Similar presentations:
Algebra Reference
1. Chapter R
Algebra ReferenceCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
2. R.1
PolynomialsCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
3.
R- 3© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
4. Your Turn 1
Perform the operation 3( x 2 4 x 5) 4(3x 2 5 x 7).Solution: Multiply each polynomial by the coefficient in front
of the polynomial and then combine like terms.
3x 2 12 x 15 12 x 2 20 x 28
9 x 2 8 x 13
R- 4
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
5. Your Turn 2
Perform the operation (3 y 2)(4 y 2 2 y 5).Solution : Using the Distributive property yields
3 y(4 y 2 2 y 5) 2(4 y 2 2 y 5)
3 y(4 y 2 ) 3 y( 2 y) 3 y( 5) 2(4 y 2 ) 2( 2 y) 2( 5)
12 y3 6 y 2 15 y 8 y 2 4 y 10
12 y 3 2 y 2 19 y 10.
R- 5
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
6. R.2
FactoringCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
7. Your Turn 1
Factor out the greatest common factor in 4 z 4 4 z 3 18z 2 .Solution: Each of these terms is divisible by 2z2.
4 z 4 4 z 3 18 z 2 2 z 2 (2 z 2 ) 2 z 2 (2 z ) 2 z 2 (9)
2 z 2 (2 z 2 2 z 9)
R- 7
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
8.
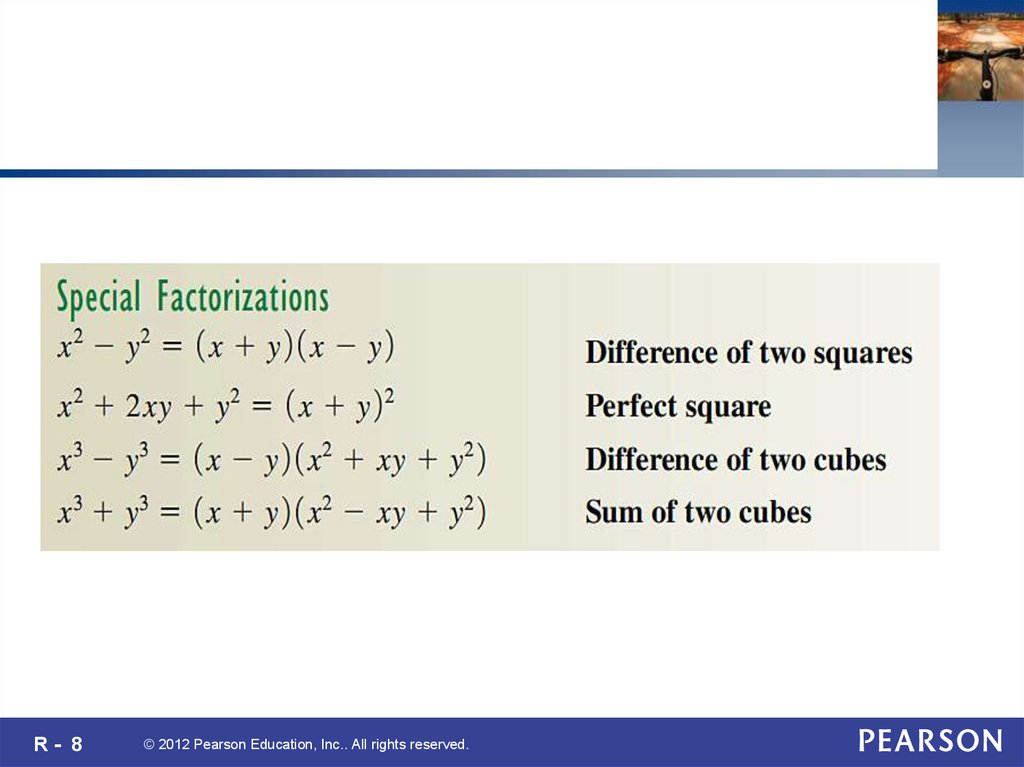
R- 8© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
9. Example 4
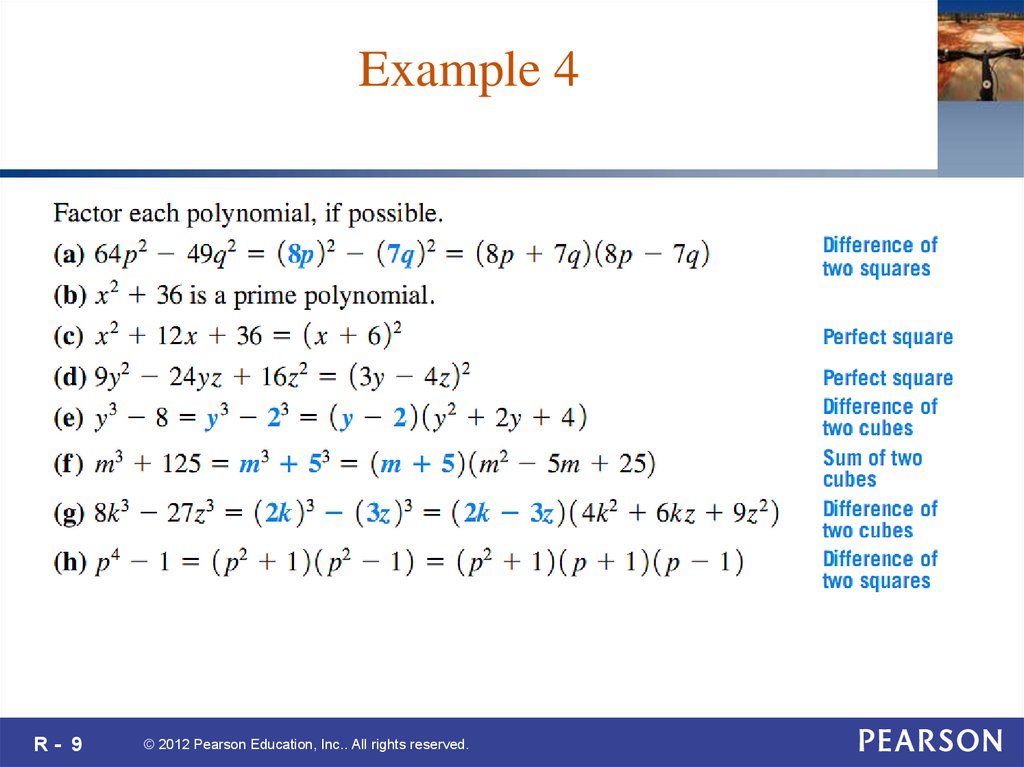
R- 9© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
10. R.3
Rational ExpressionsCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
11.
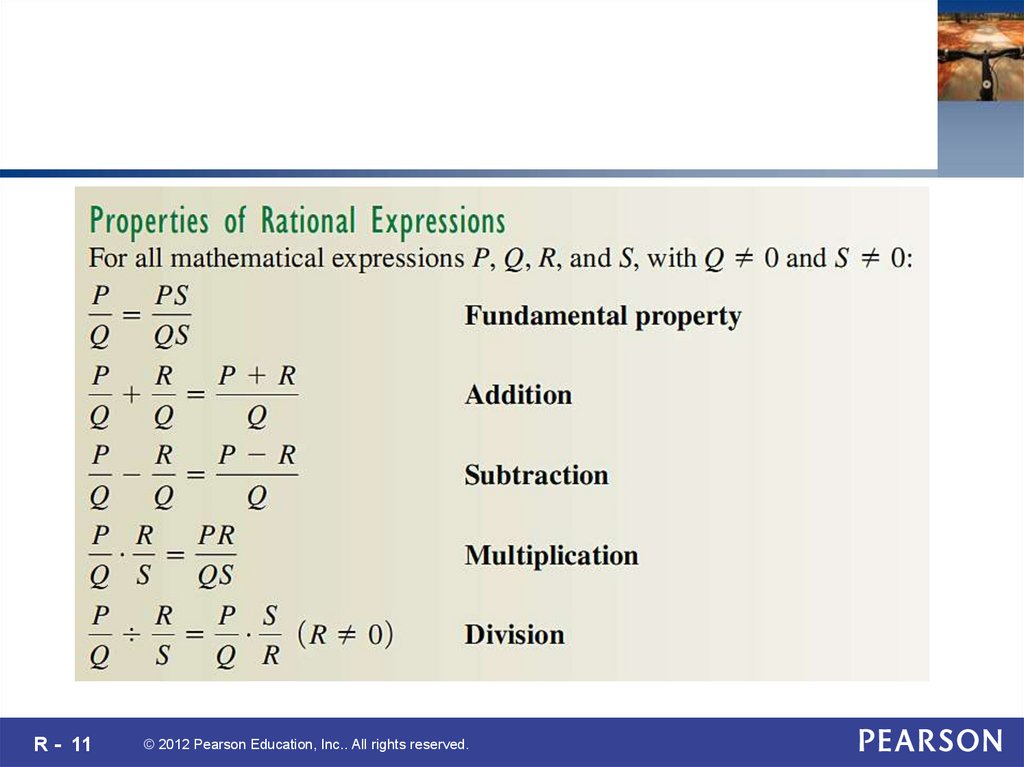
R - 11© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
12. Your Turn 1
z 2 5z 6Write in lowest terms
.
2
2z 7z 3
Solution: Factor both numerator and denominator in order to
identify any common factors.
( z 2)( z 3)
(2 z 1)( z 3)
( z 2)
(2 z 1)
The answer can not be further simplified.
R - 12
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
13. Your Turn 2
z 2 5z 6 2 z 2 z 1Perform the following operations 2
2
.
2 z 5z 3 z 2 z 3
Solution: Factor where possible.
( z 2)( z 3) (2 z 1)( z 1)
(2 z 1)( z 3) ( z 3)( z 1)
( z 2)
( z 3)
R - 13
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
14. R.4
EquationsCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
15.
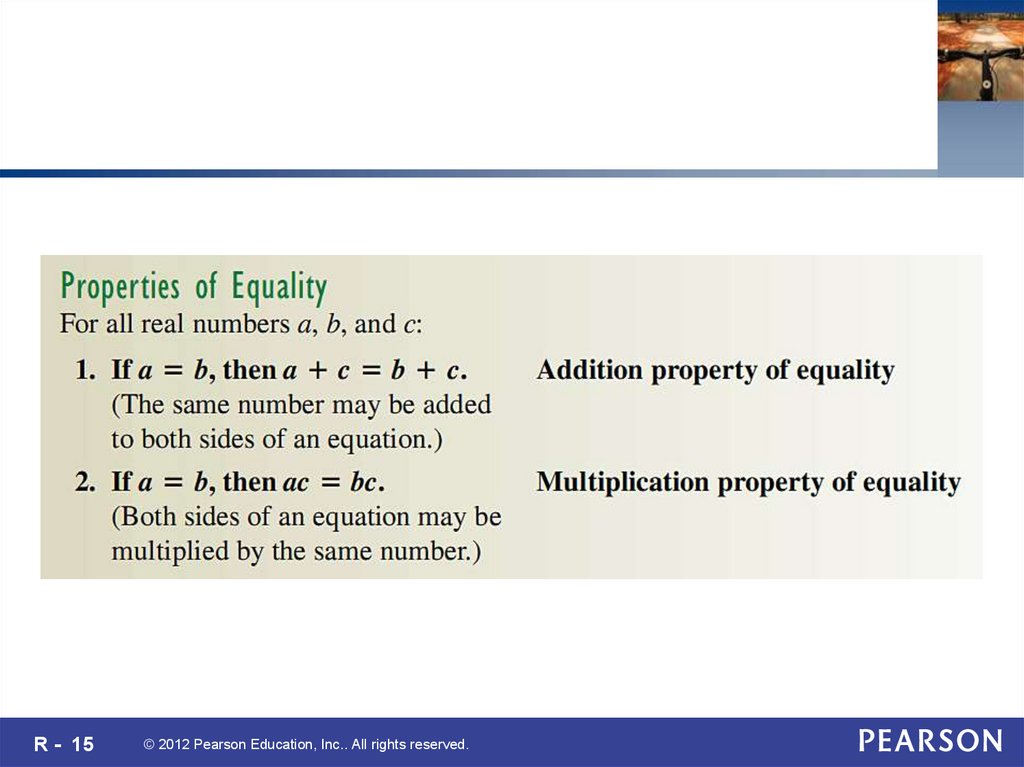
R - 15© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
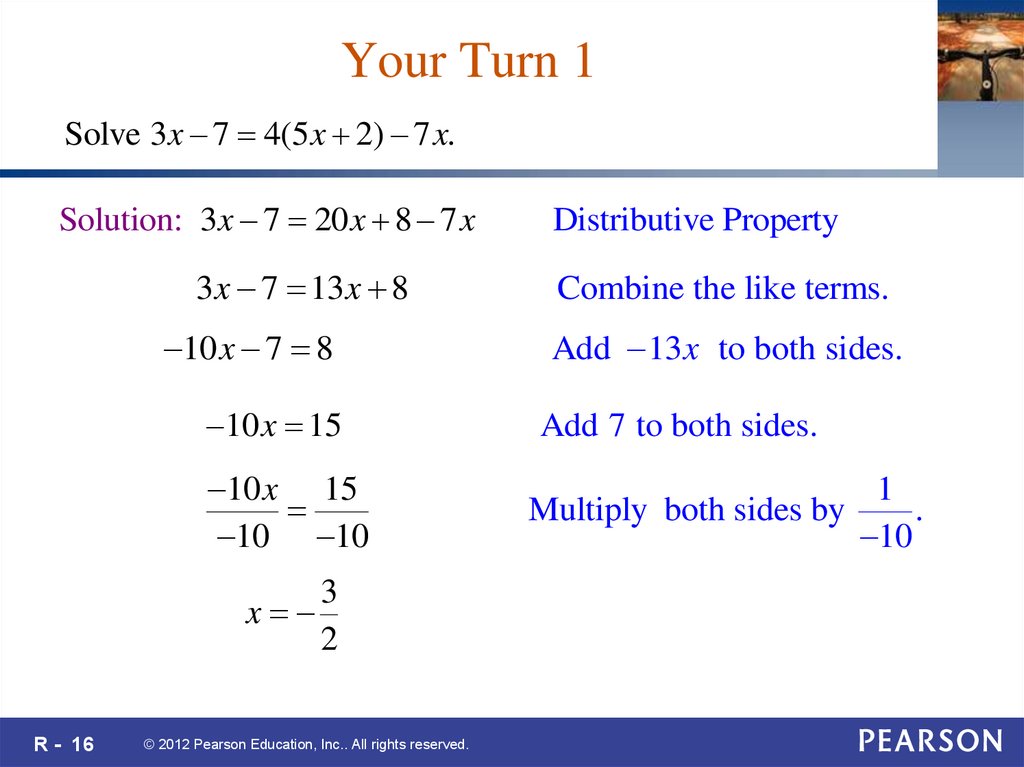
16. Your Turn 1
Solve 3x 7 4(5 x 2) 7 x.Solution: 3x 7 20 x 8 7 x
3 x 7 13 x 8
10 x 7 8
Combine the like terms.
Add 13x to both sides.
10 x 15
Add 7 to both sides.
10 x 15
10 10
1
Multiply both sides by
.
10
3
x
2
R - 16
Distributive Property
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
17.
R - 17© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
18. Your Turn 2
Solve2m2 7m 15.
Solution: First write the equation in standard form.
2m2 7m 15 0
Now factor 2m2 7m 15 to get
(2m 3)(m 5) 0.
By the zero-factor property, the product (2m 3)(m 5)
can equal 0 if and only if
2m 3 0
or
m 5 0.
Solve each of these equations separately to find that the
3
solutions are
and 5.
2
R - 18
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
19.
R - 19© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
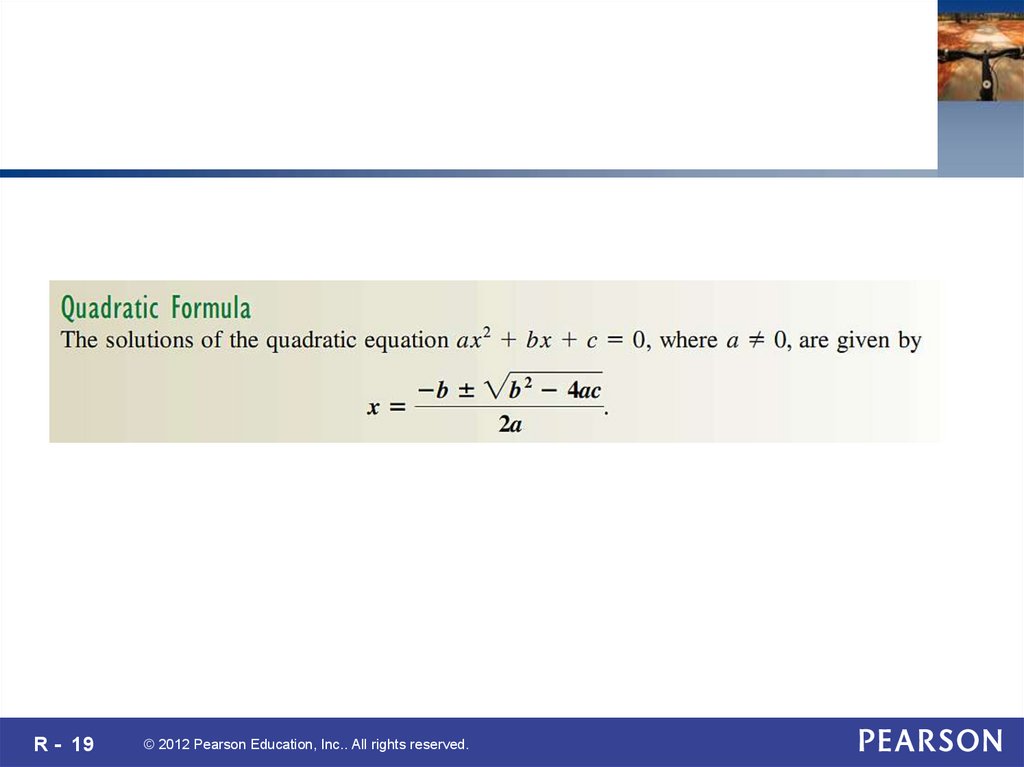
20. Your Turn 3
Solve z 2 6 8 z.Solution: First, add 8 z on both sides of the equal sign in order
to get the equation in standard form.
z 2 8 z 6 0.
Now identify the letters a, b, and c.
Here, a 1, b 8, and c 6.
Substitute these numbers into the quadratic formula.
( 8) ( 8) 2 4(1)(6)
x
2(1)
continued
R - 20
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
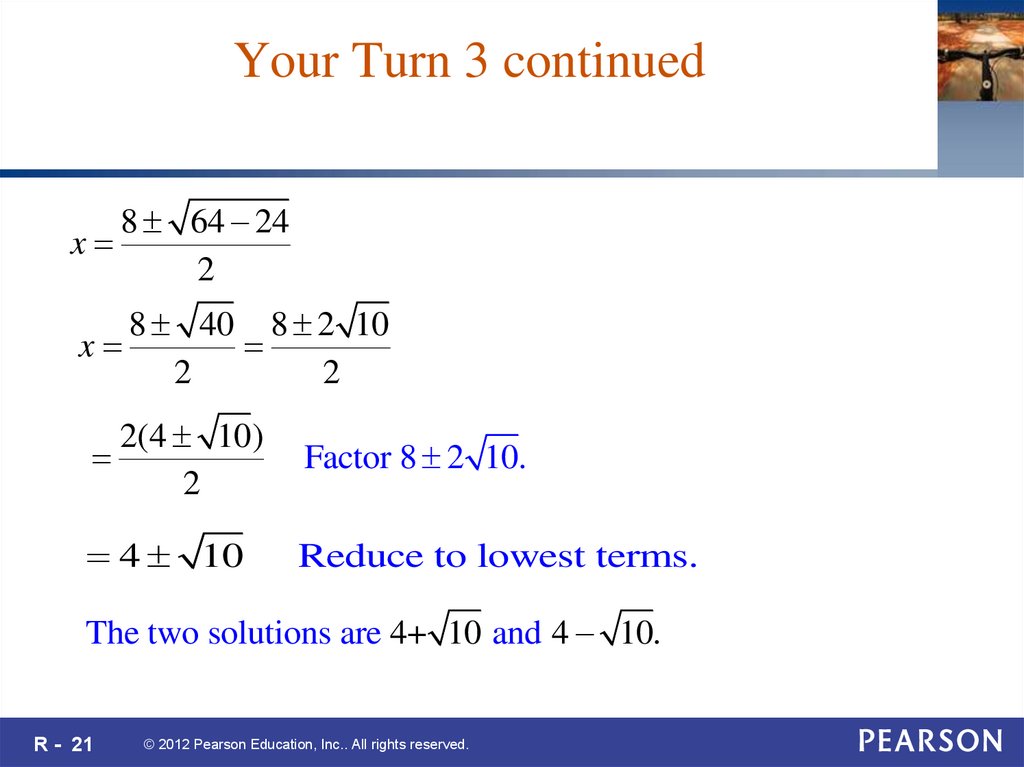
21. Your Turn 3 continued
x8 64 24
2
x
8 40 8 2 10
2
2
2(4 10)
2
Factor 8 2 10.
4 10
Reduce to lowest terms.
The two solutions are 4+ 10 and 4 10.
R - 21
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
22. Your Turn 4
12
1
Solve 2
.
x 4 x 2 x
Solution: Factor x 2 4 as ( x 2)( x 2).
1
2
1
( x 2)( x 2) x 2 x
The least common denominator for all the fractions
is x( x 2)( x 2). Multiplying both sides by x( x 2)( x 2)
gives the following:
1
2
1
x( x 2)( x 2)
x( x 2)( x 2)
x
( x 2)( x 2) x 2
continued
R - 22
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
23. Your Turn 4 continued
x 2 x( x 2) ( x 2)( x 2)x 2x2 4x x2 2x 2x 4
Distributive property
2 x2 5x x2 4
Add x 2 and 4, Rearrange terms.
x2 5x 4 0
( x 1)( x 4) 0
x 1 0
or
x 4 0
x 1
x 4
Verify that the solutions are 1 and 4.
R - 23
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
24. R.6
ExponentsCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
25.
R - 25© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
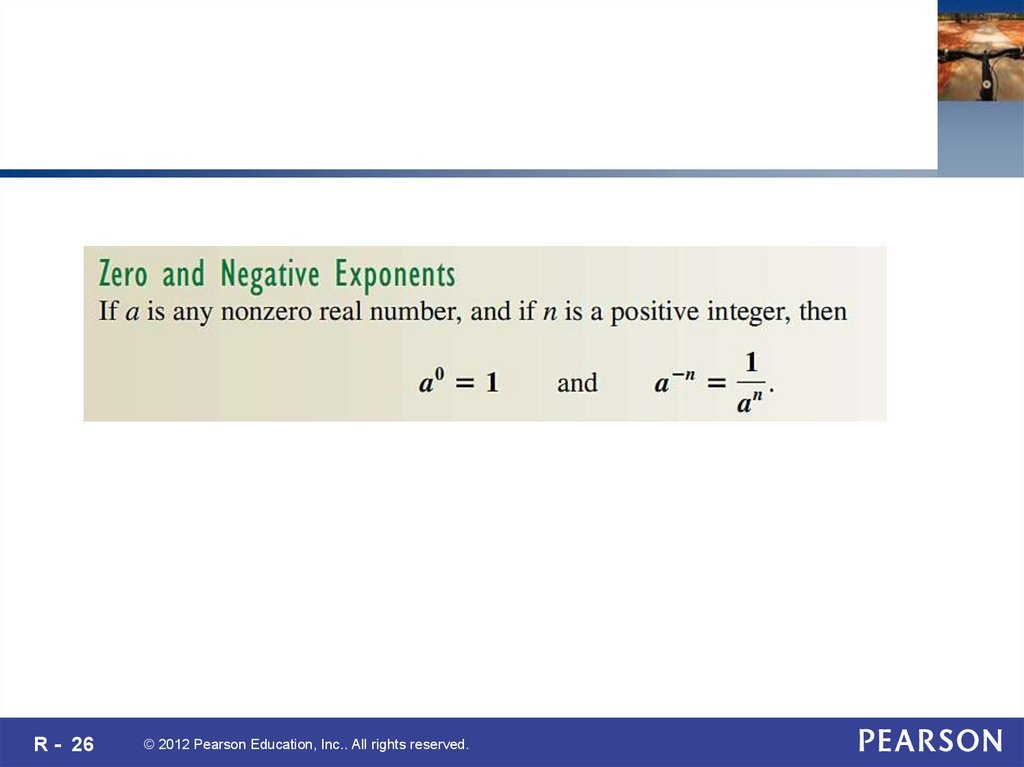
26.
R - 26© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
27.
R - 27© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
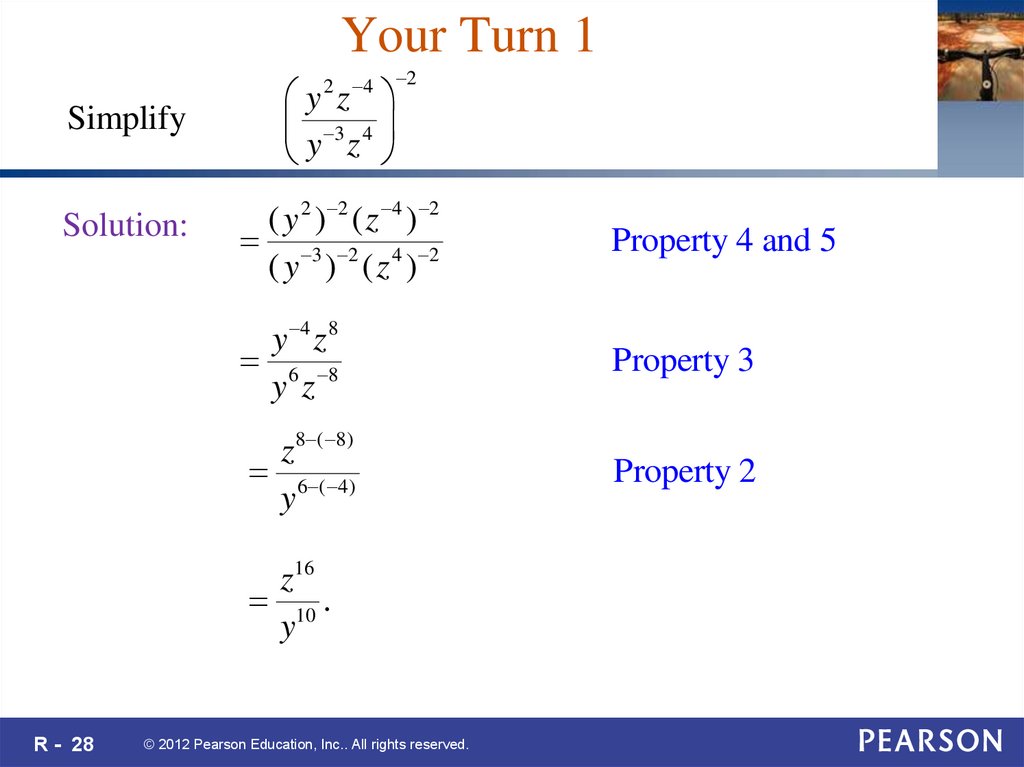
28. Your Turn 1
2 42
Simplify
y z
y 3 z 4
Solution:
( y 2 ) 2 ( z 4 ) 2
3 2 4 2
( y ) (z )
Property 4 and 5
y 4 z 8
6 8
y z
Property 3
z 8 ( 8)
6 ( 4)
y
Property 2
z16
10 .
y
R - 28
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
29.
R - 29© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
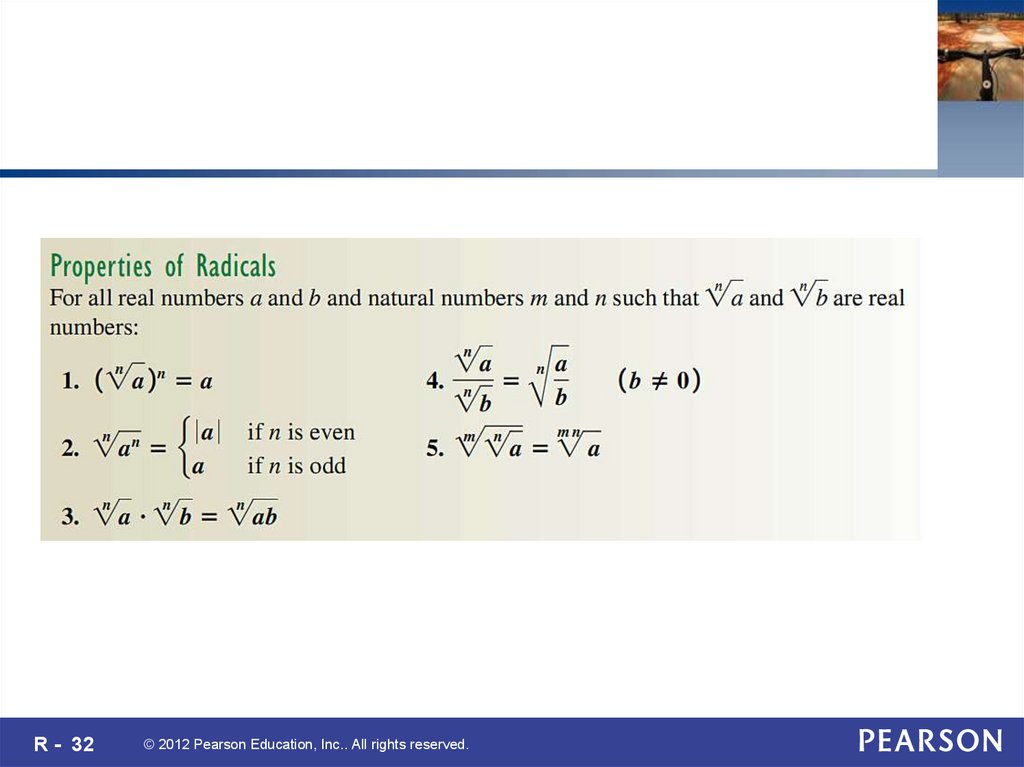
30. R.7
RadicalsCopyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
31.
R - 31© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
32.
R - 32© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
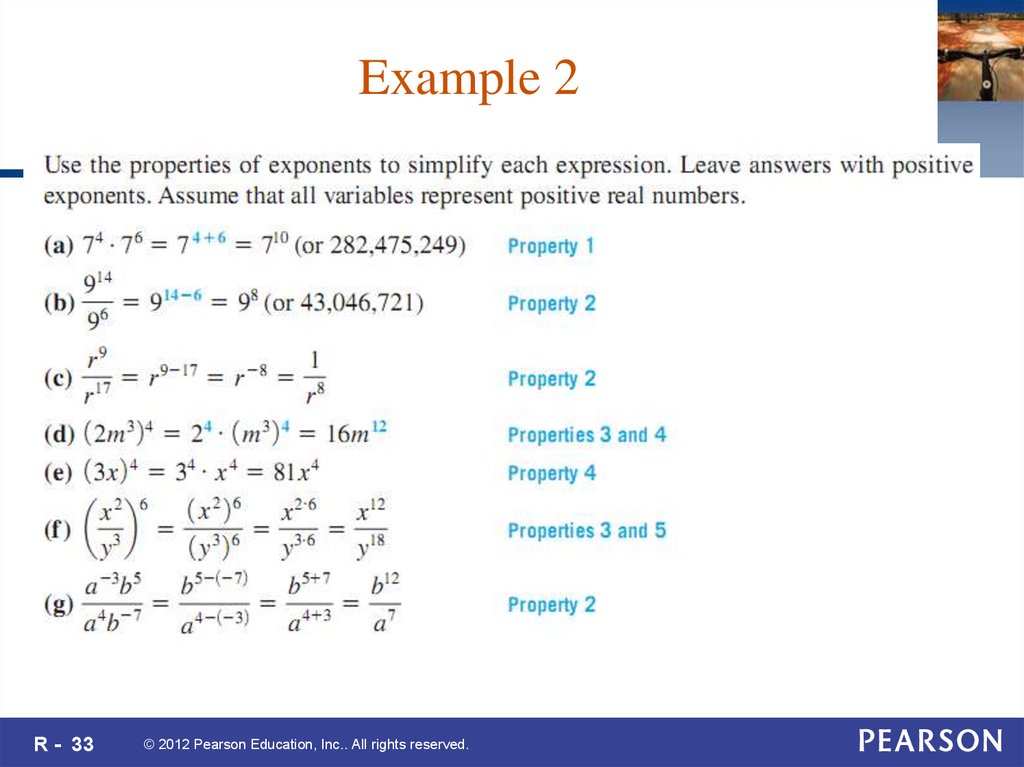
33. Example 2
R - 33© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
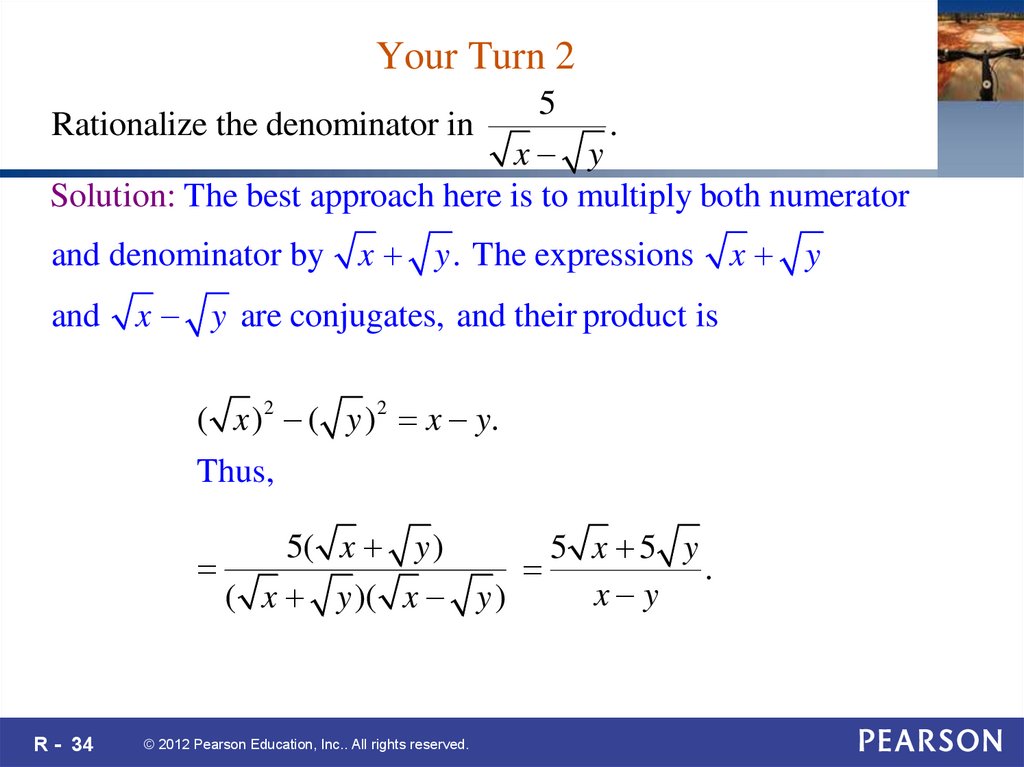
34. Your Turn 2
5Rationalize the denominator in
.
x y
Solution: The best approach here is to multiply both numerator
and denominator by
and
x y . The expressions
x y are conjugates, and their product is
( x ) 2 ( y ) 2 x y.
Thus,
5( x y )
5 x 5 y
.
x y
( x y )( x y )
R - 34
© 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.. All rights reserved.
x y






















 mathematics
mathematics








