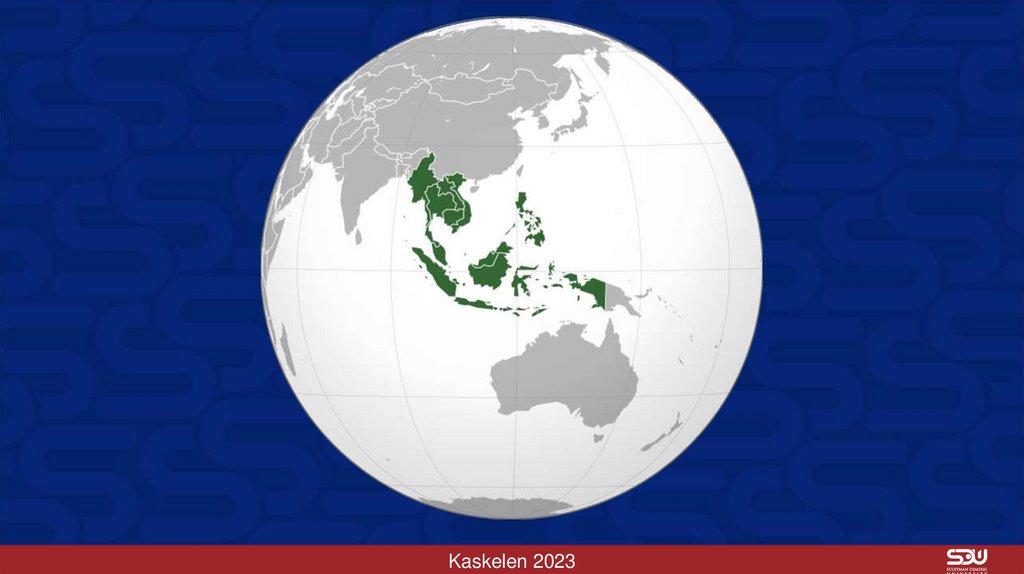
Kaskelen 202317. Regional international organizations were slower to emerge in East Asia and the Pacific than in most other areas of the world,
although more and moreorganizations have appeared in recent decades.
Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN, 1967 by Indonesia, Malaysia,
Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand).
ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum
Kaskelen 2023
18. Empires are not international organizations: they are maintained by force; the members are not sovereign states and usually are
not free to leave or join;there rarely is an independent secretariat outside the imperial power’s
government; and they are hierarchical in structure with no sharing of power,
voting, or decision-making.
“Dutch Commonwealth”, British Commonwealth, Imperial Federation League
(1884)
l’Agence de Coopération Culturelle et Technique (ACCT – la Francophonie).
Organization of Iberian-American States for Education, Science and Culture, or
OEI; Community of Portuguese Language Countries, or CPLP.
Kaskelen 2023
19. Attendance Sheet 2, Week 10 Please scan the QR code below:
Kaskelen 202320.
Home work assignment for the next week:Reading Assignment: Mackenzie, (81-107)
Seminar: Student Presentations
(see Moodle to download)
Kaskelen 2023


















 management
management


