Similar presentations:
Information & communications technologies. Computer Networks. Week 8. Laboratory work №8. Practice Packet Tracer
1.
Information &communications
technologies
INF-106
Computer Networks
Week 8
2.
Laboratory work №8Practice Packet Tracer
3.
4.
Router● The router is a piece of network hardware that connects a
local network to the internet.
● A router is a device that communicates between the internet
and the devices in your home that connect to the internet.
● As its name implies, it “routes” traffic between the devices
and the internet.
5.
Hub● A hub is a physical layer networking device which is used to connect multiple
devices in a network.
● They are generally used to connect computers in a LAN.
6.
Switch● A switch is able to handle the data and knows the specific addresses to send
the message.
● It can decide which computer is the message intended for and send the
message directly to the right computer.
● The efficiency of switch has been greatly improved, thus providing a faster
network speed.
7.
HostA network host is a computer or other device connected to a computer network.
A host may work as a server offering information resources, services, and
applications to users or other hosts on the network. Hosts are assigned at least
one network address.
8.
IP addressAn IP address is a unique address that identifies a device on the internet or a local network.
A MAC (Media Access Control) address, sometimes referred to as a hardware or physical
address, is a unique, 12-character alphanumeric attribute that is used to identify individual electronic
devices on a network.
A subnet mask is a 32 bits address used to distinguish between a network address and a host
address in IP address. A subnet mask identifies which part of an IP address is the network address
and the host address.
9.
IP● InternetProtocol
Address
● IPv4
● IPv6
10.
11.
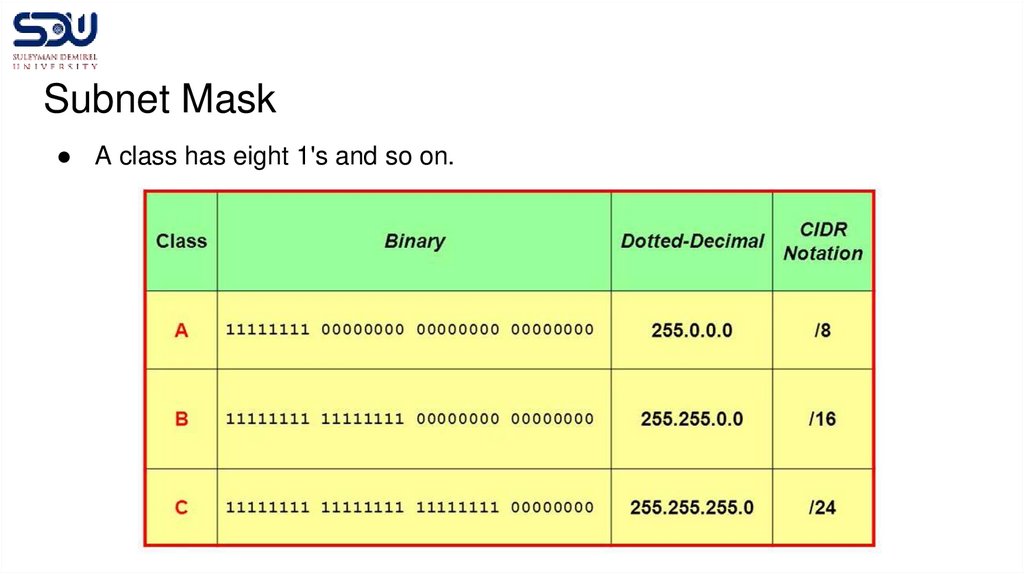
Subnet Mask● A class has eight 1's and so on.
12.
BinaryNumbers
13.
Find Network ID from IP AddressLogical ‘AND’ IP address and subnet mask to get Network ID
For example,
IP address: 192.24.134.23
Find Network ID using default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 for class C
Find the binary representation of IP address and subnet mask
Logical ‘AND’ with subnet mask
Convert binary to decimal value: Network ID: 192.24.134.0 / 24
IP: 11000000.00011000.10000110.00010111
Sm:11111111. 11111111 .11111111. 00000000
14.
15.
FormulasTo calculate 1st network address:
● 1+ last octet of network address
To calculate broadcast address:
● Find the number of degree of valid host addresses, replace that amount to 1
in 4th octet
To calculate last network address:
● Last octet of broadcast address - 1
16.
Find Number of usable hosts:1. IP address: 169.174.141.10
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
IP address:
1010100
1
1010111
0
1000110
1
00001010
Subnet Mask:
1111111
1
1111111
1
1111111
1
11110000
Network ID:
169
174
141
0
Prefix: 8+8+8+4=28
In the last part of subnet mask we have 4 zeros, so we get that 2^4=16.
Number of hosts: 16
Number of usable hosts: 16-2=14 (1 addr. for NetID and 1 for broadcast address)
Usable hosts: 169.174.141.1 - 169.174.141.14
17.
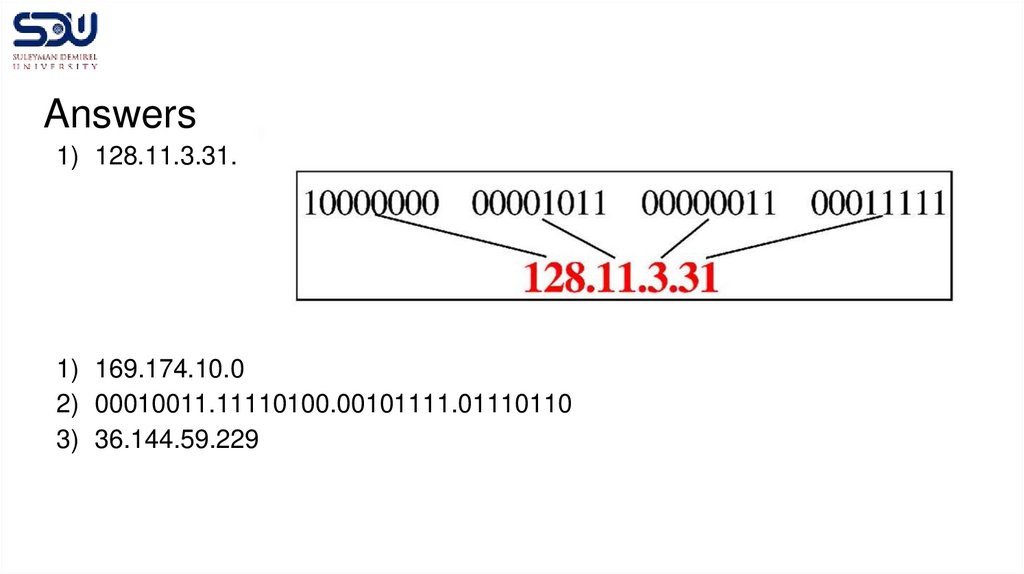
Practice1. Convert IP address to binary: 128.11.3.31
1. Convert IP address to decimal:
10101001.10101110.00001010.00000000
1. Convert IP address to binary: 19.244.47.118
1. Convert IP address to decimal:
00100100.10010000.00111011.11100101
18.
Answers1) 128.11.3.31.
1) 169.174.10.0
2) 00010011.11110100.00101111.01110110
3) 36.144.59.229
19.
Practice _ Network ID1. Mask: 255.255.248.0
IP address: 192.168.40.50
What is the Network ID?
1. Mask: 255.255.248.0
IP address: 192.168.45.55
What is the Network ID?
1. Mask: 255.255.255.192
IP address: 192.168.45.55
What is the Network ID?
20.
Answers. Easy way to find Network ID1. IP address: 192.168.40.50
Subnet Mask: 255.255.248.0
Prefix:11111111.11111111.11111000.00000000 = 8+8+5=21
the prefix size is the number of addresses available for use.
We can use: 192.168 (because subnet mask: 255.255.)
So 40 in binary:
00101000.00110010
3rd octet mask bits:11111000.00000000
00101000.00000000
Network ID:192.168.40.0 /21
21.
Answer 22. IP address: 192.168.45.55
Subnet Mask: 255.255.248.0
Prefix: 11111111.11111111.11111000.00000000 = 8+8+5=21
We can use: 192.168 (because subnet mask: 255.255.)
So 45 in binary:
00101101.00110111
3rd octet mask bits:11111000.00000000
00101000.00000000
Network ID:192.168.40.0 /21
22.
Answer3.
IP address: 192.168.45.55
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.192
Prefix: 11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000= 8+8+8+2=26
We can use: 192.168.45 (because subnet mask: 255.255.255.)
So 55 in binary:
00110111
4th octet mask bits:11000000
00000000
Network ID:192.168.45.0 /26
23.
Practice_ Find Number of usable hosts:IP address: 19.244.47.118
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.224
Number of hosts ?
Number of usable hosts ?
24.
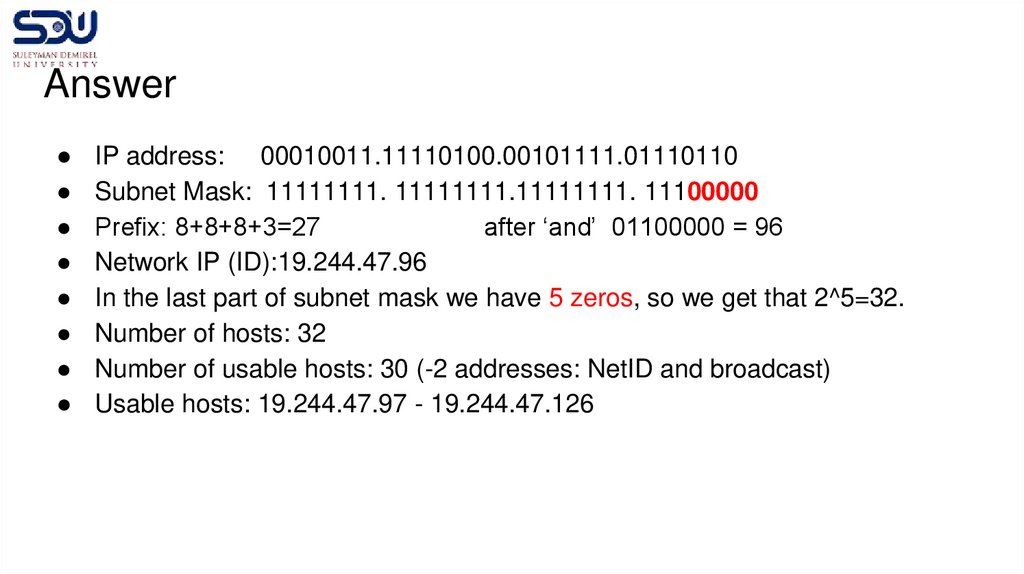
AnswerIP address: 00010011.11110100.00101111.01110110
Subnet Mask: 11111111. 11111111.11111111. 11100000
Prefix: 8+8+8+3=27
after ‘and’ 01100000 = 96
Network IP (ID):19.244.47.96
In the last part of subnet mask we have 5 zeros, so we get that 2^5=32.
Number of hosts: 32
Number of usable hosts: 30 (-2 addresses: NetID and broadcast)
Usable hosts: 19.244.47.97 - 19.244.47.126






















 informatics
informatics








