Similar presentations:
Phylogenetic disorders of respiratory system
1.
A PRESENTATION FORDEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY
CRIMEA STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
SIMFEROPOL, CRIMEA
STUDENT NAME :sheikh sana
GROUP: 191a
GUIDED BY:
ANNA ZHUKOVA ALEXANDROVNA MAM
2.
3.
PHYLOGENETIC DISORDERS OFDIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Disorder which is relating to the evolutionary development
and diversification of a species or group of organisms, or of a
particular feature of an organism.
4.
5.
1.Chrons disease2.Diabetes
3.Panreatic cancer
4.Colon cancer
5.Cystic fibrosis
6. Glucose galactose malabsorption
7.Wilsons disease
8.Zellweger syndrome
9.Gastrointestinal disease
6.
10.Adenomatous polyposis colic syndrome 111.Budd-chiari syndrome 1
12. Antitrypsin deficiency
13. Autoimmune hepatitis
14.Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) ...
15.Gallstones. ...
16.Celiac disese ..
17.Ulcerative Colitis. ...
18.Irritable Bowel Syndrome. ...
19.Hemorrhoids. ...
20.Diverticulitis.
7.
8.
DIABETES* Diabetes is a chronic condition associated with abnormally high levels of sugar (glucose) in the
blood. Insulin produced by the pancreas lowers blood glucose. Absence or insufficient
production of insulin, or an inability of the body to properly use insulin causes diabetes.
9.
Cancer that begins in the organ lying behind the lower part of the stomach (pancreas).Thepancreas secretes enzymes that aid digestion and hormones that help regulate the
metabolism of sugars. This type of cancer is often detected late, spreads rapidly, and has a
poor prognosis.
about 5 to 10 percent of pancreatic cancers are hereditary. This means that for every 20
people with pancreatic cancer, one or two likely have an inherited mutation that increased
their risk for developing the disease.
10.
11.
Budd–Chiari syndrome is a very rare condition, affecting one in a million adults. The conditionis caused by occlusion of the hepatic veins that drain the liver. It presents with the classical
triad of abdominal pain, ascites, and liver enlargement.
Budd- Chiari syndrome is caused by blood clots that completely or partially block blood flow
from the liver. The blockage may occur anywhere from the small and large veins that carry
blood from the liver (hepatic veins) to the inferior vena cava.
12.
13.
Colorectar cancer: Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer,is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine).
A cancer is the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the
body. In general, colon cancer begins when healthy cells in the colon develop changes (mutations) in
their DNA. As the cells accumulate, they form a tumor. With time, the cancer cells can grow to invade
and destroy normal tissue nearb.
14.
ADENOMATOUS POLYPOSIS COLISYNDROME
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an inherited disorder characterized by cancer of the large
intestine (colon) and rectum.
People with the classic type of familial adenomatous polyposis may begin to develop multiple
noncancerous (benign) growths (polyps) in the colon as early as their teenage years.
Zellweger syndrome is a rare congenital disorder characterized by the reduction or absence of
functional peroxisomes in the cells of an individual.[1] It is one of a family of disorders called Zellweger
spectrum disorders which are leukodystrophies. Zellweger syndrome is named after Hans
Zellweger (1909–1990), a Swiss-American pediatrician, a professor of pediatrics and genetics at
the University of Iowa who researched this disorder.
15.
Zellweger syndrome is a rare congenital disorder characterized by the reduction or absenceof functional peroxisomes in the cells of an individual.[1] It is one of a family of disorders
called Zellweger spectrum disorders which are leukodystrophies. Zellweger syndrome is
named after Hans Zellweger (1909–1990), a Swiss-American pediatrician, a professor
of pediatrics and genetics at the University of Iowa who researched this disorder.[2][3]
16.
Glucose-galactose malabsorptionGlucose-galactose malabsorption is a rare condition in which the cells lining the intestine
cannot take in the sugars glucose and galactose, which prevents proper digestion of these
molecules and larger molecules made from them. Glucose and galactose are called simple
sugars, or monosaccharides.
17.
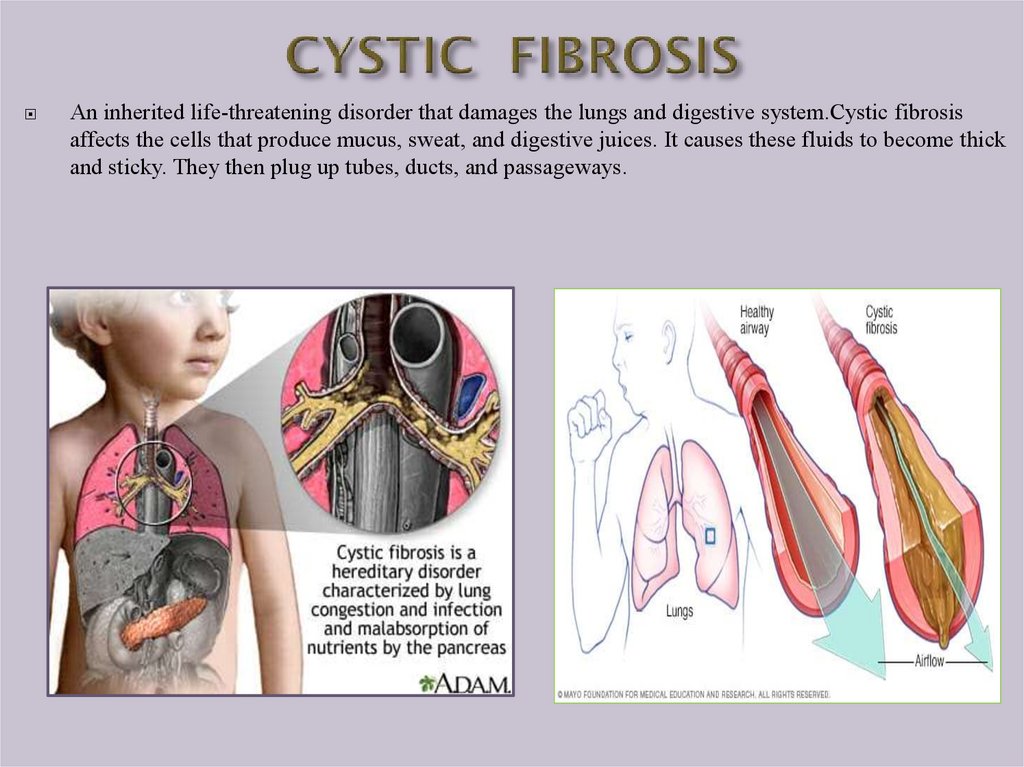
An inherited life-threatening disorder that damages the lungs and digestive system.Cystic fibrosisaffects the cells that produce mucus, sweat, and digestive juices. It causes these fluids to become thick
and sticky. They then plug up tubes, ducts, and passageways.
18.
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD)is a genetic disorder that may result in lung
disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is
typically between 20 and 50 years old. This may
result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an
increased risk of lung infections.
the signs and symptoms most people experience
with this deficiency are:Chronic
cough.Emphysema.COPD.Liver
failure.Hepatitis.Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
Jaundice. Cirrhosis.
19.
A digestive disease in which stomach acid or bile irritates the food pipe lining. This is achronic disease that occurs when stomach acid or bile flows into the food pipe and irritates
the lining. Acid reflux and heartburn more than twice a week may indicate GERD.
Symptoms include burning pain in the chest that usually occurs after eating and worsens
when lying down.
20.
Celiac disease is hereditary, meaning that it runs in families. People with a first-degree relative withceliac disease (parent, child, sibling) have a 1 in 10 risk of developing celiac disease.Celiac disease can
develop at any age after people start eating foods or medicines that contain gluten. Left untreated, celiac
disease can lead to additional serious health problems
Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disease that occurs in genetically predisposed people where the
ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. It is estimated to affect 1 in 100 people
worldwide. Two and one-half million Americans are undiagnosed and are at risk for long-term health
complications.
21.
HEMORRHOIDSHemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower
rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids can develop inside the rectum (internal
hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids).Nearly three out of
four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes,
but often the cause is unknown.
22.
Diverticula are small, bulging pouches that can form in the lining of your digestive system. Theyare found most often in the lower part of the large intestine (colon). Diverticula are common,
especially after age 40, and seldom cause problems.The presence of diverticula is known as
diverticulosis (die-vur-tik-yoo-LOE-sis). When one or more of the pouches become inflamed, and
in some cases infected, that condition is known as diverticulitis (die-vur-tik-yoo-LIE-tis).
Diverticulitis can cause severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea and a marked change in your bowel
habits.






















 medicine
medicine