Similar presentations:
Children health insurence program
1.
Children health insurenceprogram
PRAJAPATI SHAILESH
17LL1A
2.
Introduction Of CHIPThe Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) –
formerly known as the State Children's Health
Insurance Program (SCHIP) – is a program
administered by the United States Department of
Health and Human Services that
provides matching funds to states for health
insurance to families with children.
The program was designed to cover uninsured
children in families with incomes that are modest
but too high to qualify for Medicaid.
3.
History Of CHIPThe Children's Health Insurance Program grew out of years of
work in the U.S.congress to improve Americans' health
coverage. Almost a decade prior, the U.S. Bipartisan
Commission on Comprehensive Health Care was formed in
1989 and charged with recommending “legislative action to
ensure coverage for all Americans.”
The Commission, renamed the Pepper Commission
in honour of its creator and first chair Representative
Claude Pepper (D-Fla.), laid out a blueprint to
achieve universal coverage.
CHIP covered 7.6 million children during federal
fiscal year 2010, and every state has an approved
plan.
4.
Goals Of CHIPSafety: All children have the right to live in an
environment free from abuse and neglect.
Permanency: Children need a family and a
permanent place to call home.
Child and Family Well-Being: Children deserve
nurturing environments in which their physical,
emotional, educational, and social needs are
met.
5.
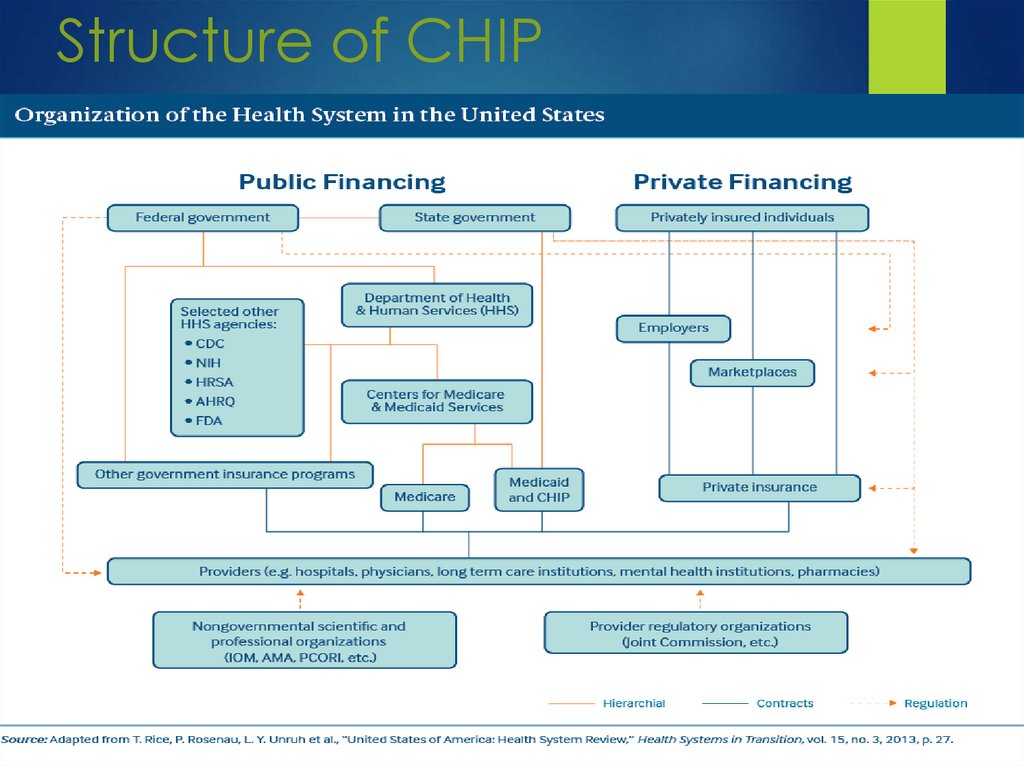
Structure of CHIP6.
CHIP builds on Medicaid’s success providing healthcoverage to children since 1965. States can use their federal
CHIP funds to finance coverage for children whose family
incomes are too high to qualify for Medicaid under the rules
the state had in place as of June 1997.
States may opt to use CHIP funds to expand Medicaid for
children beyond the June 1997 levels, cover children
through a separate CHIP program, or combine the two
approaches. As of January 1 2017, 15 states (including the
District of Columbia) opted to use CHIP funds to expand
their Medicaid programs. In the remaining 36 states, map
here, CHIP funds are used to run a combination or separate
health insurance program.
7.
FINANCE OF CHIPFederal and state governments jointly finance
CHIP, although the federal government assumes
a larger share of the financing with an enhanced
federal matching rate ranging from 65 to 82
percent, an average of 15 percentage points
higher than Medicaid’s matching rate.
This capped funding is distributed through statespecific allotments established by a statutory
formula that accounts for the state’s actual use of
CHIP funds and is adjusted for health care
inflation and child population growth.
8.
States facing funding shortfalls can obtain additionalfunding through a child enrollment contingency fund
and allotment increases are available for states with
approved plans to expand eligibility or benefits.
9.
ELIGIBILITYChildren :States have broad flexibility to set their CHIP
income eligibility levels. Most states cover children up to
or above 200 percent of the federal poverty level (FPL);
the median across states is 255 FPL. States expanding
coverage up to 300 percent of the FPL receive an
enhanced federal match rate. States opting to expand
coverage to children above 300 percent on or after FY
2009 receive the regular Medicaid match for their
coverage
Age :States may cover children up to 19 years of age.
10.
Pregnant Women: CHIPRA (2009) allowed a state to amendits CHIP plan to cover pregnant women with CHIP funds.
States using their CHIP plan to cover pregnant women must
cover up to at least 185 percent of FPL. The income eligibility
level must also be equal to or greater than income limits in
Medicaid. This coverage is eligible for the enhanced federal
match. Currently.
Parents and Other Adults: CHIP law does not allow
coverage of parents and adults. Although a handful of
states previously obtained waivers from the federal
government to cover uninsured adults and parents, these
waivers expired and are no longer allowed in CHIP. States
may be able to receive funding outside of CHIP to continue
coverage for those already enrolled.
11.
RELATION WITH INDIACHIP has a partnership with many indian private
and goverment companys which list is followed
below :
HDFC health suraksha.
Apollo munich optima restore family.
Star family health optima.
Oriantle insurance happy family floater policy.
SBI life smart health insurance.











 law
law pedagogy
pedagogy








