Similar presentations:
The Markets for the Factors of Production. Chapter 18
1.
Principles of Economics, Ninth EditionN. Gregory Mankiw
PowerPoint Slides prepared by:
V. Andreea CHIRITESCU
Eastern Illinois University
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
1
2.
Chapter 18The Markets for the Factors of Production
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
2
3.
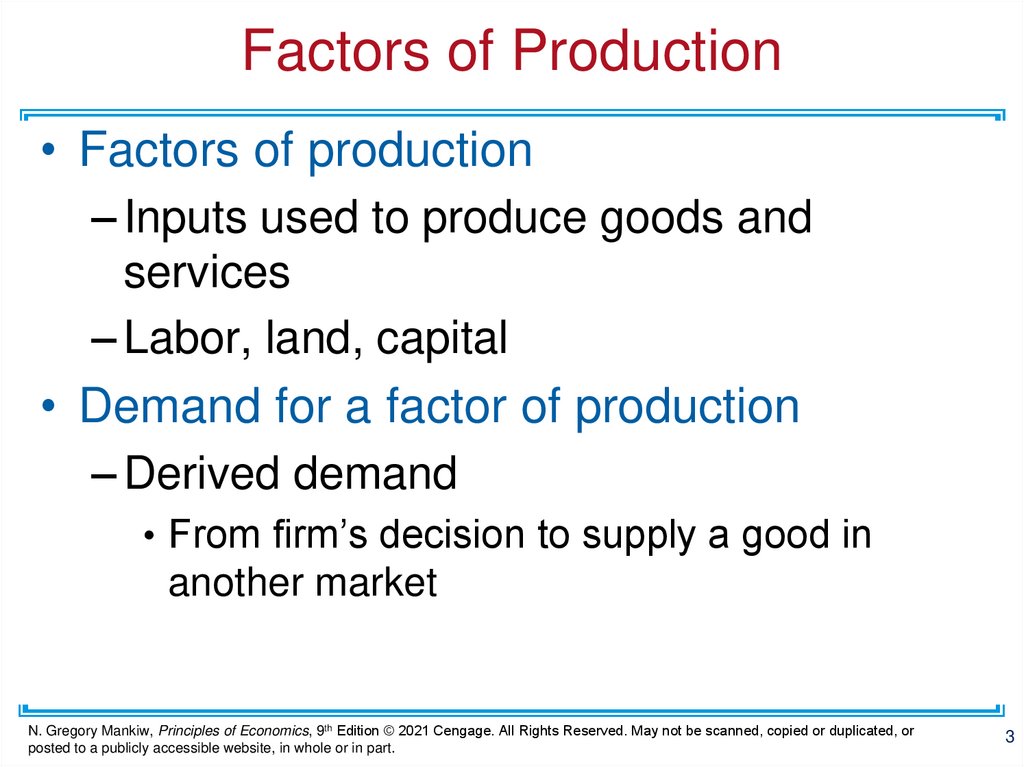
Factors of Production• Factors of production
– Inputs used to produce goods and
services
– Labor, land, capital
• Demand for a factor of production
– Derived demand
• From firm’s decision to supply a good in
another market
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
3
4.
The Demand for Labor, Part 1• Labor market
– Governed by supply and demand
• Labor demand
– Derived demand
– Labor services = inputs into the production
of other goods
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
4
5.
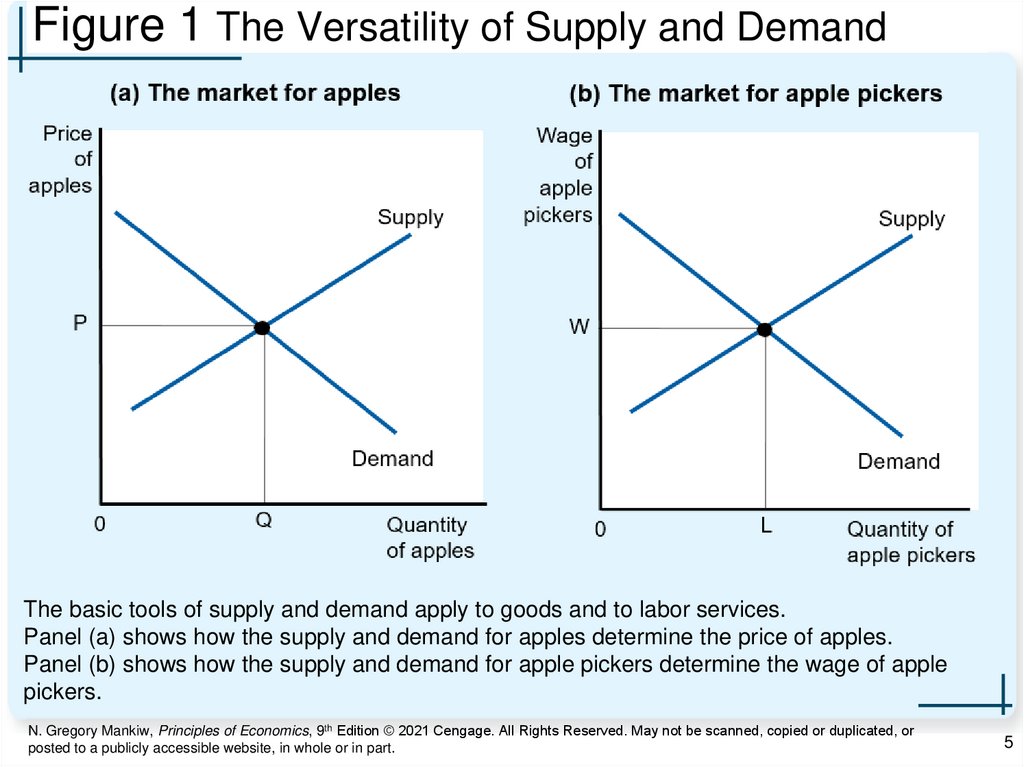
Figure 1 The Versatility of Supply and DemandThe basic tools of supply and demand apply to goods and to labor services.
Panel (a) shows how the supply and demand for apples determine the price of apples.
Panel (b) shows how the supply and demand for apple pickers determine the wage of apple
pickers.
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
5
6.
The Demand for Labor, Part 2• Assumptions for the firm
– Firm is competitive in both markets
• For goods and for labor
• Price taker
– Pay the market wage
– Get the market price for goods
• Decide
– Quantity of goods to sell
– Quantity of labor to hire
– Firm is profit-maximizing
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
6
7.
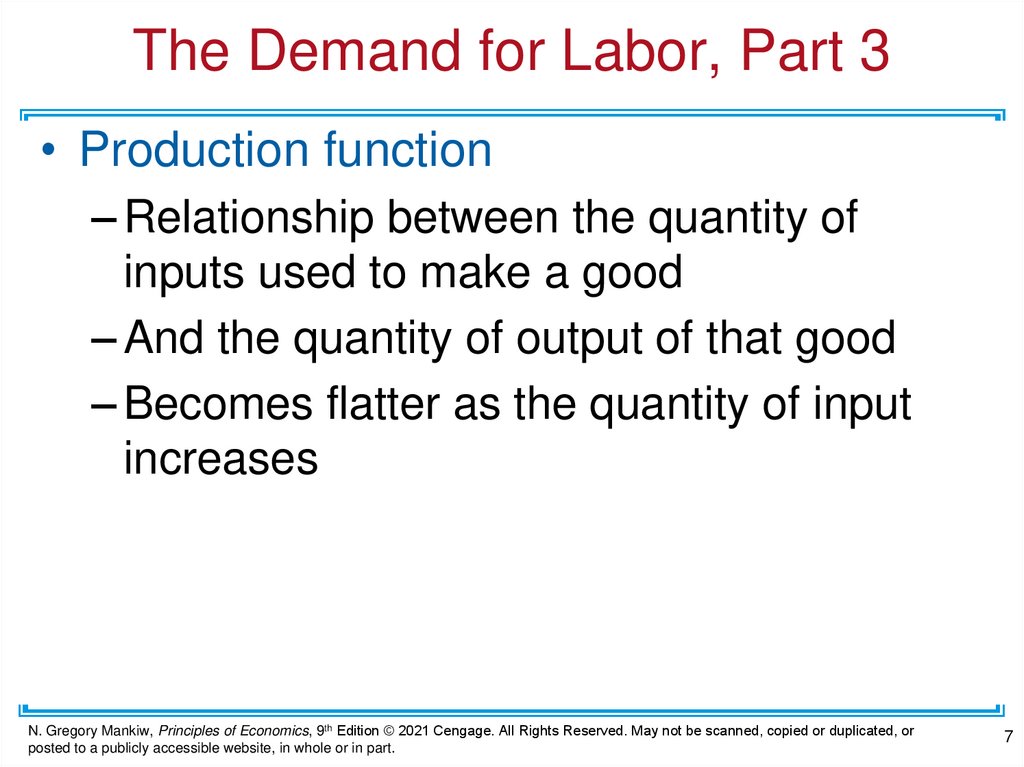
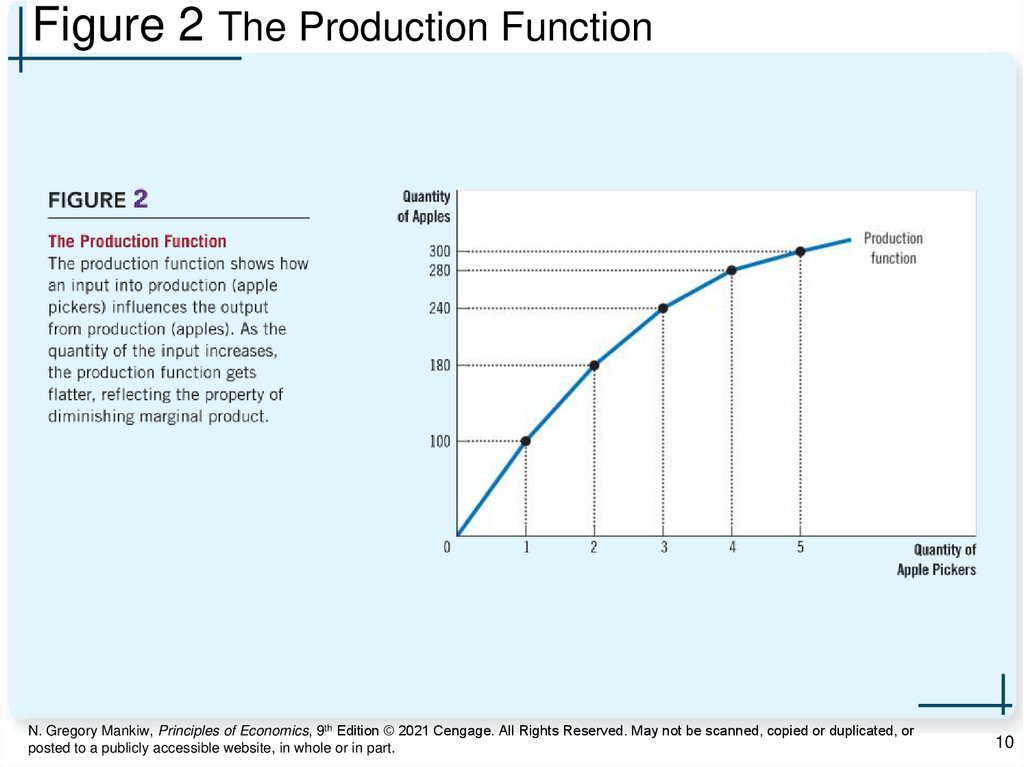
The Demand for Labor, Part 3• Production function
– Relationship between the quantity of
inputs used to make a good
– And the quantity of output of that good
– Becomes flatter as the quantity of input
increases
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
7
8.
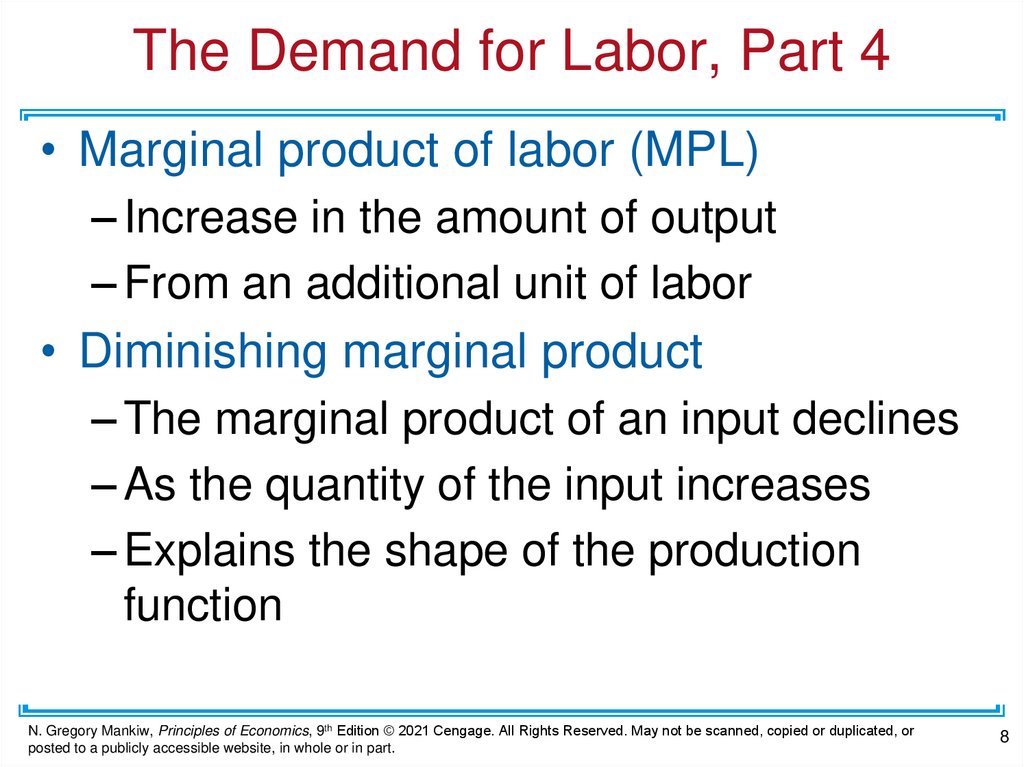
The Demand for Labor, Part 4• Marginal product of labor (MPL)
– Increase in the amount of output
– From an additional unit of labor
• Diminishing marginal product
– The marginal product of an input declines
– As the quantity of the input increases
– Explains the shape of the production
function
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
8
9.
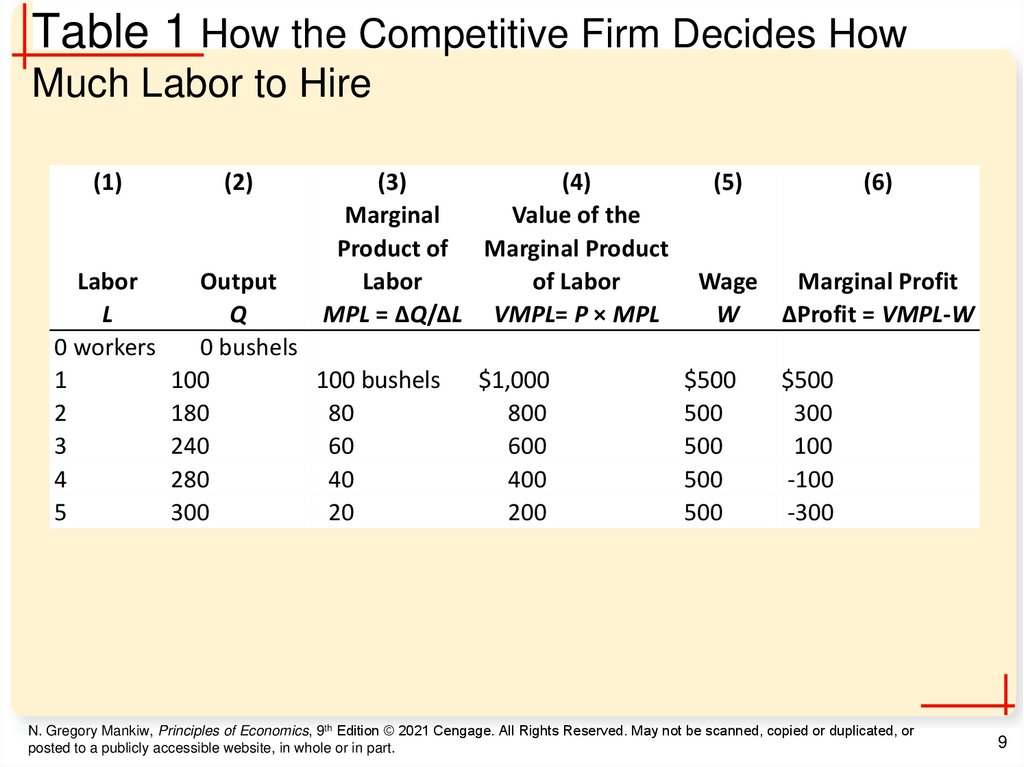
Table 1 How the Competitive Firm Decides HowMuch Labor to Hire
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Marginal
Value of the
Product of Marginal Product
Labor
of Labor
MPL = ΔQ/ΔL VMPL= P × MPL
Labor
Output
L
Q
0 workers
0 bushels
1
100
100 bushels
2
180
80
3
240
60
4
280
40
5
300
20
$1,000
800
600
400
200
(5)
(6)
Wage
Marginal Profit
W
ΔProfit = VMPL-W
$500
500
500
500
500
$500
300
100
-100
-300
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
9
10.
Figure 2 The Production FunctionN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
10
11.
The Demand for Labor, Part 5• The value of the marginal product of labor
(VMPL)
– Marginal product of labor times the price
of the output
– Marginal revenue product
• Additional revenue from hiring one additional
unit of labor
– Diminishes as the number of workers rises
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
11
12.
Figure 3 The Value of the Marginal Product of LaborN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
12
13.
The Demand for Labor, Part 6• Competitive, profit-maximizing firm
– Hires workers up to the point where the
value of the marginal product of labor =
wage
• The value-of-marginal-product curve
– Is the labor-demand curve
• Labor-demand curve
– Reflects the value of marginal product of
labor
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
13
14.
The Demand for Labor, Part 7• Shift in the labor-demand curve (VMPL)
– Change in the output price
• Demand for labor: VMPL = MPL × P of output
– Technological change
• Technological advance can raise MPL:
increase demand for labor
• Labor-saving technology can reduce MPL:
decrease demand for labor
– Supply of other factors
• Affect marginal product of other factor
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
14
15.
The Supply of Labor, Part 1• People face trade-offs
• Trade-off
– Work versus leisure
• Labor-supply curve
– Reflects how workers’
decisions about the laborleisure trade-off
– Respond to a change in
opportunity cost of leisure
“I really didn’t enjoy
working five days a week,
fifty weeks a year for forty
years, but I needed the
money.”
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
15
16.
The Supply of Labor, Part 2• Shift in the labor-supply curve
– Changes in tastes
• Change in attitude toward work
– Changes in alternative opportunities
• Opportunities available in other labor markets
– Immigration
• Movement of workers from region to region or
country to country
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
16
17.
ASK THE EXPERTS, Part 1Immigration
“The average US citizen would be better off if a
larger number of highly educated foreign
workers were legally allowed to immigrate to
the US each year.”
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
17
18.
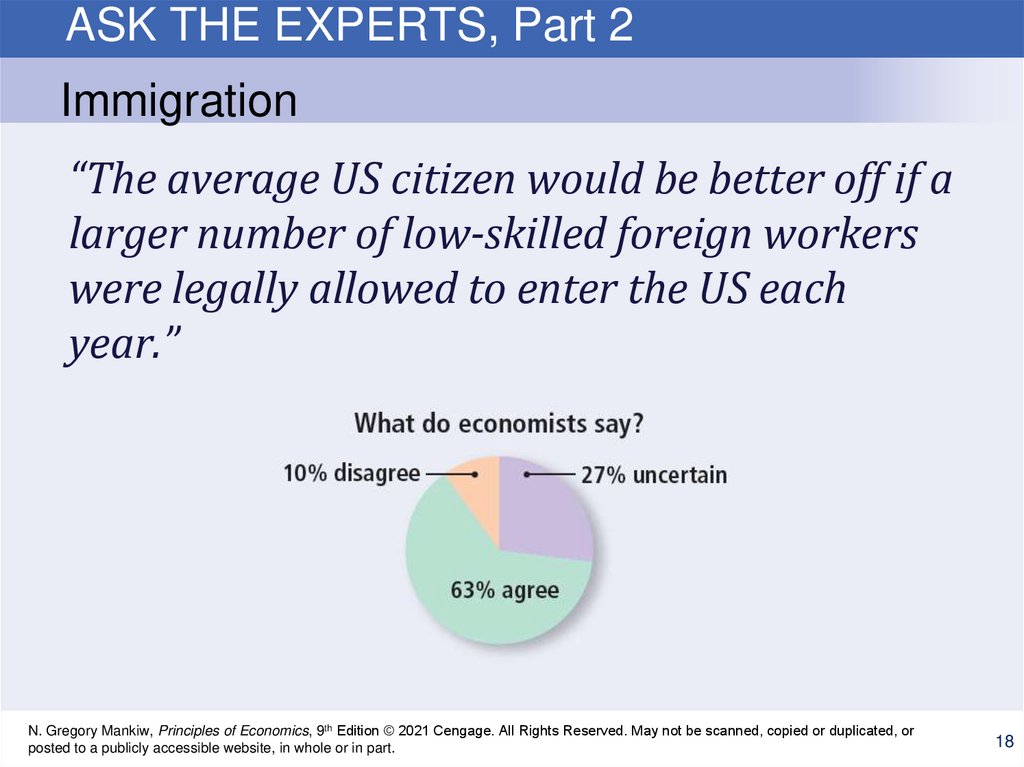
ASK THE EXPERTS, Part 2Immigration
“The average US citizen would be better off if a
larger number of low-skilled foreign workers
were legally allowed to enter the US each
year.”
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
18
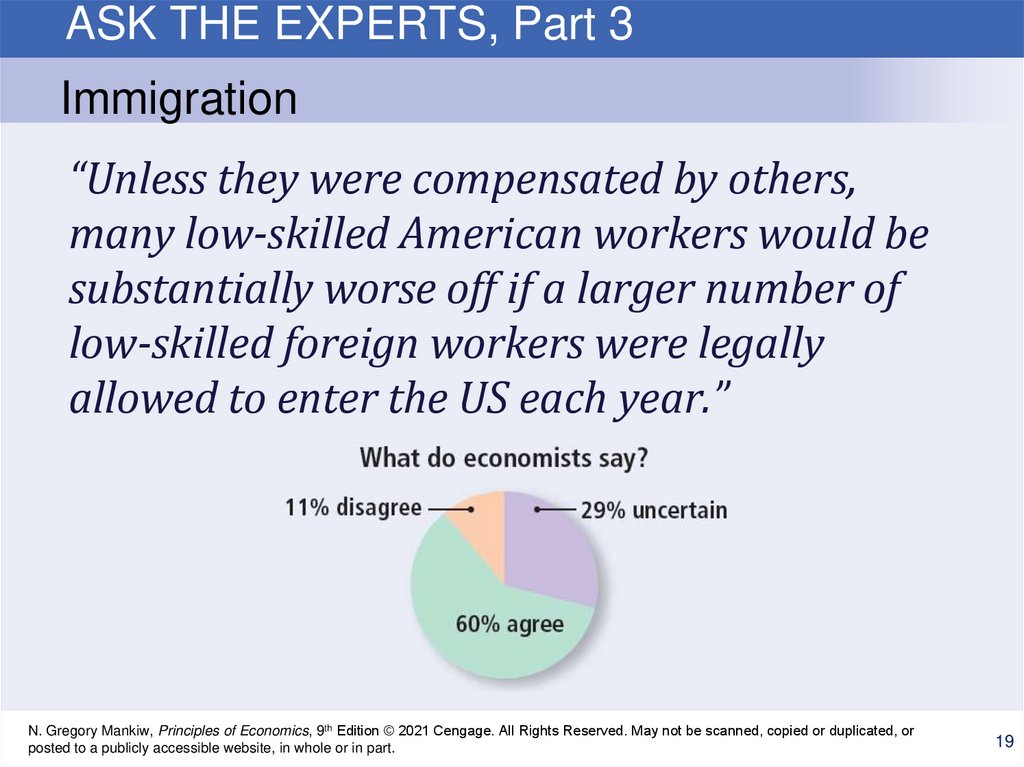
19.
ASK THE EXPERTS, Part 3Immigration
“Unless they were compensated by others,
many low-skilled American workers would be
substantially worse off if a larger number of
low-skilled foreign workers were legally
allowed to enter the US each year.”
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
19
20.
Equilibrium in the Labor Market, Part 1• Wages in competitive labor markets
– Adjusts to balance the supply & demand
for labor
– Equals the value of the marginal product
of labor (VMPL)
• Changes in supply or demand for labor
– Change the equilibrium wage
– Change the value of the marginal product
by the same amount
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
20
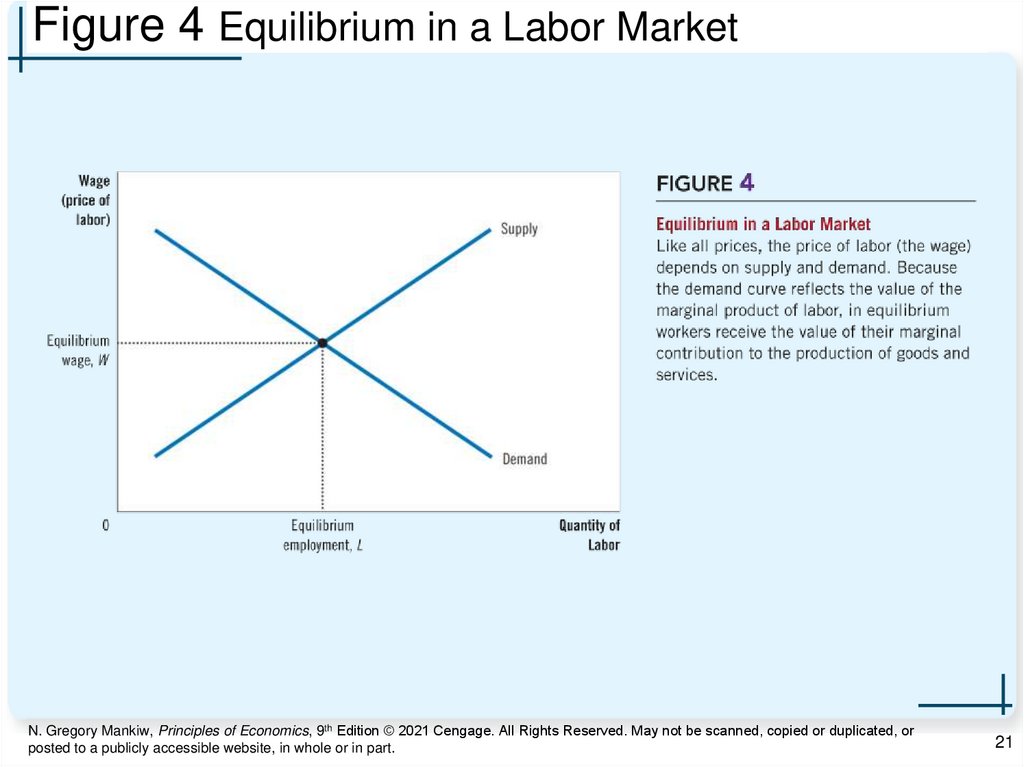
21.
Figure 4 Equilibrium in a Labor MarketN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
21
22.
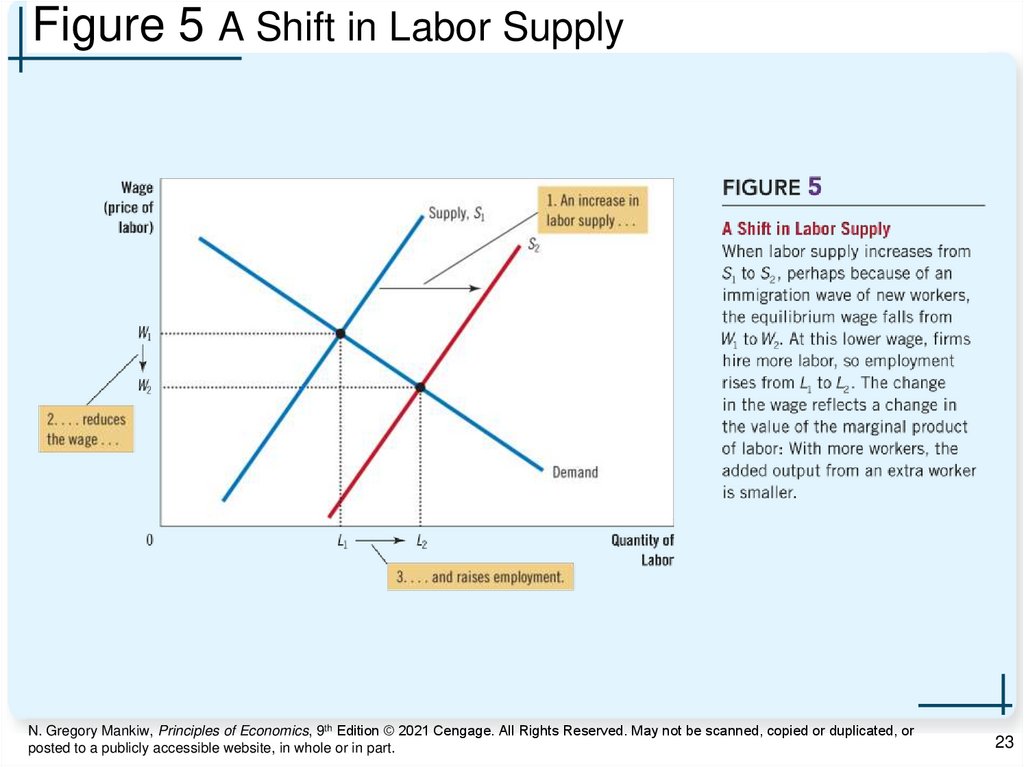
Equilibrium in the Labor Market, Part 2• Increase in supply
– Decrease in wage
• Lower marginal product of labor
• Lower value of marginal product of labor
– Higher employment
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
22
23.
Figure 5 A Shift in Labor SupplyN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
23
24.
Equilibrium in the Labor Market, Part 3• Economics of immigration
– Variety of labor markets for different kinds
of workers
– A wave of immigration (physicians)
• Lower wages in those labor markets in which
the new immigrants seek work (lower wages
for physicians)
• Higher wages in other labor markets
(physicians buy more apples; derived labor
demand; higher wages for apple pickers)
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
24
25.
Equilibrium in the Labor Market, Part 4• Increase in demand
– Higher wage
• No change in marginal product of labor
• Higher value of marginal product of labor
– Higher employment
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
25
26.
Figure 6 A Shift in Labor DemandN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
26
27.
Productivity and Wages, Part 1• Standard of living
– Depends on our ability to produce goods
and services
• Wages = productivity
– As measured by the value of the marginal
product of labor
– Highly productive workers are highly paid
– Less productive workers are less highly
paid
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
27
28.
Productivity and Wages, Part 2• Workers today
– Are better off than workers in previous
generations
• Productivity and real wages growth
– 1960 to 2017
• Productivity (output per hour of work) grew
about 2.0% per year
• Real wages (wages adjusted for inflation)
grew at 1.8% per year
• Productivity and real wages double every 35
years
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
28
29.
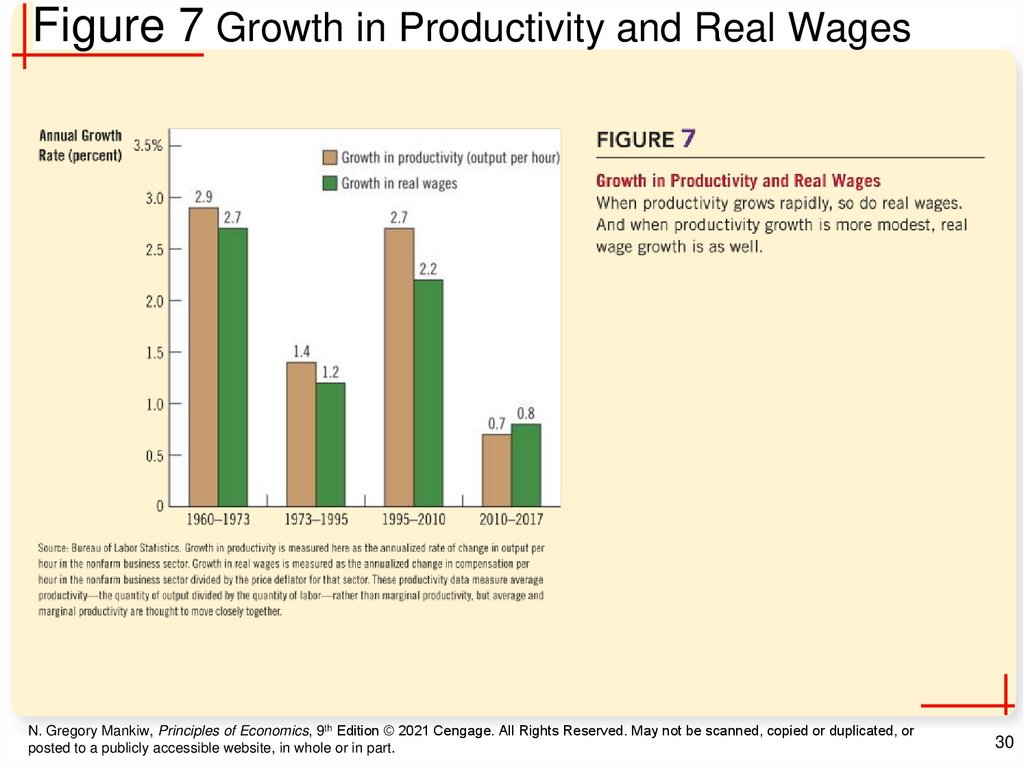
Productivity and Wages, Part 3• Productivity and real wages growth
– 1973 – 1995: significant slowdown in
productivity growth (from 2.7 to 1.4%)
• Slowdown in real wage growth: from 2.7 to
1.2%
– 2010 – 2017: productivity growth = 0.7%
per year
• Real wages grew by 0.8% per year
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
29
30.
Figure 7 Growth in Productivity and Real WagesN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
30
31.
Land and Capital, Part 1• Capital
– Equipment and structures used to produce
goods and services
• Equilibrium
– Purchase price
• Price a person pays to own that factor of production
indefinitely
– Rental price
• Price a person pays to use that factor for a limited
period of time
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
31
32.
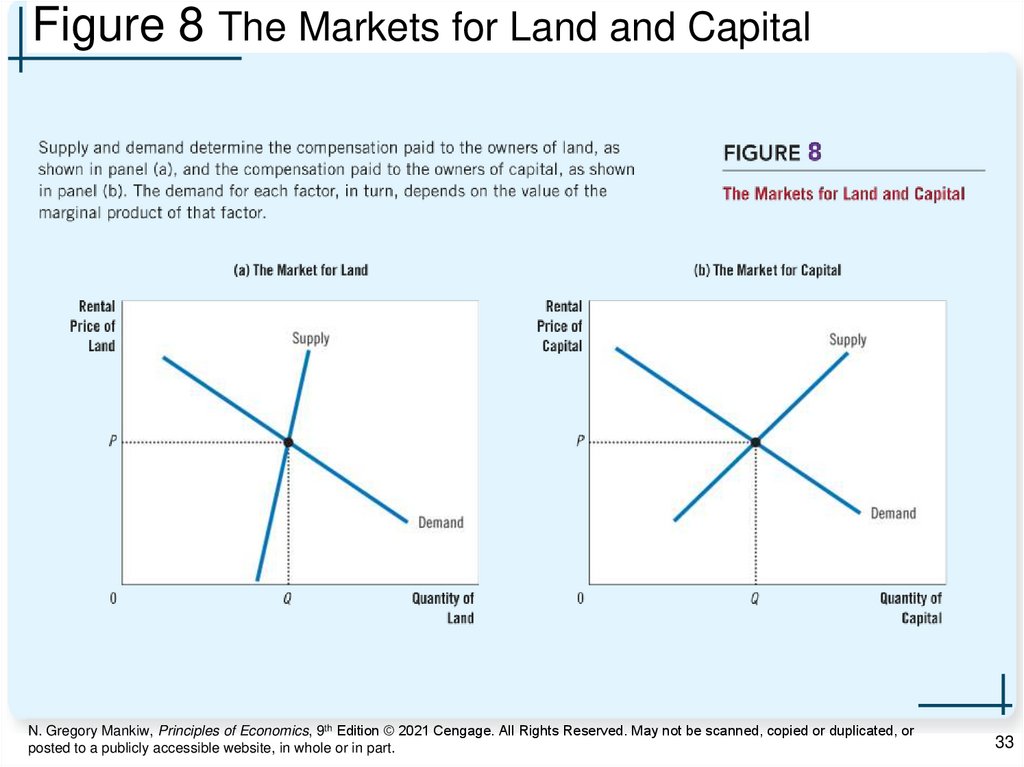
Equilibrium: Land and Capital, Part 1• Wage
– Rental price of labor
• Rental price of land and capital
– Determined by supply and demand
– Demand is a derived demand
• Reflects marginal productivity of the factor
• Each factor’s rental price
– Value of marginal product for the factor
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
32
33.
Figure 8 The Markets for Land and CapitalN. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
33
34.
Equilibrium: Land and Capital, Part 2• Equilibrium purchase price depends on
– Current value of the marginal product
– Value of the marginal product expected to
prevail in the future
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
34
35.
Land and Capital, Part 2• Linkages among the factors of production
– Price paid to any factor of production
= Value of the marginal product of that factor
– Marginal product of any factor depends on
• Quantity of that factor that is available
• Diminishing marginal product
– Factor in abundant supply
• Low marginal product
• Low price
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
35
36.
Land and Capital, Part 3• Diminishing marginal product
– Factor in scarce supply
• High marginal product
• High price
• Change in supply of a factor
– Change in equilibrium factor price
– Change in earnings of the other factors
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
36
37.
The Economics of the Black Death, Part 1• 14th century Europe,
Black Death (bubonic
plague)
– Wiped out about onethird of the population
within a few years
– Grisly natural
experiment to test the
theory of factor
markets
“Workers who survived the
plague were lucky in more ways
than one.”
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
37
38.
The Economics of the Black Death, Part 2• Effects of the Black Death on survivors
– Reduced population: Smaller supply of
workers
– Marginal product of labor rises: Higher
wages
• Wages doubled
• Economic prosperity for peasant classes
– Marginal product of land fell: Lower rents
• Rents declined 50% or more
• Reduced income for the landed classes
N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 9th Edition © 2021 Cengage. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or
posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
38



















 economics
economics








