Similar presentations:
Early options. A provider’s guide to medical abortion
1.
EARLY OPTIONSA PROVIDER’S GUIDE TO MEDICAL ABORTION
Medical Education Series
© 2005 National Abortion Federation
2.
EARLY OPTIONSA PROVIDER’S GUIDE TO MEDICAL ABORTION
Overview of Medical Abortion:
Clinical and Practice Issues
3. Objectives
• Discuss mifepristone’s history• Provide an overview of medical abortion agents
and regimens.
• Review important components of medical
abortion practice, including counseling, eligibility
screening, side effects, and follow-up
• Discuss general administrative and legal issues
related to medical abortion practice
4. Overview
• Mifepristone history• Overview of medical abortion agents and
regimens
• Medical abortion in practice
• Administrative and legal issues
5. Definition of Medical Abortion
Early pregnancy termination, generally before9 weeks’ gestation, resulting from abortioninducing medications and without primary
surgical intervention
6. Use of Mifepristone Worldwide
Millions of women have used mifepristone for medical abortion.Year that mifepristone was licensed
France-1988
China-1988
UK-1991
Sweden-1992
Austria-1999
Belgium-1999
Denmark-1999
Finland-1999
Germany-1999
Greece-1999
Israel-1999
Luxembourg-1999
Netherlands-1999
Spain-1999
Switzerland-1999
Norway-2000
Russia-2000
Taiwan-2000
Tunisia-2000
Ukraine-2000
US-2000
New Zealand-2001
South Africa-2001
Azerbaijan—2002
Belarus—2002
Georgia--2002
India--2002
Latvia--2002
Uzbekistan--2002
Vietnam—2002
Estonia—2003
Guyana—2004
Moldova--2004
7. The Path to FDA Approval
1993:
1994:
1994-95:
1996:
1999:
• 2000:
Clinton executive order
Roussel Uclaf donates US patent
US clinical trials
FDA grants “approvable” status
Manufacturing and labeling
information submitted
FDA approves Mifeprex®
8. Abortions by Gestational Age in U.S.
3530
24.7
percentage
25
17.7
20
18.9
16.3
15
9.9
10
6.1
4.2
5
1.4
0
≤ 6
7
8
9-10
11-12
13-15
16-20
21+
Weeks of gestation
Strauss et al. MMWR, 2004
9. Overview
• Mifepristone history• Overview of medical abortion agents and
regimens
• Medical abortion in practice
• Administrative and legal issues
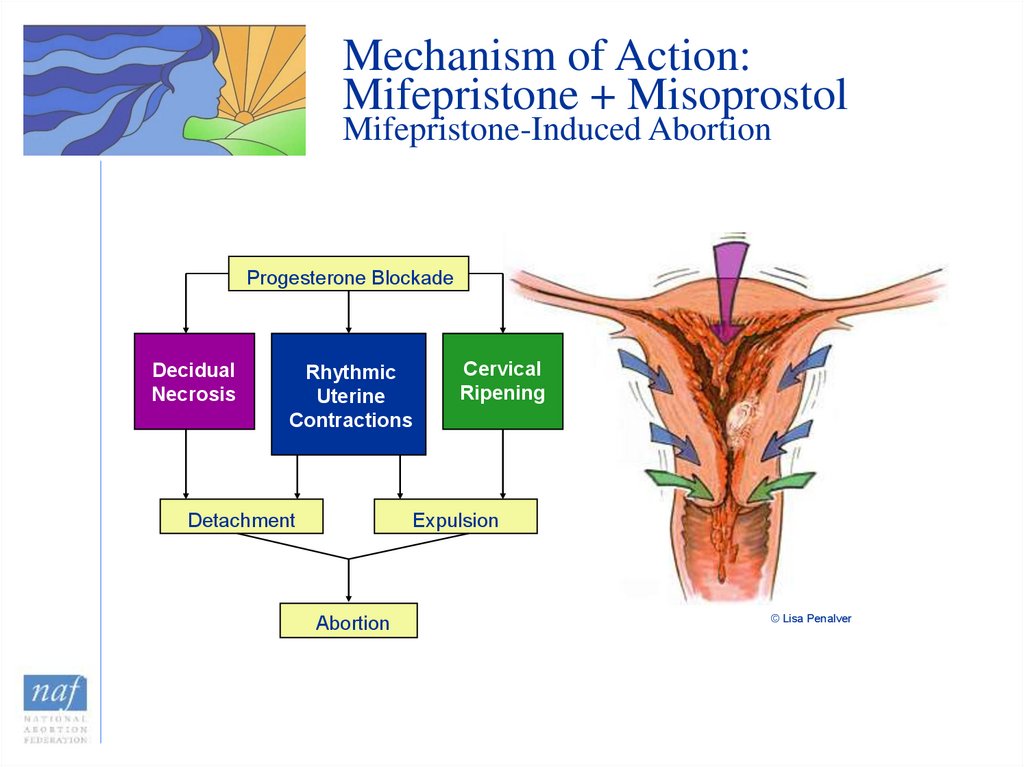
10. Mechanism of Action: Mifepristone + Misoprostol Mifepristone-Induced Abortion
Progesterone BlockadeDecidual
Necrosis
Rhythmic
Uterine
Contractions
Detachment
Cervical
Ripening
Expulsion
Abortion
© Lisa Penalver
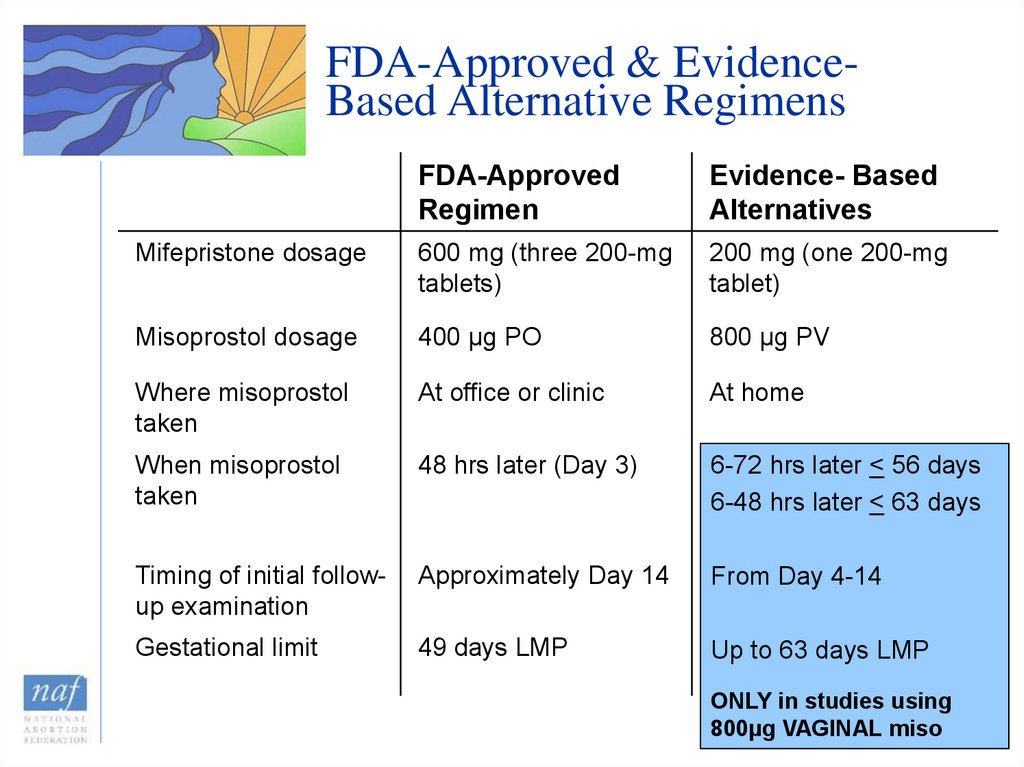
11. FDA-Approved & Evidence-Based Alternative Regimens
FDA-Approved & EvidenceBased Alternative RegimensFDA-Approved
Regimen
Evidence- Based
Alternatives
Mifepristone dosage
600 mg (three 200-mg
tablets)
200 mg (one 200-mg
tablet)
Misoprostol dosage
400 µg PO
800 µg PV
Where misoprostol
taken
At office or clinic
At home
When misoprostol
taken
48 hrs later (Day 3)
6-72 hrs later < 56 days
6-48 hrs later < 63 days
Timing of initial followup examination
Approximately Day 14
From Day 4-14
Gestational limit
49 days LMP
Up to 63 days LMP
ONLY in studies using
800µg VAGINAL miso
12. Evidence-Based Alternative Regimens
• 200-mg dose of mifepristone• Vaginal administration of misoprostol
– Lower incidence of side effects compared to oral
misoprostol
– More rapid expulsion compared to oral misoprostol
– Increases efficacy of medical abortion for gestations
up to 63 days
– Decreases continuing pregnancy rate
• Home use of misoprostol
• Flexibility in day of vaginal misoprostol use
• Flexibility in initial follow-up evaluation
13. Contraindications
• Allergy to mifepristone, misoprostol, or otherprostaglandin analogues
• Concurrent long-term systemic corticosteroid
use
• Chronic adrenal failure
• Hemorrhagic disorder or concurrent
anticoagulant therapy
• Intrauterine device in situ
• Possible ectopic pregnancy
• Inherited porphyria
14. Special Considerations
• Chronic medical conditions–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Cardiovascular disease
Hypertension
Hepatic disease
Renal disease
Pulmonary disorders
IDDM
Severe anemia
Heavy smoking
• Breast-feeding
• Women over 35 who smoke > 10 cigarettes daily
15. Overview
• Mifepristone history• Overview of medical abortion agents and
regimens
• Medical abortion in practice
-Features of medical abortion
-Counseling
-Eligibility screening
-Expected side effects
-Follow-up care
• Administrative and legal issues
16.
Features of Medical Abortionand Vacuum Aspiration
Medical
Vacuum Aspiration
• High success rate (about 95-99%)
• High success rate (99%)
• Usually avoids surgical procedure
• Instruments inserted into the
uterus
• Requires at least two visits
• Can be done in one visit
• Procedure is completed in 5-10
• Abortion occurs within 24 hours of
minutes
second medication, for most women
• May be used in early pregnancy
• May be used in early pregnancy
• Oral pain medication can be used
• Anesthesia/Sedation can be used
• Some of the process may happen at • Procedure is done in a medical
office or clinic
home
• Medications cause a process similar • Health care provider performs the
procedure
to a miscarriage
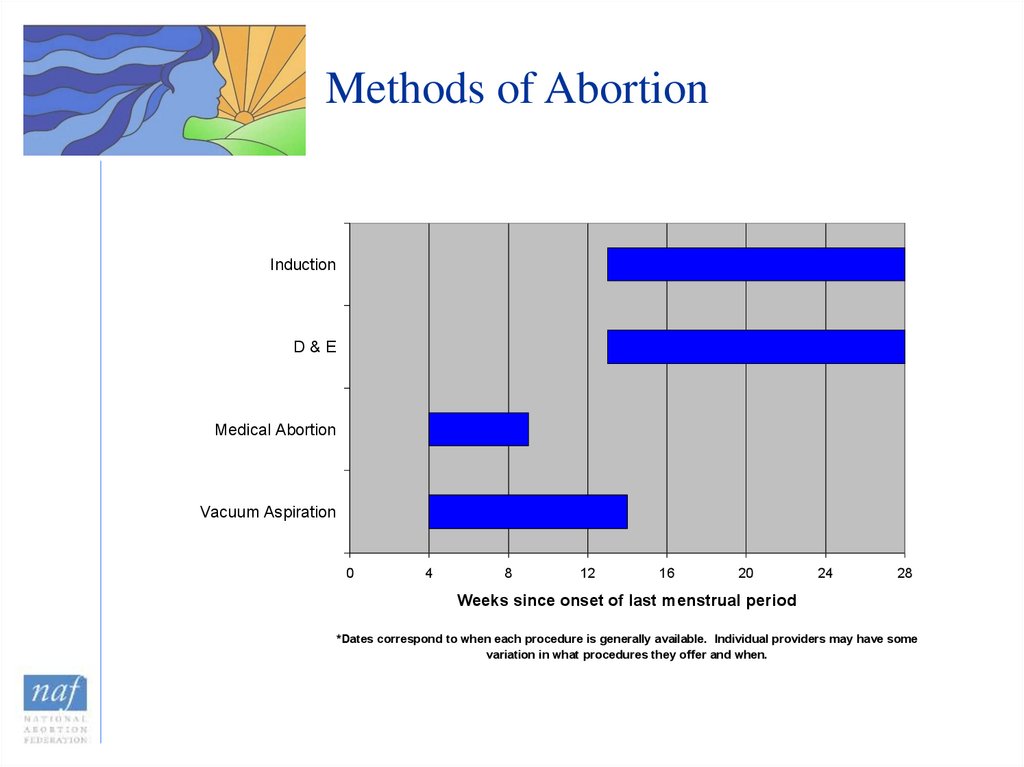
17. Methods of Abortion
InductionD&E
Medical Abortion
Vacuum Aspiration
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
Weeks since onset of last menstrual period
*Dates correspond to when each procedure is generally available. Individual providers may have some
variation in what procedures they offer and when.
18. Features of Medical Abortion
19. Why Women Choose Medical Abortion
• Avoids surgery, noninvasive• Perceived by some women as:
– “Better” or “easier” than vacuum aspiration
– More natural, like a miscarriage
20. Medical Abortion: Acceptability
• Generally well-accepted by providersand patients
• Patient attitudes towards
mifepristone/misoprostol
– “Satisfactory” or “very satisfactory”: 88%–97%
– % of eligible women choosing mifepristone
varies
– More than half of eligible women choose
mifepristone in France, Scotland & Sweden
– Patients dislike multiple-visit requirements
Winikoff, et al. Int Fam Plann Perspect 1997
Winikoff, et al. Arch Fam Med 1998
Ngoc, et al. Int Fam Plann Perspect 1999
Jones, et al. Perspect Sexual Reprod Health 2002
21.
Counseling andEligibility Screening
22. Counseling for Medical Abortion
• The quality of counseling correlates with thelevel of patient satisfaction with abortion care
• Abortion can be an emotional issue for patients
and providers
• Clarify provider values
• Assumes a large role in
medical abortion services
• Requires adequate time
23. Challenges Specific to Medical Abortion Counseling
• Greater patient autonomy• Patients must be knowledgeable and prepared
to participate in the process
• Preparing women for side effects is a critical
component of counseling
• Patients may not acknowledge process
as an abortion
• Patients must understand importance of
vacuum aspiration completion, if needed
24. Protocol: Special Issues
• Home administration of misoprostol• Viewing products of conception
• Anxiety about participating in the abortion process
• Support person, child care, time off from job
• Privacy issues
25. Common Questions About the Medical Abortion Protocol
• Efficacy• Safety
• Side effects
– Pain
– Bleeding
– Other
• Timeline for the process
26. Completion of Medical Abortion
• Timing varies somewhat depending onmifepristone regimen
• Onset of bleeding
–
–
–
–
Bleeding after mifepristone can occur
80-92% bleed within 4 hours of misoprostol
Average onset 2-4 hours post misoprostol
98% of women bleed within 24 hours of
misoprostol
• Expulsion
– 60-93% abort within 5 hours of misoprostol
– ~90% abort within 24 hours after misoprostol
Schaff, et al. Contraception 1999
Wiebe, et al. Obstet Gynecol 2002
Creinin, et al. Obstet Gynecol 2004
27. Eligibility Screening
Patient certain about abortion decision
Gestational age
Able to follow treatment protocol and follow up
Willing to have vacuum aspiration if needed
Able to give informed consent
Phone access
Access to emergency care
28. Patient Instruction Sheet
• Given to patients at initial visit• Covers:
–
–
–
–
–
–
Misoprostol administration
Use of analgesics with medication restrictions
Symptoms and side effects
24-hour contact number
When to call for help or medical advice
When to return for follow-up
29.
Expected Side Effects:Patient Preparation and
Management
30. Definitions
Side EffectEffect of treatment, other than the intended
outcome, that might include physiological
or psychological consequences
Complication
Effect resulting from treatment that has
potentially serious clinical consequences
and requires medical intervention
31. Expected Side Effects of Medical Abortion
• Pain• Bleeding
• Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
• Short-term temperature elevation or chills
• Headache, dizziness
32. Management of Common Side Effects: Pain
• Cramping occurs in > 90% of patients1- Variable in intensity
- Generally peaks after misoprostol
• Provide pain medications with initiation
of treatment
• Discuss additional comfort measures
• Counseling and reassurance crucial to
pain management
1
Spitz IM, New Engl J Med, 1998
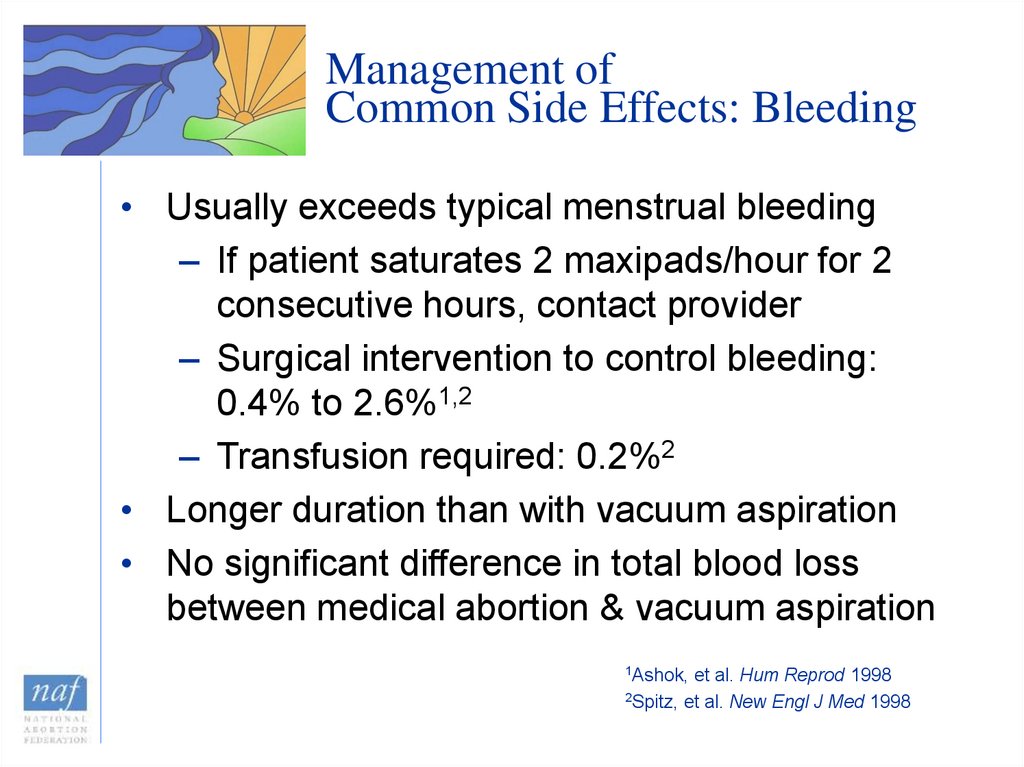
33. Management of Common Side Effects: Bleeding
• Usually exceeds typical menstrual bleeding– If patient saturates 2 maxipads/hour for 2
consecutive hours, contact provider
– Surgical intervention to control bleeding:
0.4% to 2.6%1,2
– Transfusion required: 0.2%2
• Longer duration than with vacuum aspiration
• No significant difference in total blood loss
between medical abortion & vacuum aspiration
1Ashok,
et al. Hum Reprod 1998
2Spitz, et al. New Engl J Med 1998
34. Management of Common Side Effects: GI, Temperature Elevation
• Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea– Usually short in duration
– Rarely needs medication
• Short-term fever and chills
– Result of misoprostol or the abortion process
– Antipyretics as appropriate
– Suspect infection with:
• Sustained fever > 100.4°F
• Fever 24 hours or more after misoprostol
35. Emergency Preparedness
• Recognizing the need for emergency care• Access to phone, transportation, acute care
• Instructions on when to call for help
– Saturating > 2 maxipads/hour for 2 consecutive
hours
– Intractable pain
• Reassure patient that hemorrhage is rare
36. On-Call Services
• A clinician must be available around the clock• Call volume compared to vacuum aspiration is
variable
– In one study, 2/3 report fewer or same number
– May be associated with quality of counseling and
patient preparation
• On-call duties can rotate among qualified staff
members
37.
Follow-Up Care38. Follow-up Care
• Determine if abortion is complete• Continuity of care preferable
• Provide emotional support and assistance, as
needed
• Provide information, ask/answer questions,
listen, and observe
39. Meta-Analysis: Various Regimens Mifepristone/Misoprostol (< 49 days)
Meta-Analysis: Various RegimensMifepristone/Misoprostol (< 49
days)
100%
96.0%
75%
50%
25%
2.9%
1.1%
Incomplete
Abortion
Continuing
Pregnancy
0%
Success
Kahn, et al. Contraception 2000
40. Successful Treatment
• Focus on patient experience– Emotional/physical
– Management of side effects, feelings
• Concerns and questions
• Review contraceptive options
• Provide information on EC, STDs, and
additional health services as appropriate
41. Unsuccessful Treatment
• Counsel patient regarding options– Observation
– Repeat misoprostol
– Vacuum aspiration
• Be open to patient concerns and potential
feelings of disappointment
• Allow patient to regain some control
42. Vacuum Aspiration in Cases of Unsuccessful Medical Abortion
• Vacuum aspiration required in event of medicalabortion failure
• Manual or Electric Vacuum Aspiration
• Often does not require dilation
• Rarely emergent
43. Overview
• Mifepristone history• Overview of medical abortion agents and
regimens
• Medical abortion in practice
• Administrative and legal issues
-Ordering medications
-FDA requirements
-Malpractice insurance
-Legal issues
44. Ordering Medications
•Mifepristone– Prescriber’s agreement
– Order from specific distributors only
– Not available from general pharmacies
•Methotrexate and Misoprostol
– Order from pharmaceutical distributors
– Also available from pharmacies
45. FDA Labeling
• Prescriber’s Agreement requires care be providedby or under the supervision of a physician able to:
–Assess gestational age
–Diagnose ectopic pregnancy
–Perform vacuum aspiration or appropriate referral
• Counseling and informed consent includes:
–Mifeprex® medication guide
–Mifeprex® patient agreement
• Patient access to emergency care
46. Evidence-Based Use of Medications
• Package labeling– Approved by FDA
– Gives detailed information to clinicians and
patients about how to use the medication
• Clinicians can use approved medications in
ways that are different from the package labeling
(“off-label” use) as long as:
– The use is evidence-based and consistent with
current, accepted medical practice
– The clinician receives informed consent from
the patient
47. Malpractice Insurance
• Abortion may or may not be covered undercurrent policy
• Notify insurer of “material change” in practice
– Are steps of a medical abortion consistent with
services in current practice?
– Complex issue
• Consultation with individual insurance carriers
may help clarify
48. Legal Issues
• Medical abortion generally regulated as muchas other abortion methods
• Providers must
– Be alert to federal, state, and local requirements
– Consult with their own legal counsel
49. Legal Issues
• Role of advanced practice clinicians and scopeof practice
• TRAP regulations
• Tissue examination and disposal
• Reporting requirements
• Parental involvement
• Waiting periods/ “Informed consent”
50. Conclusion
• FDA approved mifepristone in 2000• High efficacy (95-99%) and extremely safe
• Counseling and education: critical for
success and patient satisfaction
• Common side effects: pain, bleeding,
GI symptoms
• Medical abortion practice incorporates
administrative and legal components
51.
EARLY OPTIONSA PROVIDER’S GUIDE TO MEDICAL ABORTION
This educational program does not define a standard of care, nor does it dictate
an exclusive course of management. It contains recognized methods and
techniques of medical care that represent currently appropriate clinical practice.
Variations in patient needs and available resources may justify alternative
approaches.
Laws governing abortion, informed consent, and medical
malpractice vary among states. These materials are strictly for informational
purposes, and do not constitute legal advice or representation. These materials
are not intended as a substitute for the advice of a health care provider. Neither
NAF nor its agents are responsible for adverse clinical outcomes that might occur
where they are not expressly and directly involved in the role of primary caregiver.
This educational program is protected by copyright.
Any unauthorized
duplication, reproduction, or alteration of the presentations or any part of the
presentations contained therein is strictly prohibited. This educational program is
intended for the use of the original recipient and his/her agents and cannot be
sold, distributed, transmitted or transferred in any form without prior written
authorization by the National Abortion Federation.
© 2005 National Abortion Federation















































 medicine
medicine








