Similar presentations:
Common carp
1.
Penza Agro-industrial CollegePresentation
«Common carp»
Prepared by a 3d year student
Group 18 Icht
Viktorija Borisova
2.
The common carp or European carp (Cyprinus carpio) is a widespreadfreshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers
in Europe and Asia. The native wild populations are considered vulnerable to
extinction by the International Union for Conservation of Nature , but the
species has also been domesticated and introduced into environments
worldwide, and is often considered a destructive invasive species, being included
in the list of the world's 100 worst invasive species. It gives its name to
the carp family, Cyprinidae.
3.
TaxonomyThere are three subspecies:
1 - C. c. carpio is native to
much of Europe (notably
the Danube and Volga Rivers);
2 - C. c. yilmaz (Deniz carp) is
from Anatolian Turkey (notably
around Çorum);
3 - C. c. haematopterus (Amur
carp).
4.
HistoryThe common carp is native to Europe and Asia, and has been introduced to
every part of the world except the poles. They are the third most frequently
introduced (fish) species worldwide, and their history as a farmed fish dates
back to Roman times. The original common carp was found in the inland delta
of the Danube River about 2000 years ago, and was torpedo-shaped and goldenyellow in colour. It had two pairs of barbels and a mesh-like scale pattern. it
was later maintained in large, specially built ponds by the Romans in southcentral Europe.
The common carp's native range also extends to the Black Sea, Caspian
Sea and Aral Sea.
5.
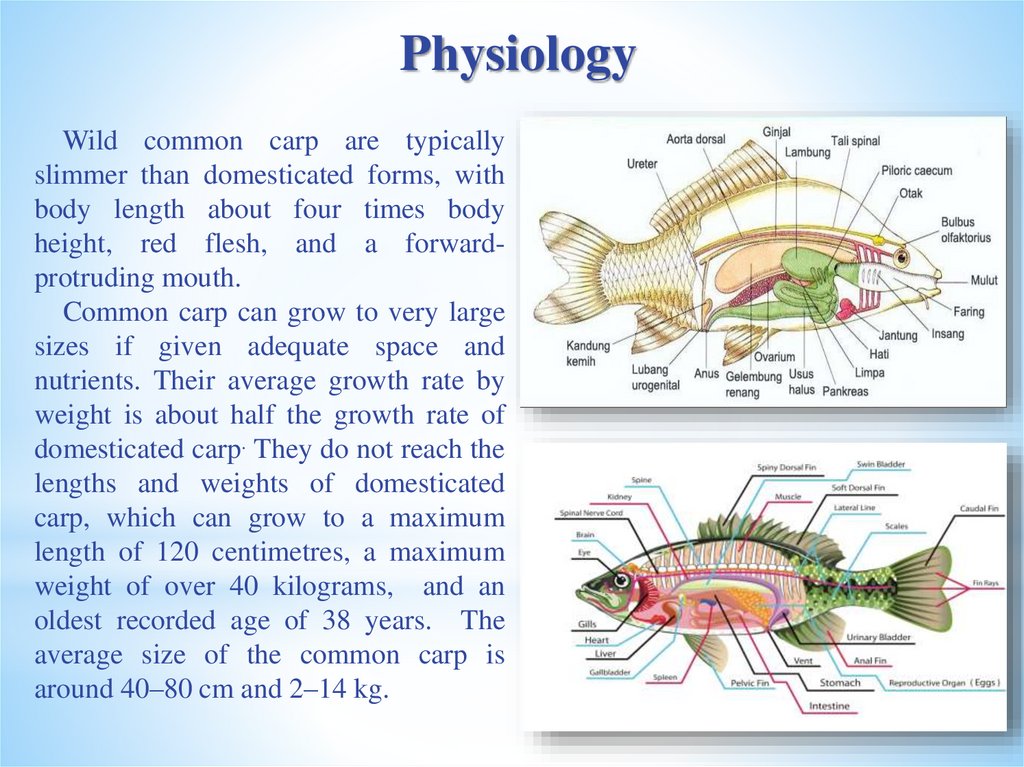
PhysiologyWild common carp are typically
slimmer than domesticated forms, with
body length about four times body
height, red flesh, and a forwardprotruding mouth.
Common carp can grow to very large
sizes if given adequate space and
nutrients. Their average growth rate by
weight is about half the growth rate of
domesticated carp. They do not reach the
lengths and weights of domesticated
carp, which can grow to a maximum
length of 120 centimetres, a maximum
weight of over 40 kilograms, and an
oldest recorded age of 38 years. The
average size of the common carp is
around 40–80 cm and 2–14 kg.
6.
HabitatAlthough tolerant of most
conditions, common carp prefer large
bodies of slow or standing water and
soft, vegetative sediments. As
schooling fish, they prefer to be in
groups of five or more. They
naturally live in temperate climates
in fresh or slightly brackish water
with a temperatures of 3 to 35 °C.
The ideal temperature is 23 to 30 °C,
with spawning beginning at 17 to
18 °C; they easily survive winter in a
frozen-over pond, as long as some
free water remains below the ice.
Carp are able to tolerate water with
very low oxygen levels, by gulping
air at the surface.
7.
DietCommon carp are omnivorous.
They can eat a herbivorous diet of
aquatic plants, but prefer to
scavenge the bottom
for insects, crustaceans (including
zooplankton), crawfish,
and benthic worms.
8.
ReproductionAn egg-layer, a typical adult female can
lay 300,000 eggs in a single spawn.
Although carp typically spawn in the
spring, in response to rising water
temperatures and rainfall, carp can spawn
multiple times in a season.
In commercial operations, spawning is
often stimulated using a process called
hypophysation, where lyophilized pituitary
extract is injected into the fish.
9.
Introduction into other habitatsCommon carp have been
introduced to most continents
and some 59 countries. In
absence of natural predators
or commercial fishing they may
extensively
alter
their
environments due to their
reproductive rate and their
feeding habit of grubbing
through bottom sediments for
food. In feeding, they may
destroy, uproot, disturb and eat
submerged vegetation, causing
serious damage to native duck,
such as canvasbacks, and fish
populations.
10.
Common carp aquacultureCommon carp contributed
around 4.67 million tons on
a global scale during 2019–
2020, roughly accounting for
7.4% of the total global
inland fisheries production.
In Europe, common carp
contributed 1.8% of the
total
inland
fisheries
production during 2019–
2020. It is a major farmed
species
in
European
freshwater aquaculture with
production
localized
in
central
and
eastern
European countries.
11.
Common carp aquaculture2.5 thousand tons of
marketable fish were grown
in the Penza region in 2020.
According to this indicator,
the region took the second
place in the Volga Federal
District.












 biology
biology