Similar presentations:
Introduction to Software Testing. Software Development Life Cycle
1.
Introduction to Software Testing.Software Development Life Cycle.
2.
Agenda• Testing / Quality Control / Quality Assurance
• Verification and validation
• Software Project Team Roles
• Software Development Life Cycle
• Software Testing Life Cycle
• Testing Principles
2
3.
Software TestingSoftware Testing a method to check
whether the actual software product matches expected requirements
and to ensure that software product is defect free.
3
4.
What are the benefits of Software Testing?Cost-Effective
Security
Product Quality
Customer Satisfaction
4
5.
Testing / Quality Control / Quality Assurance5
6.
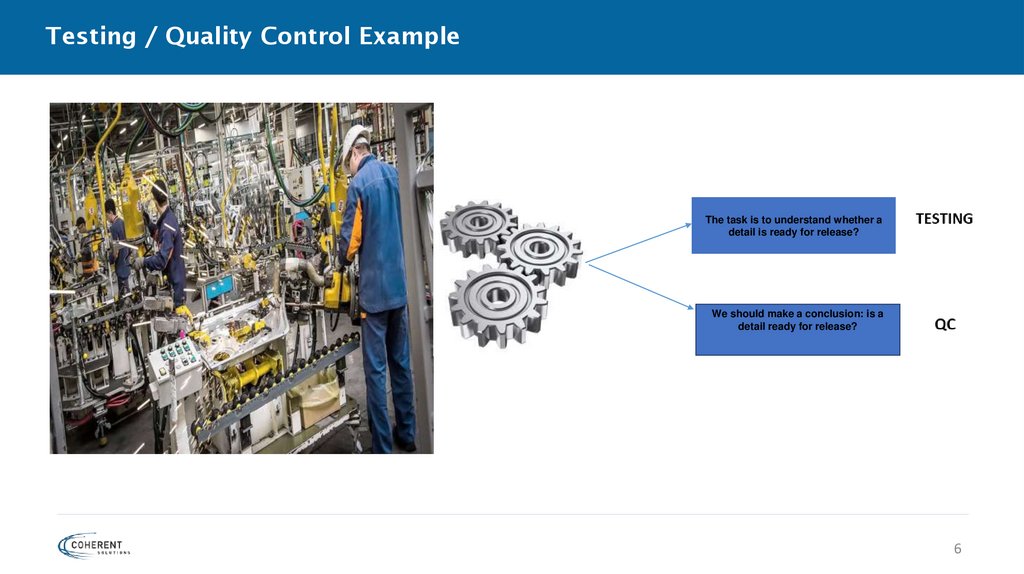
Testing / Quality Control ExampleThe task is to understand whether a
detail is ready for release?
We should make a conclusion: is a
detail ready for release?
6
7.
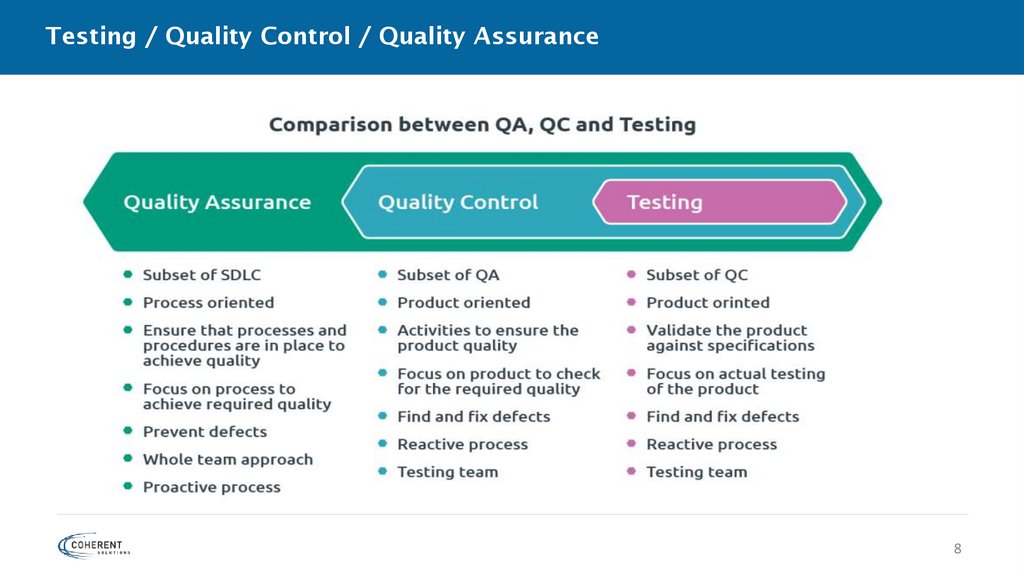
Testing / Quality Control / Quality AssuranceTesting - the process consisting of all lifecycle activities, both static and dynamic, concerned
with planning, preparation and evaluation of a component or system and related work
products to determine that they satisfy specified requirements, to demonstrate that they are
fit for purpose and to detect defects.
Quality control (QC) – a set of activities designed to evaluate the quality of a component or
system.
Quality assurance (QA) - activities focused on providing confidence that quality requirements
will be fulfilled.
7
8.
Testing / Quality Control / Quality Assurance8
9.
Verification/ValidationVerification is testing that your product meets the specifications / requirements you have
written. "Did I build what I said I would?".
Validation tests how well you addressed the business needs that caused you to write those
requirements. It is also sometimes called acceptance or business testing. "Did I build what I
need?"
9
10.
Verification/Validation (Example)When you order blueberry pancakes, what do you expect to see?
How do you determine that you have received what you ordered?
10
11.
Verification/Validation (Example)1.
Does the food look like what pancakes typically appear to be?
2.
Are the blueberries to be seen?
3.
Do they smell right?
This is verification: all when you are yet to eat but are checking on a few things by reviewing the
subject.
When you need to be sure about whether the food is as you expected: You will have to eat it.
Validation is when you eat the product to see if it is right.
11
12.
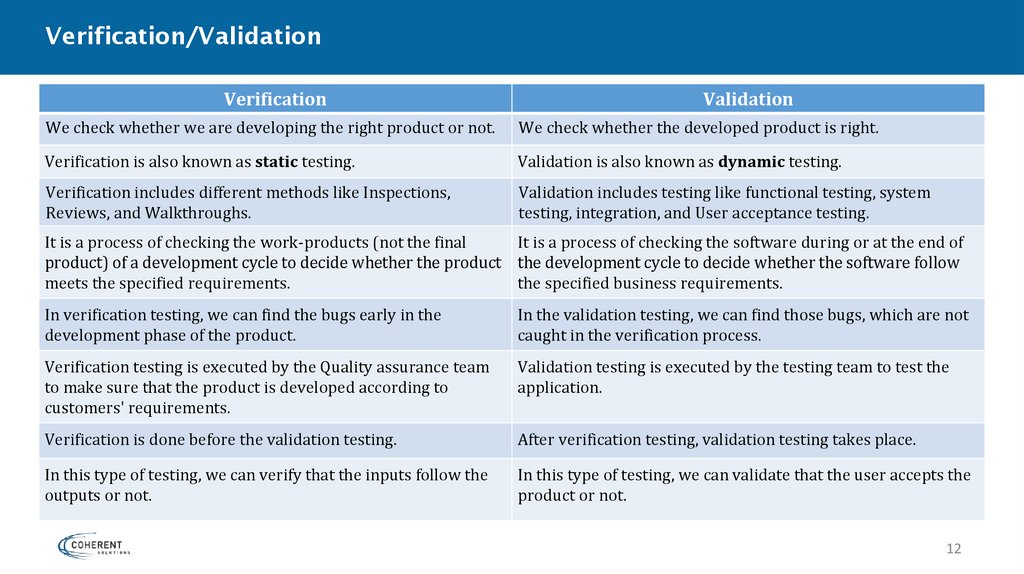
Verification/ValidationVerification
Validation
We check whether we are developing the right product or not.
We check whether the developed product is right.
Verification is also known as static testing.
Validation is also known as dynamic testing.
Verification includes different methods like Inspections,
Reviews, and Walkthroughs.
Validation includes testing like functional testing, system
testing, integration, and User acceptance testing.
It is a process of checking the work-products (not the final
It is a process of checking the software during or at the end of
product) of a development cycle to decide whether the product the development cycle to decide whether the software follow
meets the specified requirements.
the specified business requirements.
In verification testing, we can find the bugs early in the
development phase of the product.
In the validation testing, we can find those bugs, which are not
caught in the verification process.
Verification testing is executed by the Quality assurance team
to make sure that the product is developed according to
customers' requirements.
Validation testing is executed by the testing team to test the
application.
Verification is done before the validation testing.
After verification testing, validation testing takes place.
In this type of testing, we can verify that the inputs follow the
outputs or not.
In this type of testing, we can validate that the user accepts the
product or not.
12
13.
Software Project Team RolesQA Engineer
Business Analyst (BA)
Manager:
• Product Manager
• Delivery Manager
• Project Manager
13
14.
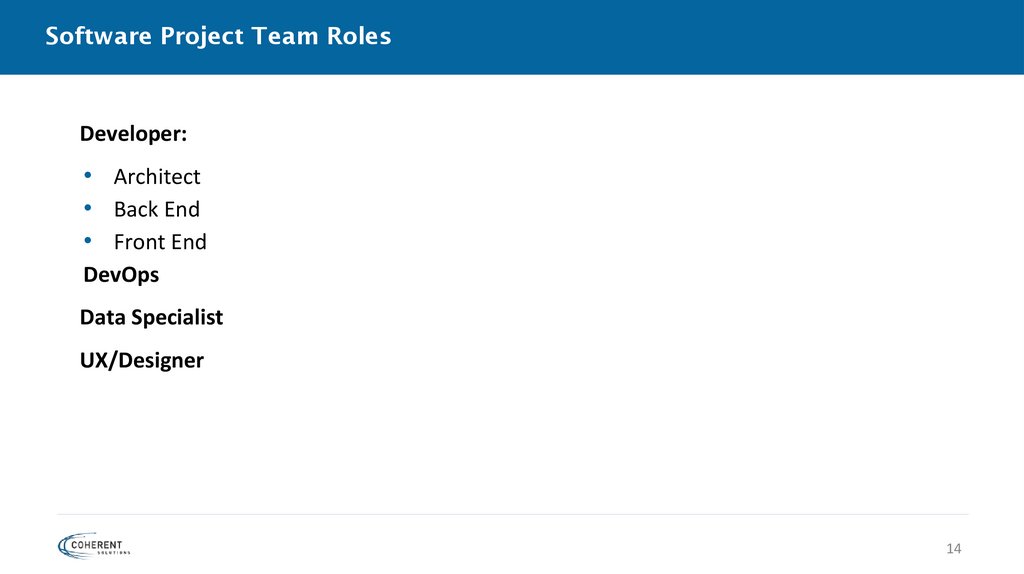
Software Project Team RolesDeveloper:
• Architect
• Back End
• Front End
DevOps
Data Specialist
UX/Designer
14
15.
Software Development Life Cycle15
16.
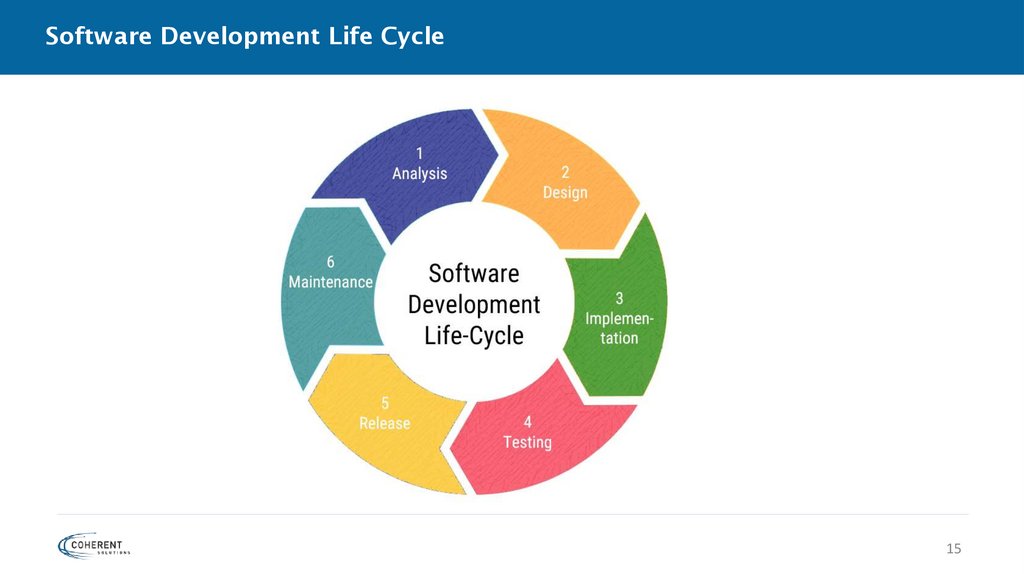
2. Design• Defining system architecture (System Architecture documents)
• Preparation of system and software design (Functional Design documents, Technical design
documents)
Main Roles:
• Architect/Developer
• DevOps
• Designer
16
17.
3. Implementation• Writing code using the chosen programming language and according to the
requirements and the design discussed in previous phases.
Main Roles:
• Developer
• Data Specialist
17
18.
4. Testing• Verifying whether the application behaves as expected and according to what was
documented in the requirements analysis phase.
• Find defects within the system.
Main Roles:
• QA
18
19.
5. Deployment• Release the final version of software to the customer for their use.
Main Roles:
• DevOps/Developer
• Product Manager
19
20.
6. Maintenance• User issues fixing
• Upgrade - Upgrading the application to the newer versions of the Software
• Enhancement - Adding some new features into the existing software
Main Roles:
• Support Specialist
• Developer
• QA
20
21.
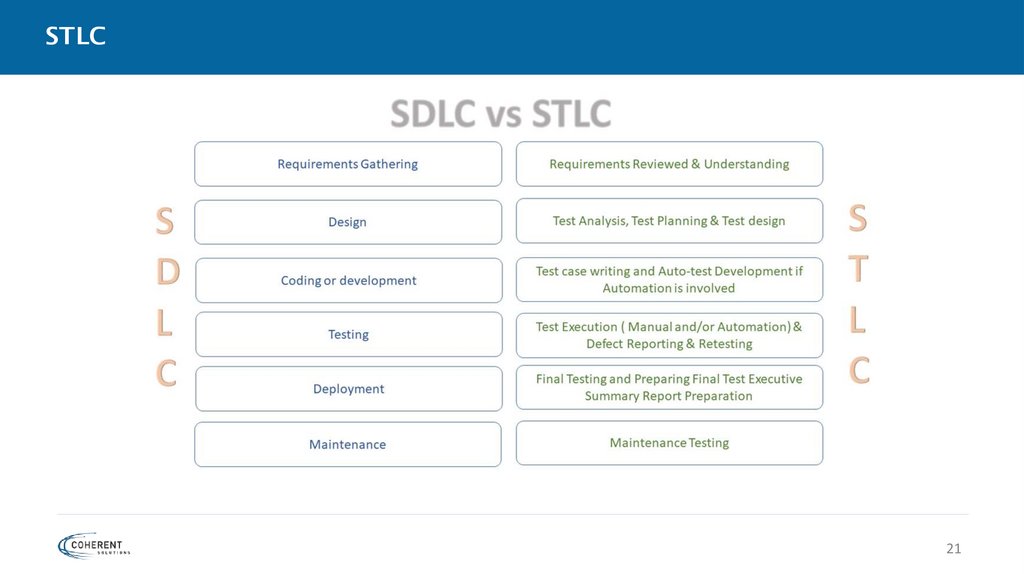
STLC21
22.
Testing Principles• Testing shows presence of defects
• Exhaustive testing is impossible
• Early testing
• Defect clustering
• Pesticide paradox
• Testing is context dependent
• Absence of errors fallacy
22












 software
software








