Similar presentations:
Early Britain
1. EARLY BRITAIN
2.
PRE-HISTORIC BRITAIN (BEFORE 43)about 500,000 - Stone Age,
people used stone tools to hunt
and fish.
One of the
earliest Venus
figures, Malta
The Iberians - peoples
from the eastern and
southern coasts of the
Iberian peninsula Portugal and Spain
3.
Bronze Ages (4500 to 600BC)6,000 BC Britain becomes an Island
3,000 BC New Stone Age First stone circles erected
Swinside stone circle, in the Lake District
4.
A long barrow is a prehistoric monument usually dating to the early Neolithicperiod. They are traditionally interpreted as a collective tomb.
A well-preserved earthen long
barrow in Dorset, England
West
Kennet
Long
Barrow,
inside
5.
2,100 BC Bronze Age beginsFirst metal workers
People learn to make bronze weapons and tools.
Introduction of cremation of the dead and burials in round barrows.
Round barrows on the chalk ridge of Bronkam Hill in Dorset, England.
6.
2,800 BC -2,000 BC building ofStonehenge
Beaker culture - their name is
thought to originate from the
distinctive beakers that accompanied
their burials. They were farmers and
archers. They lived in round huts
Beakers
7.
750 BC Iron Age began•Iron replaces bronze as most
useful metal.
•Population about 150,000.
•800 - 500 BC -The Celtic
people (the Gaels - The
Britons, the Scotts, the
Belgae) arrive from Central
Europe
•The Celts were farmers and
lived in small village groups in
the centre of their arable
fields. They were also warlike
people.
8.
"Most of the inland inhabitants [of Britain] do not sow corn, but live on milkand flesh, and are clad with skins. All the Britons indeed, dye themselves
with woad, which occasions a bluish colour, and thereby have a more
terrible appearance in fight. They wear their hair long, and have every part
of their body shaved except their head and upper lip. "
Julius Caesar (A Roman Emperor)
9.
Queen of the CelticIceni tribe who led an
uprising in Roman
Britain.
In 61 A.D. Boadicea
leads the Iceni in revolt
against the Romans
Boadicea and Her Daughters, a
bronze sculptural group in
London near Big Ben.
10.
In 55 BC Julius Caesar heads firstRoman Invasion but later withdraws
In 43 A.D. Romans invade and
Britain becomes part of the
Roman Empire
In 70 A.D. Romans conquer Wales
and the North
In 122 - 128 A.D. Emperor Hadrian
builds a wall on the Scottish Border
In 140 A.D. Romans conquer
Scotland
401 - 410 the Romans withdraw
from Britain: Anglo Saxons migrants
begin to settle
11.
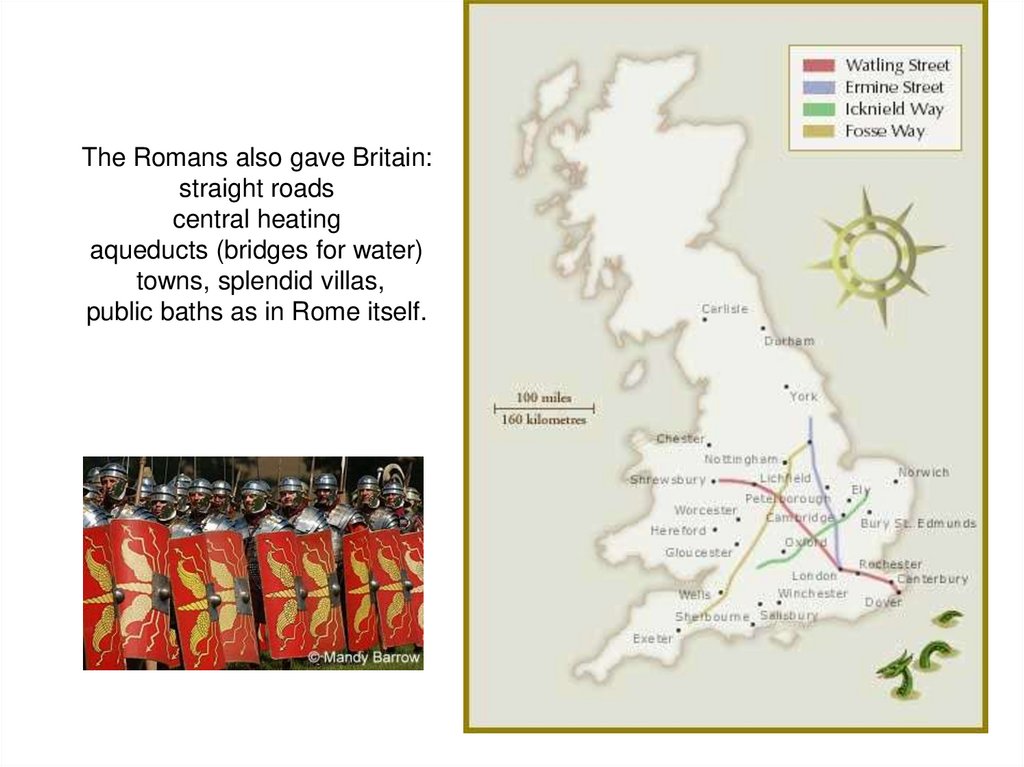
The Romans also gave Britain:straight roads
central heating
aqueducts (bridges for water)
towns, splendid villas,
public baths as in Rome itself.
12.
Wheeldale Roman Road,North York Moors
13.
The Roman road now known as the Stanegate lookingeast at Corbridge (Northumberland)
14.
The Roman spa city of Bath15.
Before the Roman conquestthe typical building in most
parts of Britain was the
'round house'. Some of them
were big enough to house a
family of twenty or more
people as well as some of
their animals.
Reconstruction of part of the
Roman native settlement at
Chysauster (Cornwall).
16.
•Many words of Modern English have come from Latin.•The word “street” – “strata”– road.
•Port – porta
•Wall – vallum.
•The names of many English towns are of Latin origin too.
•The Roman towns were called castra, which means camp. English towns ending
in –chester, -cester, -caster was once a Roman camp or a city: Chester,
Winchester, Manchester, Dorchester, Lancaster.
•Vicus – village – Norwich (/ˈnɒrɪdʒ/, Woolwich /ˈwʊlɪtʃ/
Portus – port – Bridport, Portsmouth.
•“Milk” – the word was known by the Celts, but the word “cheese” and “butter” have
Latin origin. They are called the Latin of the first layer. Also some plants and fruit:
“pear”, “cherry” (“plum”) – Latin origin.















 history
history geography
geography








