Similar presentations:
Architecture of computer systems
1.
Architecture of computer systems2.
A computer architect is a conceptual model ofa computer system embodied in its
components, their interaction between
themselves and the environment, which also
includes the principles of its design and
development
There are several levels of computer
organization (computer architecture), from two
or more:
3.
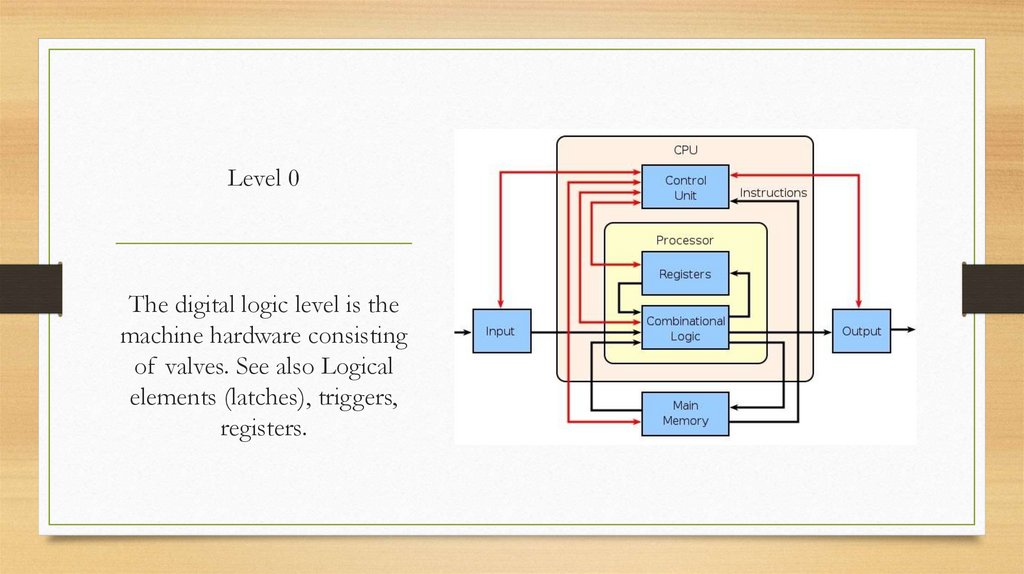
Level 0The digital logic level is the
machine hardware consisting
of valves. See also Logical
elements (latches), triggers,
registers.
4.
Level 1Microarchitectural level, interpretation
(microprograms) or direct execution.
Electronic circuits execute machinedependent programs. The set of
processor registers forms local
memory. See also arithmetic and logical
device, control device. Its task is to
interpret level 2 commands (level of
command architecture). Currently, at
the command architecture level, there
are usually simple commands that are
executed in one cycle (such as RISC
machines, in particular).
5.
Level 2Command system
architecture level, broadcast
(assembler).
6.
Level 3Operating system level, broadcast
(assembler). This is a hybrid layer:
one part of the commands is
interpreted by the operating system
and the other by firmware. See also
virtual memory, files.
7.
Level 4Assembler language level, broadcast (compiler). The fourth level
and above is used for writing applications, from the first to the
third - system programs. Programs in a human-friendly form are
broadcast into the language of levels 1-3.
8.
Level 5High-level language. Programs in
high-level languages are usually
broadcast to levels 3 and 4.
The first documented computer
architecture was in correspondence
between Charles Babbage and Ada
Lovelace, describing the
mechanism of analysis. When
creating the Z1 computer in 1936,
Konrad Zuse described his future
projects in two patent applications.





 programming
programming








