Similar presentations:
Team-building Workshop
1.
Key Points2.
(Mallory, 1991)3.
To solve problems by drawing on thetalents of
variety of individuals.
To foster togetherness in the workplace while
tackling projects.
To reduce or eliminate a lack of communication
among staff members on projects.
To heighten productivity by encouraging an
atmosphere of cooperation.
To achieve a solution that might be unpopular to
some but is the desire of the majority.
4.
To lighten the workload of the supervisor(this requires delegation.)
To make workers transfer knowledge to
one another to save educational costs
(these people need training.)
To determine the opinions and working
styles of the staff (this organization need
improved communication.)
To get the staff to work harder (they need
better supervision or motivation and
rewards.)
5.
Executive positions.Nearly every executive
must, at one time or another , work with or
direct a team.
Mid-level managers. Whether you supervise
two or 200 people, you could be called upon
to form a team. Having learned the
necessary skills gives you an advantage when
the situation occurs.
6.
Entrepreneurs.Knowing how to lead a
team comes in handy if you are selfemployed, operate your own business or
are part of a network of associates.
You’ll be able to tap the brain power and
knowledge of others in a group setting.
Working with people. Any position where
you work with people requires good
human relations skills. By exposing
yourself to the teamwork process, you’ll
get greater insight into individual
differences and how these differences can
be managed to achieve a collective goal
7.
Team LeaderCritic
Implementer
External Contact
Coordinator
Ideas Person
Inspector
8.
1.2.
3.
4.
Dominant
Influencer
Balancer
Loyalist
9.
Performance ResultsMutual
Problem
Solving
Technical/
function
Small number
of people
Interpersonal
Individual
Specific goals
Common approach
Meaningful purpose
Collective work
Products
Commitment
Personal Growth
10.
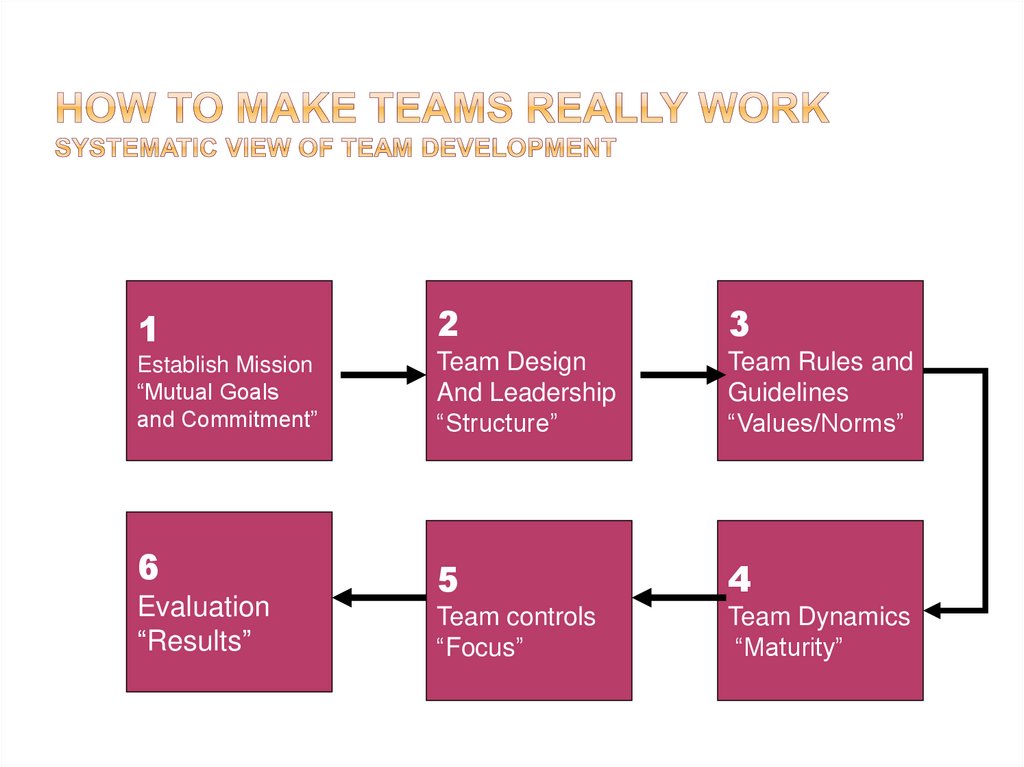
12
3
Establish Mission
“Mutual Goals
and Commitment”
Team Design
And Leadership
“Structure”
Team Rules and
Guidelines
“Values/Norms”
5
4
Team controls
“Focus”
Team Dynamics
“Maturity”
6
Evaluation
“Results”
11.
A clear elevating goalA collaborative
A results –driven
climate
Standards of
excellence
External support and
recognition
Principled leadership
structure
Competent members
Unified commitment
12.
When people believe in each other, whenthey believe that each team member will bring
superior skills to a task or responsibility, that
disagreements or opposing views will be worked out
reasonably, that each member’s view will be treated
seriously and with respect, that all team members
will give their best effort at all times, and that
every one will have the team’s overall best interest
at heart, then excellence can become a sustainable
reality.











 management
management business
business








