Similar presentations:
Theory of Factors of Production and Production Function
1. Theory of Factors of Production and Production Function
Galiya Berdykulova2. Learning outline
To categorize the factors of productionTypes of Factors of Production
Economic nature of factors of production
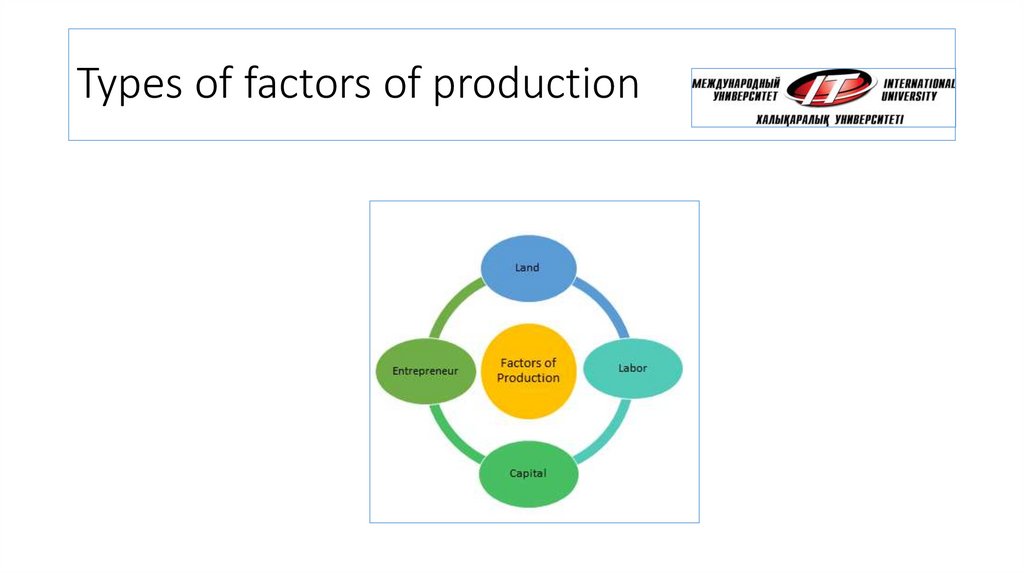
3. Types of factors of production
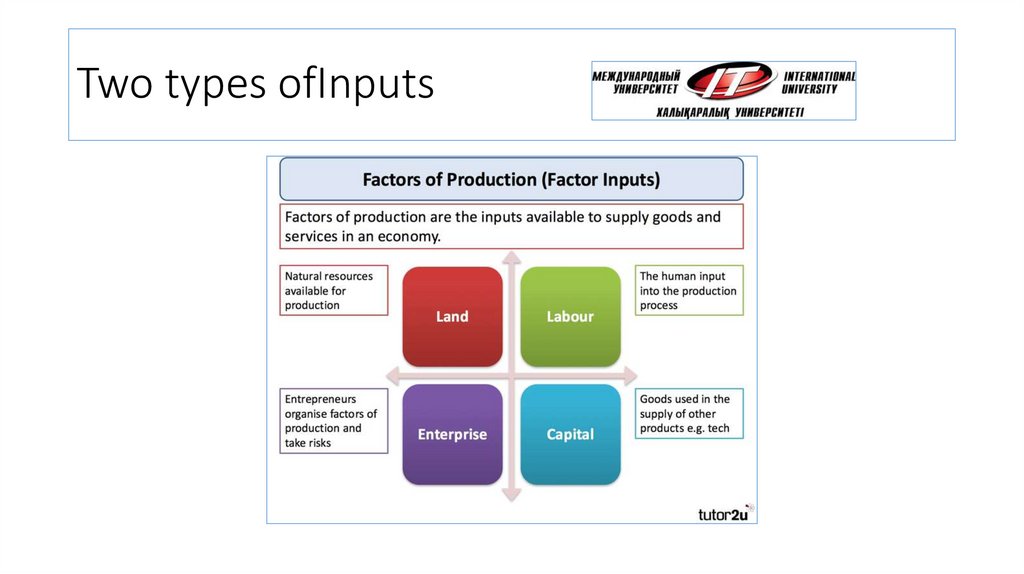
4. Two types ofInputs
5. Factors of production
6. Land
• It refers to all natural resources. All natural resources either on thesurface of the earth or below the surface of the earth or above the
surface of the earth is Land.
• One uses the land to produces goods. It is the primary and natural
factor of production. All gifts of nature such as rivers, oceans, land,
climate, mountains, mines, forests etc. are land.
7. Characteristics of Land as a Factor of Production
• The land is a free gift of nature.• The land has no cost of production.
• It is immobile.
• The land is fixed and limited in supply.
8. Types of Land
• Residential• Commercial
• Recreation
• Cultivation
• Extraction
• Uninhabitable
9. Residential Land
• A residential area is a land used in which housing predominates, asopposed to industrial and commercial areas.
• Residential development is real estate development for residential
purposes.
10. Commercial areas
Commercial areas in a city are areas, districts, or neighbourhoodsprimarily composed of commercial buildings, such as
a downtown, central business district, financial district, "Main
Street", commercial strip, or shopping center.
Commercial activity within cities includes the buying and selling of
goods and services in retail businesses, wholesale buying and
selling, financial establishments, and a wide variety of uses that are
broadly classified as "business."
11. Recreational land
Recreational land is land used for purposes of recreation.Examples:
sports fields,
gymnasiums,
playgrounds, public parks and green areas,
public beaches and swimming pools,
and camping sites.
12. Cultivation land
Cultivation land isarable land that is worked by plowing and sowing and raising crops.
Agriculture is
the science, art, or occupation concerned with cultivating land, raising c
rops, and feeding, breeding, and raising livestock; farming.
Agriculture in Kazakhstan remains a small scale sector
of Kazakhstan's economy. Agriculture's contribution to
the GDP is under 10% - it was recorded as 6.7%, and as
occupying only 20% of labor. At the same time, more than
70% of its land is occupied in crops and animal
husbandry.
Compared to North America, a relatively small percentage
of land is used for crops, with the percentage being higher
in the north of the country. 70% of the agricultural land is
13. Extraction land
Extraction is the act or process of extracting something.Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other
geological materials from the earth, usually from an
orebody, lode, vein, seam, reef or placer deposit.
These deposits form a mineralized package that is of
economic interest to the miner.
14. Uninhabitable land
UninhabitableIs unsuitable for living in.
This theory divides the earth into three zones that
are uninhabitable owing to extreme temperatures and two zones that
are temperate and therefore inhabitable.
15. Labor
• All human effort that assists in production is labour. This effort can bemental or physical. It is a human factor of production. It is the worker
who applies their efforts, abilities, and skills to produce.
• The payment for labour is the wage.
16. Characteristic
• It is a human factor.• One cannot store labour.
• No two types of labour are the
same.
Types of Labor
• Unskilled
• Semi-skilled
• Skilled
• Professional
17. Capital
Types of CapitalPhysical
• Fixed
• Working
• Venture
Financial
• Own
• Borrowed
Types of Capital
• Natural
• Human
• Social
18. Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is a person who brings other factors ofproduction in one place. He uses them for the production
process. He is the person who decides
• What to produce
• Where to produce
• How to produce
• A person who takes these decisions along with the associated
risk is an entrepreneur.
• The payment for entrepreneur is profit.
19. Characteristics
• He has imagination.• He has great administrative power.
• An entrepreneur must be a man of action.
• An entrepreneur must have the ability to organize.
• He should be a knowledgeable person.
• He must have a professional approach.
20. Solved Examples on Factors of Production
Solved Examples on Factors of ProductionQ. Problem: All things used in
producing goods, services,
buildings, ideas are
• Natural resources
• Capital resources
• Resources
• Human Resources
• Problem: Which of the
following is one of the three
economic questions?
• In what order should I produce
• What color should I produce?
• How many should I produce?
• What should I produce?
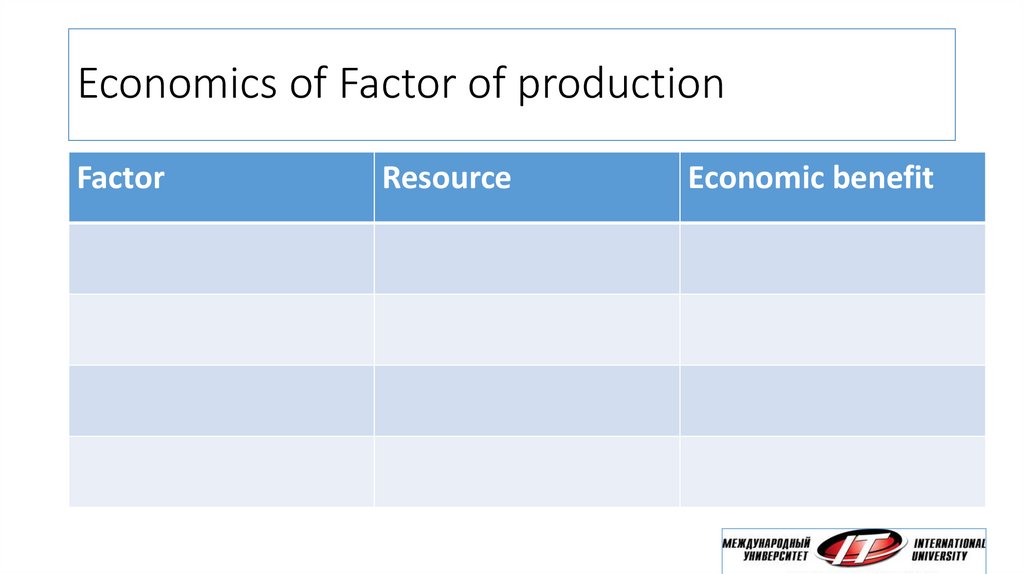
21. Economics of Factor of production
FactorResource
Economic benefit
22. Learning outcomes
??