Similar presentations:
The United Kingdom’s System of Government
1. The United Kingdom’s System of Government
1.The British Constitution and its pecularities2.The Monarchy
3.Legislature-the Westminster Parliament
• the House of Lords;
• the House of Commons;
• legislative process
4.The UK executive
5.The UK parliamentary election system
6.The political party system
4.
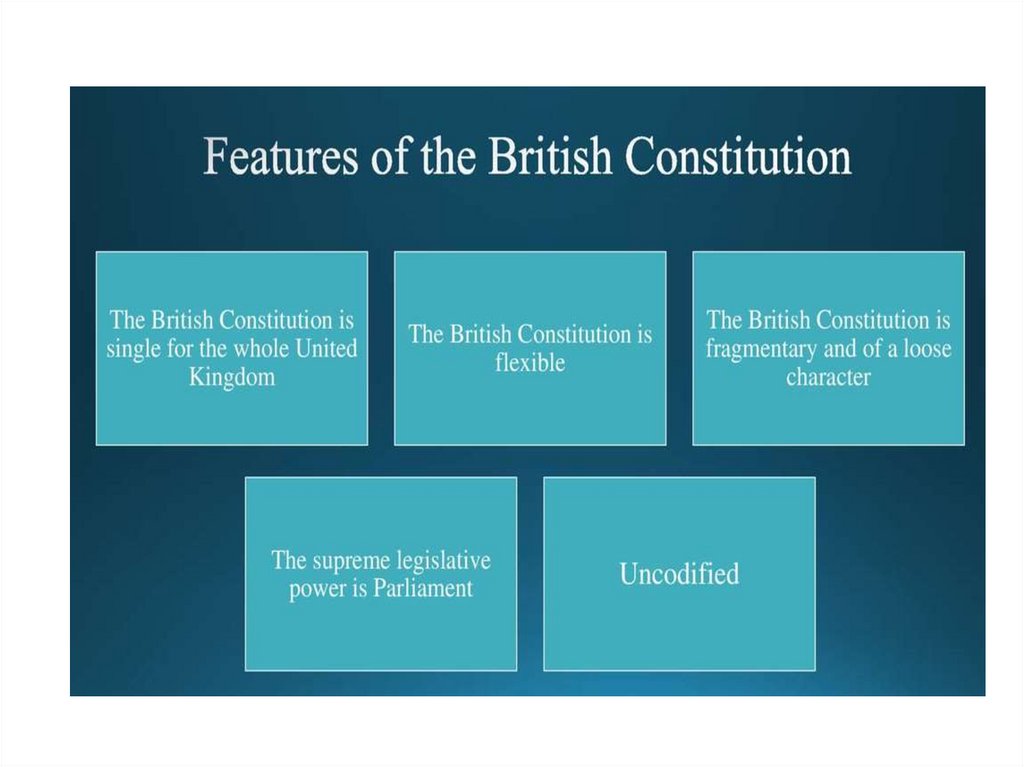
2. The British Constitution and its peculiarities
• The most important constitutional documents areThe Magna Carta, Libertata, Habeas Corpus
Act(1679) The Bill of Rights (1689) Petition of
Rights (1628) The Reform Act(1832) Statute
of Westminster (1931) and others.
• In 1997 referendums held in Scotland and
Wales endorsed proposals to devolve power
from Parliament at Westminster to Scottish
Parliament and National Assembly for Wales.
3. The Magna Carta is Britain’s best known constitutional document. It protects the community against the crown.
4. Petition of rights
• In 1628 the Parliament opposition unitingthe bourgeoisie and gentry scored a
victory: the king was made to sign a
document limiting his power.
The Bill of Rights of 1689
Stated the main ideas of the constitutional
monarchy with the legislative power in the
parliament’s hands. The document
extended the power of Parliament and
made it impracticable for the Sovereign to
ignore the wishes of the Government.
5.
6. The Monarchy
The Queen in law is:• head of the executive;
• an integral part of legislature;
• Head of the judiciary;
• Commander-in-chief of all the armed
forces of the crown;
• The supreme governor of the established
Church of England.
7. The Queen takes part in the acts of government:
• 1. Summoning(созыв);• 2.proroguing(назначение перерыва в
работе парламента);
• 3.dissolving(роспуск);
• 4. gives Royal assent to Bills
(законопроект);
5.pardoning (помилование);
• 6. appointing the Prime Minister.
8. Legislature-the Westminster Parliament
• The Westminster Parliament, Britain’slegislature, is made up of 3 elements:
• The Queen;
• The House of Lords;
• The House of Commons,which is elected.
9. The main functions of the Parliament
• To examine proposals for new laws;• To provide, by voting for taxation ,the
means of carrying on the work of
government;
• To scrutinize government policy and
administration, including proposals for
expenditure;
• To debate the major issues of the day.
10.
• The parliament has two chambers :• A) the House of Lords which consists of :
90 hereditary peers
• Life peers –(Lords of Appeal or Law Lords)
• All other life peers;
• Archbishops of Canterburry and York, the
bishops of London, Durham and
Winchester and the 21 senior bishops of
the Church of England.
11.
• The House of Lords is presided over bythe Lord Chancellor.
• The official seat of the Lord Chancellor is
called the Woolsack.
• The House of Lords also acts as the final
Court of Appeal
12.
• The House of Commons which consistsof 659 directly elected Members of
Parliament
• Out of 650(659) seats:
• 520-for England;
• 72- for Scotland;
• 40- for Wales;
• 18-for Northern Ireland
13.
• The chief officer of the House of commonsis the Speaker.Other officers include the
three Deputy Speakers:
• Frontbenchers,
• Backbenchers,
• Dispatch boxes.
• Members of the legislative body called
whips.
14. The legislative process
• MPs vote by walking through two corridorsknown as the Aye-Lobby and the NoLobby
• Amendment is the change to the bill.
• The Royal Assent in practice is a
formality.
15. The UK executive
• The executive consists of:• The government: the Cabinet and other
ministers responsible for national policies;
• Government departments, responsible for
national administration;
• Local authorities;
• Public corporations,responsible for operating
nationalized industries, subject to ministerial
control.
• The Scottish, Welsh and N.I.Executives
16.
• The Lord Chancellor is always a memberof the House of Lords.
• The Prime-Minister is also First Lord of
the Treasury and Minister for the Civil
Service.
• The Cabinet is composed of 20 -to 25
ministers.
17. The UK Parliamentary election system
• People not entitled to vote include:• Patients detained under mental health
legislation
• Sentenced prisoners and people convicted
within the previous 5 years of corrupt or
illegal election practices
• Members of the House of Lords
18.
• Those disqualified are:• Undischarged bancrupts;
• People sentenced to more than one year
imprisonment;
• Clergy of the Church of England,
• Clergy of the Church of Scotland,
• Clergy of the Church of Ireland,
19.
Politicalparties of
Great Britain
20. Plan :
I. The Conservativeparty
II.The liberal party
III.The Labour Party
IV.Test
21. The Political Parties
The British democratic system dependson political parties, the oldest and until
the last years of the 19th century they
were the only parties elected to the
House of Commons.
The
Conservative
The Liberal
Party
22.
TheConservative
Or the
Tories
the party of big business,
industry, commerce and
landowners.
23.
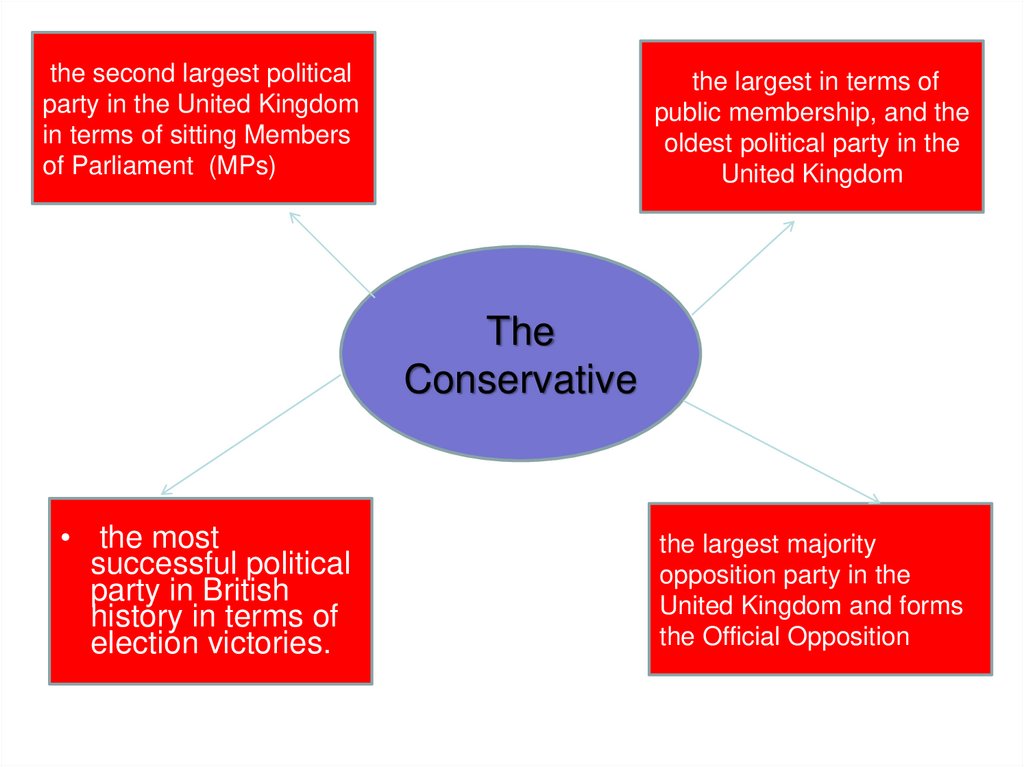
the second largest politicalparty in the United Kingdom
in terms of sitting Members
of Parliament (MPs)
the largest in terms of
public membership, and the
oldest political party in the
United Kingdom
The
Conservative
• the most
successful political
party in British
history in terms of
election victories.
the largest majority
opposition party in the
United Kingdom and forms
the Official Opposition
24. The symbol of the Conservative party
oak tree(replacing the freedom
torch)
25.
Margaret Thatcher-leader of theOpposition (1975 - 1979)
Conservatives after Thatcher
David Cameron, leader of the
Conservative Party.
26. The leaders of the Conservative Party
Nick CleggDecember ,2009
Sir Ming Campbel
January ,2010
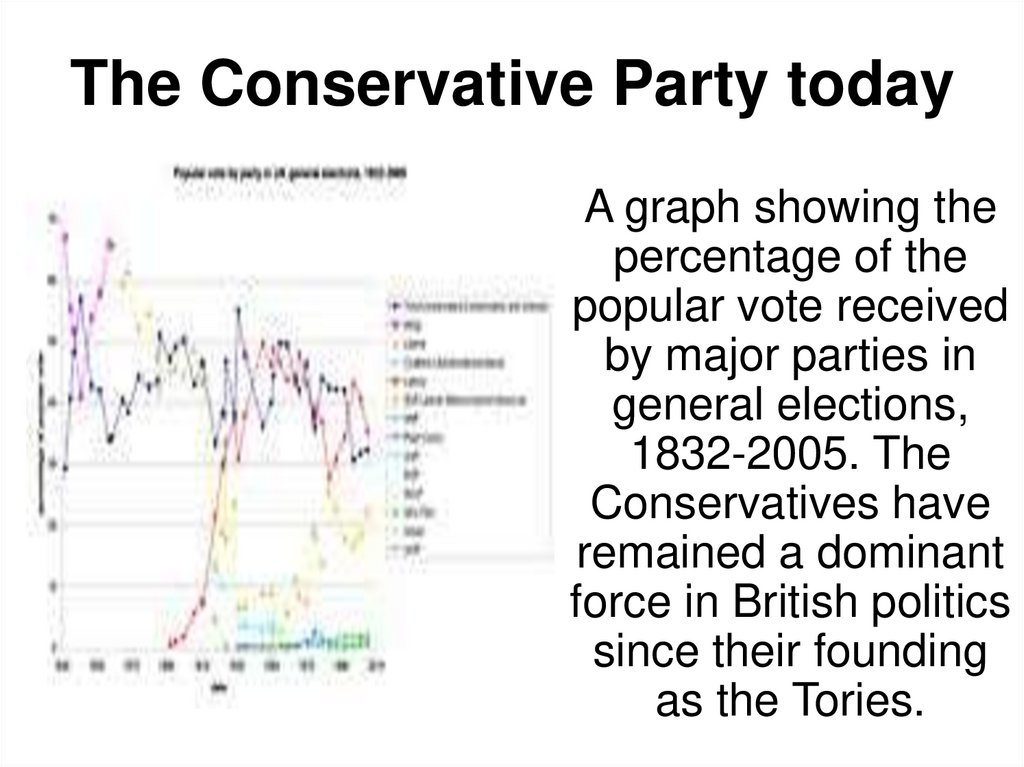
27. The Conservative Party today
A graph showing thepercentage of the
popular vote received
by major parties in
general elections,
1832-2005. The
Conservatives have
remained a dominant
force in British politics
since their founding
as the Tories.
28.
29.
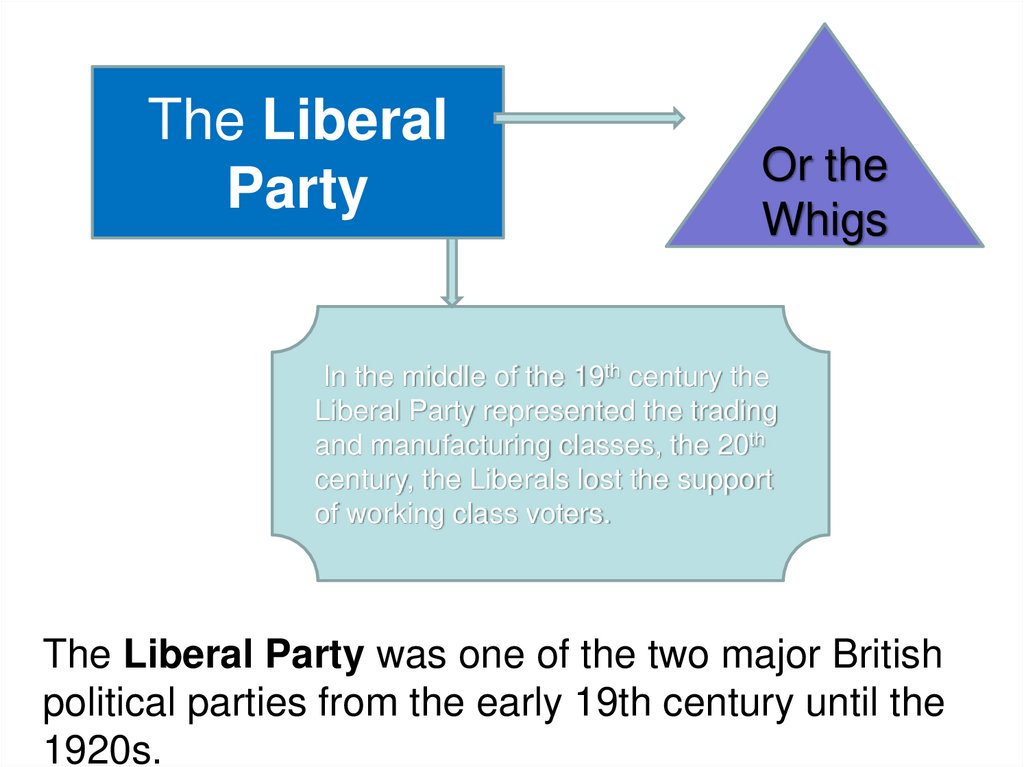
The LiberalParty
Or the
Whigs
In the middle of the 19th century the
Liberal Party represented the trading
and manufacturing classes, the 20th
century, the Liberals lost the support
of working class voters.
The Liberal Party was one of the two major British
political parties from the early 19th century until the
1920s.
30.
The first leader of the Liberal party Viscount PalmerstonIn 1988 the Liberals and Social
Democrats merged to create what
came to be called the Liberal
Democrats.
31. The recent years
As was the case with the Liberal Party formost of the 20th century, the Liberal
Democrats face constant questioning
about which of the other two parties they
are closest to, in particular about which
they would support in the event of a hung
parliament. The party is keen to maintain
its independent identity however, and
argues that the need for a modern Liberal
force in British politics has never been
greater.
32.
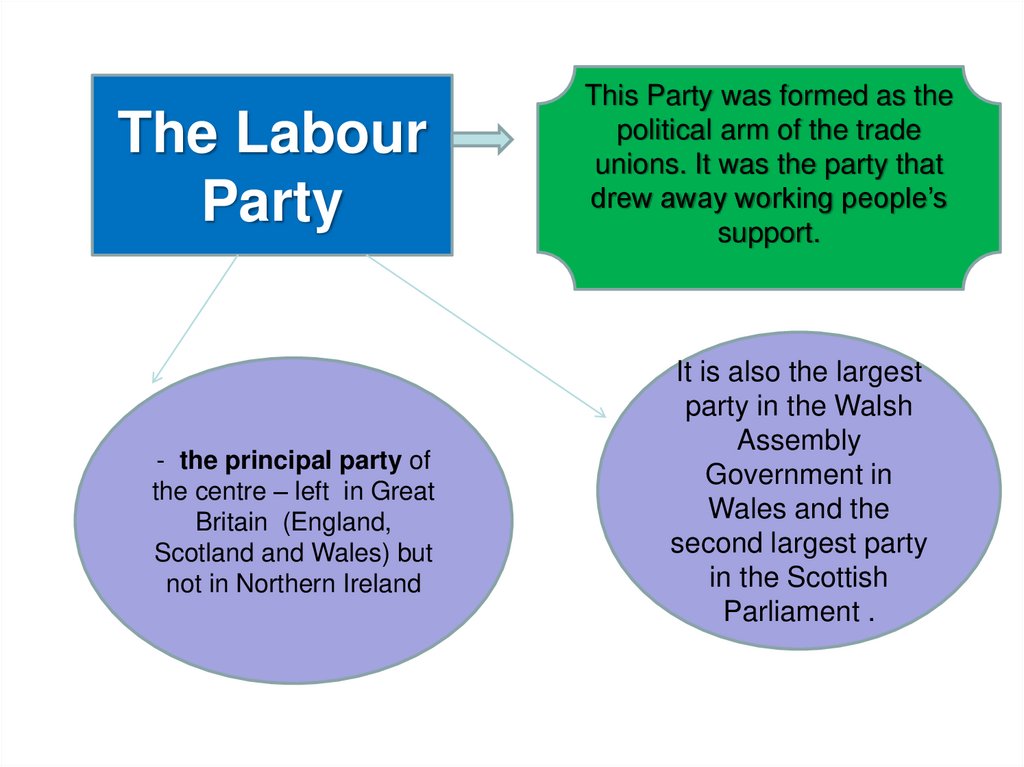
The LabourParty
- the principal party of
the centre – left in Great
Britain (England,
Scotland and Wales) but
not in Northern Ireland
This Party was formed as the
political arm of the trade
unions. It was the party that
drew away working people’s
support.
It is also the largest
party in the Walsh
Assembly
Government in
Wales and the
second largest party
in the Scottish
Parliament .
33. 1920s - The Labour Party surpassed the Liberal Party as the main opposition to the Conservatives,so it was the rise of the
Labour Party.The symbol of the Labour party
34.
Party ideologySince the mid-1980s, under the leadership of Neil
Kinnock, John Smith and Tony Blair the party has
moved away from its traditional socialist position
towards what is often described as the "Third Way"
adopting some free market and Thatcherite policies,
after losing four general elections between 1979 and
1997.
35.
First Labour governments under MacDonaldRamsay MacDonald- the first Labour Prime
Minister, 1924, 1929–35.
36. New Labour In government
• Tony BlairLabour Prime
Minister
1997-2007
37. Gordon Brown (2007-2010)
38. David Cameron(2010-2016) the leader of the Conservative party.
39. Theresa May(2016-2019) the leader of the Conservative party.
40.
• Boris Johnson-representative ofConservative party.
Prime minister from 2019.



































 policy
policy








