Similar presentations:
The System of State Bodies of India
1.
The System Of State BodiesOf India
Name :- Dev Alkadi R.
Group :- 20LL7A
2.
Content1. The Head of the State President
2. Election
3. Legislative Power
4. Council Of Ministers
3.
The Head of the State President• The Government of Gujarat, also known as the State Government of Gujarat, or locally
as State Government, is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state
of Gujarat and its 33 districts. It consists of an executive of the legislators appointed by
the Governor of Gujarat, a judiciary and of a publicly elected legislative body.
• Like other states in India, the head of state of Gujarat is the Governor, appointed by
the President of India on the advice of the Central (Union) government. His or her post
is largely ceremonial, but considers the legislative composition and appoints the Chief
Minister, who is the main head of government, as chair of the Council of Ministers of
Gujarat and is vested, in some instances alone but as to most executive powers by
Council consensus with virtually all of the executive powers.
• Gandhinagar, the capital of Gujarat, houses the relevant Vidhan Sabha (also known as
the Gujarat Legislative Assembly) and the secretariat. The Gujarat High
Court in Ahmedabad, has jurisdiction over the state as to state laws.
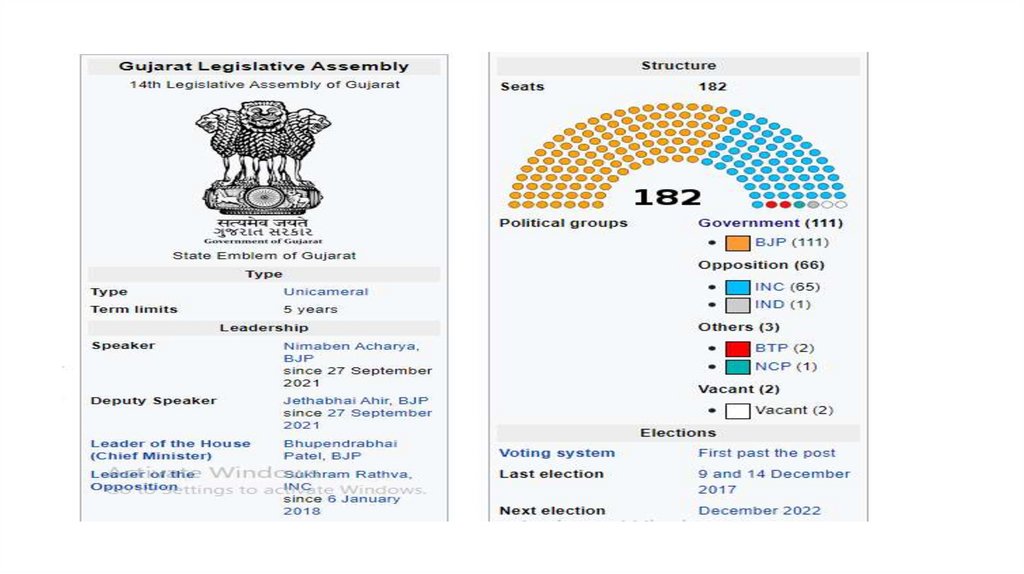
• The present legislative assembly is unicameral, consisting of 182 Members of the
Legislative Assembly (M.L.As). Its term is 5 years, unless sooner dissolved.
4.
• C.R. Patil (Chandrakant Raghunath Patil, sometimes his last name is speltPaatil) is a member of the 17th Lok Sabha of India, elected from Navsari in
Gujarat. In 2019, he won election with a record margin of 689,668 votes.[1] In
2014, won election with a record margin of 5,58,116 votes- the 3rd highest of
votes across entire India.
• He is India's first Member of Parliament to obtain an ISO certification 9001:
2015 for office. The ISO certificate was issued for his office for quality
management system applicable for monitoring and administration of the
government services for the constituency.
• He has played a pivotal role in the development of Surat. Be it policy making
for Textiles and Diamond industries or Infrastructure development in Surat or
development of Surat airport into a fully functioning one with multiple flights
giving air connectivity to Surat with the rest of India and also initiation of
International flights from Surat.
5.
ElectionElections in Gujarat are being conducted since 1962 to elect the members of
the Gujarat Vidhan Sabha and the members of the lower house of the Indian
Parliament, the Lok Sabha. There are 182 Vidhan Sabha constituencies and 26 Lok
Sabha constituencies in the state.
Major Political Parties :The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and the Indian National Congress (INC) are the
most powerful parties in the state. Other parties which have been influential in
the past include Swatantra Party, Praja Socialist Party (PSP), Indian National
Congress (Organisation) (NCO), Janata Party, Janata Dal, Janata Dal
(Gujarat) (JDG), All India Majlis-e-Ittehadul Muslimeen (AIMIM) and Rashtriya
Janata Party (RJP).
6.
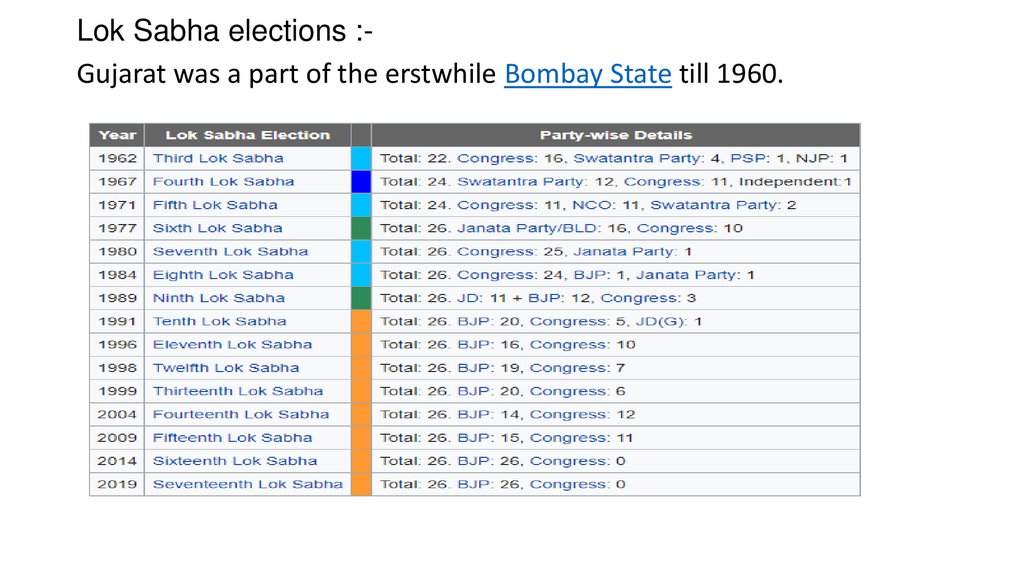
Lok Sabha elections :Gujarat was a part of the erstwhile Bombay State till 1960.7.
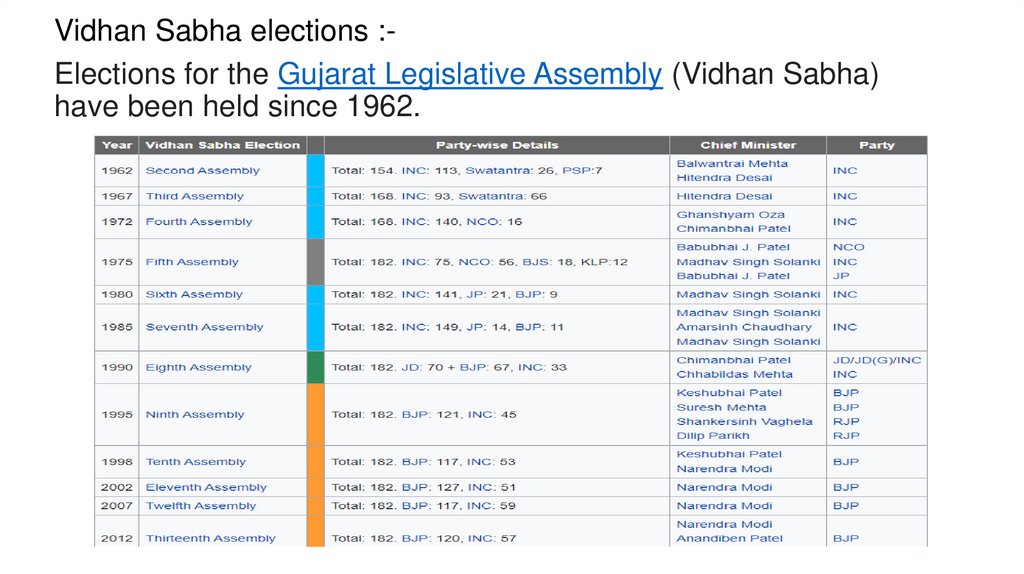
Vidhan Sabha elections :Elections for the Gujarat Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha)have been held since 1962.
8.
Legislative Power• Gujarat Legislative Assembly or Gujarat Vidhan Sabha is
the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Gujarat, in the state
capital Gandhinagar. Presently, 182 members of the Legislative Assembly
are directly elected from single-member constituencies (seats). It has term
of 5 years unless it is dissolved sooner. 13 constituencies are reserved for
scheduled castes and 27 constituencies for scheduled tribes. From its
majority party group or by way of a grand coalition cabinet of its
prominent members, the state's Executive namely the Government of
Gujarat is formed.
9.
10.
Council Of Ministers• The Gujarat Council of Ministers (Gujarati: ગુજરાતનુું મુંત્રીમુંડળ)
exercises executive authority of the Indian State of Gujarat. The
council is chaired by the Chief Minister of Gujarat. The council
serves as the highest decision-making body in the State of Gujarat
and advises the Governor of Gujarat in the exercise of his or her
functions. The Council of Ministers is responsible to the Gujarat
Legislative Assembly.
11.
Types of MinistersThe Gujarat Council of Ministers follows the westminster's model of cabinet.
There are two type of ministers.
1. Cabinet Ministers.
2. Ministers of State.
1.Cabinet Ministers
• Actual power of decisions vests with cabinet ministers. The cabinet is
chaired by the Chief Minister.
2.Ministers of State
• They are also known as Deputy Ministers. They are appointed to assist
cabinet ministers. However, many times, they are given independent charge
of their department. In that case, they enjoy a latitude for decision making
similar to a cabinet minister, with respect to those decisions under the aegis
of their respective departments. However, Ministers of State do not
participate in cabinet meetings.









 law
law








