Similar presentations:
Marketing for Hospitality and Tourism. The Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning. Chapter 3
1.
Marketing for Hospitality and TourismKotler, Bowen and Makens
The Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning
Chapter 3
2.
Learning Objectives1. Explain company-wide strategic planning.
2. Understand the concepts of stakeholders, processes,
resources, and organization as they relate to a highperforming business.
3. Explain the four planning activities of corporate strategic
planning.
4. Understand the processes involved in defining a company’s
mission and setting goals and objectives.
5. Discuss how to design business portfolios and growth
strategies.
6. Explain the steps involved in the business strategy planning
process.
3.
Characteristics of a HighPerformance BusinessStakeholders
Processes
Resources
Organization
4.
Stakeholders• Customers
• Employees
• Suppliers
• Communities where businesses are
located.
A business must at least strive to satisfy the minimum expectations of
each
stakeholder group just mentioned.
5.
Process• Company work is traditionally carried on by departments. However,
departmental organization poses some problems. Departments
typically operate to
maximize their own objectives, not necessarily the company’s. There
is usually less-than ideal cooperation. Work is slowed down and plans
often are altered as they pass through departments.
• Ex: Las Vegas Hillton (Market segment accounting)
6.
This hotel wanted answers to the following questions1. What is the relative profitability of the gaming guest? The
premium-gaming
guest? The tour and travel guest?
2. How many room nights can each segment fill a year?
3. How much money should be spent to attract each
segment?
4. How should rooms be priced for each segment?
5. How should these rooms be allocated to the segments
during critical periods of
the year?
7.
Resources• To carry out processes, a company needs such resources as
personnel, materials,
machines, and information. Traditionally, companies sought to own
and control
most of the resources that entered the business. Now that is
changing.
Ex: Outsourcing
8.
• Strategic Analysis: Questions That Generate Creative Ideas1. How can this firm take advantage of changes that are expected to occur in
society?
2. How can this firm use its relationships with customers to maximize its position in
existing
or future businesses?
3. Are there any stakeholders that should be seriously considered for partnerships?
4. Does the firm possess any resources or capabilities that are likely to lead to
competitive
advantage?
5. Are there any resources or capabilities the firm should consider developing to
achieve
competitive advantage?
6. Can the firm form joint ventures or other alliances with competitors or other
stakeholders
to acquire valuable knowledge, skills, or other resources?
7. Are there any resources or capabilities the firm does not possess, the absence of
which
might put it at a competitive disadvantage?
8. Are there any looming threats in the broad environment that the firm should
consider in
developing its strategy?
9.
Organization• The organizational side of a company consists of its structure,
policies, and culture, all of which tend to become dysfunctional in a
rapidly changing company.
Although structure and policies can be changed, the company is the
hardest to
change. Companies must work hard to align their organization’s
structure, policies,
and culture to the changing requirements of business strategy
10.
Corporate Strategic Planning: DefiningMarketing’s Role
11.
Defining the Corporate Mission• A hospitality organization exists to accomplish something
• According to Peter Drucker, ask:
• What is our business?
• Who is the customer?
• What do customers value?
• What should our business be?
12.
Developing Growth StrategiesMarket
Concentration
(penetration)
Strategy
Diversification
Growth
Market
Development
Strategy
Integrative
Growth
Product
Development
13.
Ansoff product-market expansion grid14.
Diversification GrowthConcentric
Diversification
Conglomerate
Diversification
Horizontal
Diversification
15.
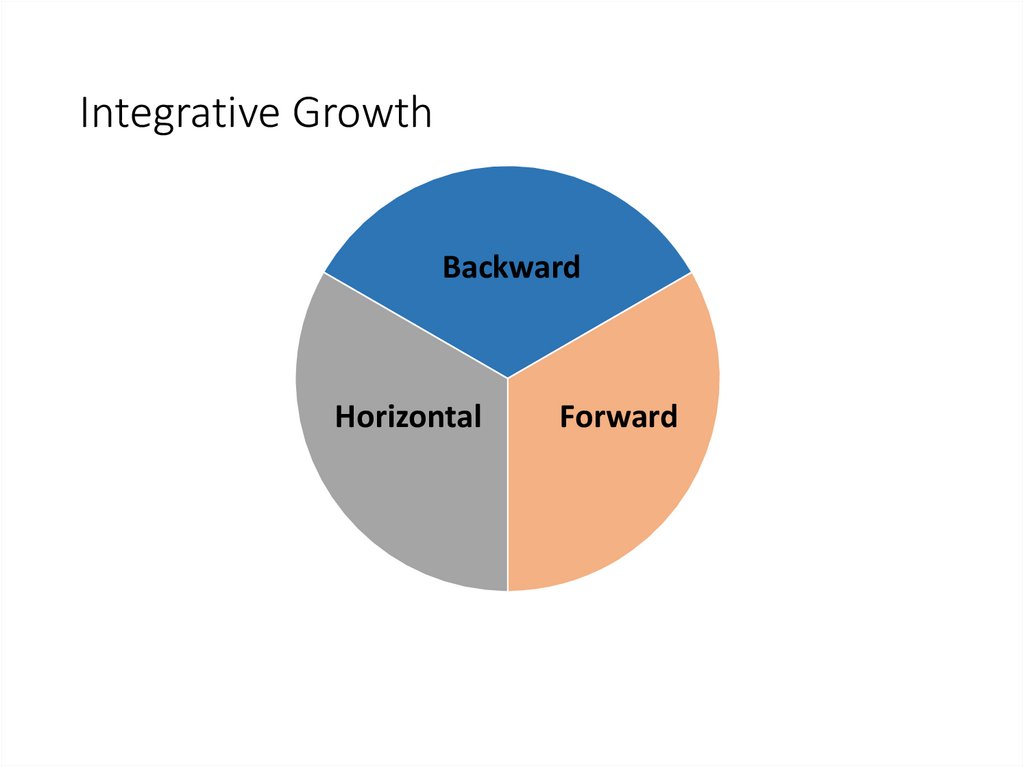
Integrative GrowthBackward
Horizontal
Forward
16.
Customer-Driven Marketing StrategyMarket
Segmentation
Market
Targeting
Market
Differentiation
Market
Positioning
17.
18.
19.
20.
Benefit segmentation21.
22.
What can you say about it?23.
24.
Developing an Integrated Marketing Mix4 Ps
4 Cs
Product
Customer Solution
Price
Customer Cost
Place
Convenience
Promotion
Communication
25.
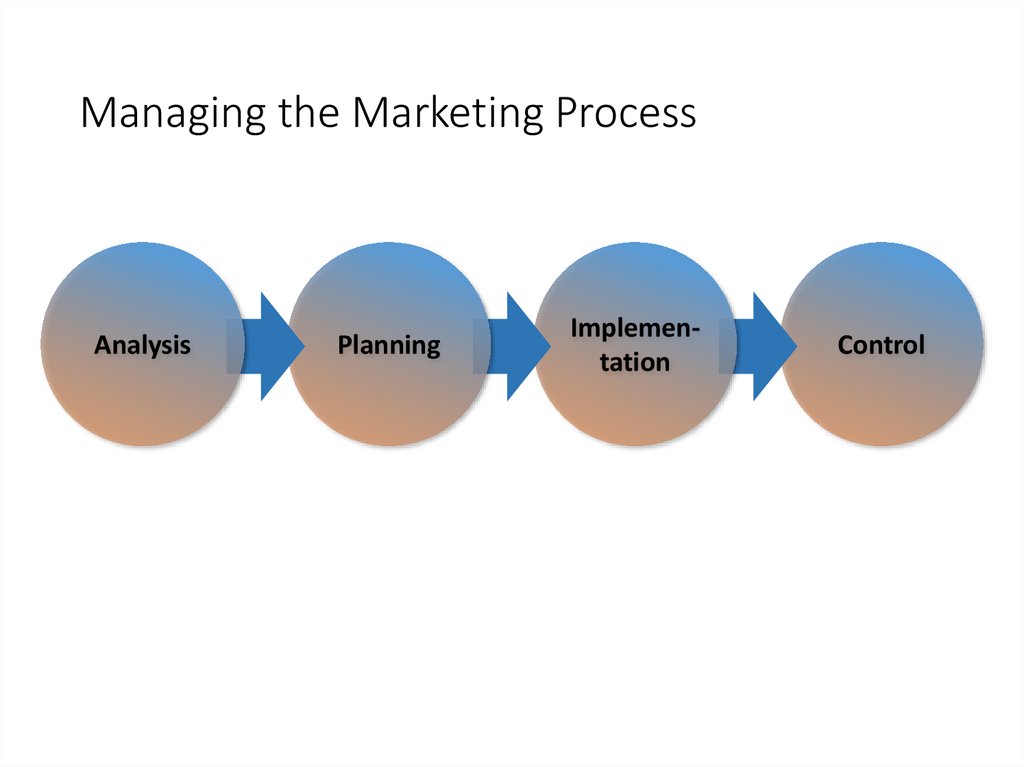
Managing the Marketing ProcessAnalysis
Planning
Implementation
Control
26.
SWOT AnalysisInternal Environmental Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
External Environmental Analysis
Opportunities
Threats
27.
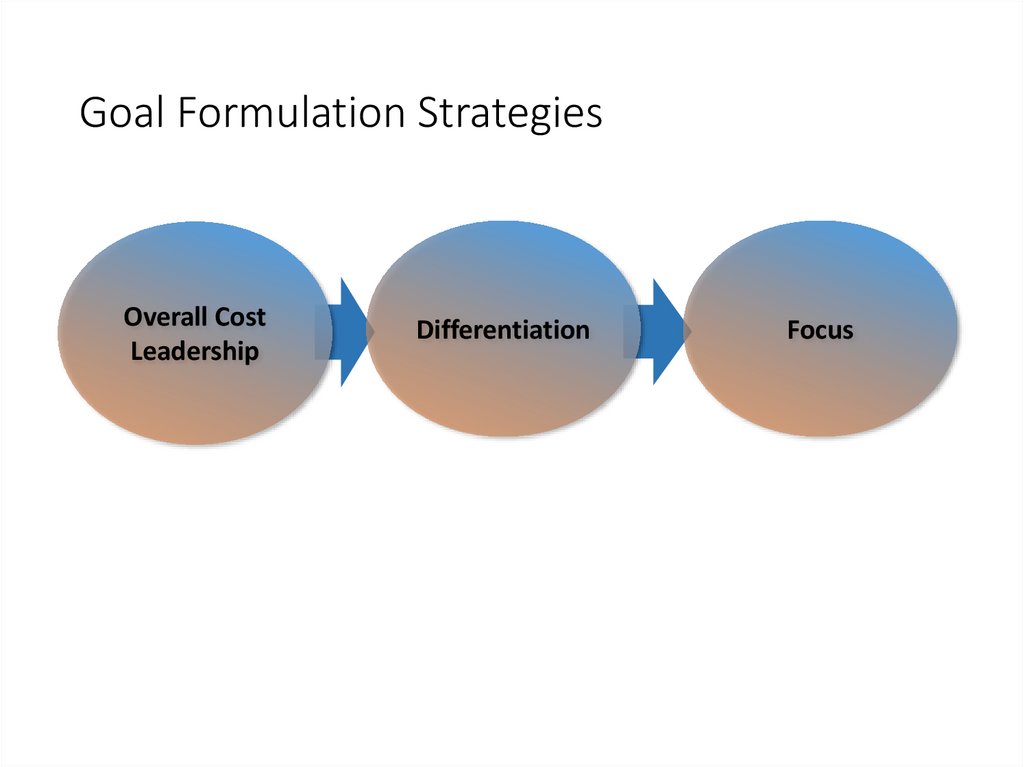
Goal Formulation StrategiesOverall Cost
Leadership
Differentiation
Focus
28.
Key TermsAnsoff product–market expansion
grid A matrix developed by cell, plotting
new products and existing products with
new products and existing products. The
grid provides strategic insights into growth
opportunities.
Conglomerate diversification strategy
A product growth strategy in which a
company seeks new businesses that have
no relationship to the company’s current
product line or markets.
Corporate mission statement A guide
strategy by which companies acquire
businesses supplying them with products
or services (e.g., a restaurant chain
purchasing a bakery).
to provide all the publics of a company
with a shared sense of purpose, direction,
and opportunity, allowing all to work
independently, yet collectively, toward the
organization’s goals.
Concentric diversification strategy
Forward integration A growth strategy
definition to look like this. Definition to
look like this.
by which companies acquire businesses
that are closer to the ultimate consumer,
such as a hotel acquiring a chain of travel
agents.
Backward integration A growth
29.
Key Terms (cont.)Horizontal diversification strategy A
Market segmentation The process of
product growth strategy whereby a
company looks for new products that could
appeal to current customers that are
technologically unrelated to its current line.
dividing a market into distinct groups of
buyers who have different needs,
characteristics, or behavior who might
require separate products or marketing
programs.
Horizontal integration A growth
strategy by which companies acquire
competitors.
Marketing opportunity An area of
need in which a company can perform
profitably.
Macroenvironmental forces
Demographic, economic, technological,
political, legal, social, and cultural factors.
Marketing strategy The marketing logic
Market development strategy Finding
by which the company hopes to create this
customer value and achieve these
profitable relationships.
and developing new markets for your
current products.
Microenvironmental forces
Customers, competitors, distribution
channels, and suppliers
30.
Key Terms (cont.)Product development Offering
Strategic planning The process of
modified or new products to current
markets.
developing and maintaining a strategic fit
between the organization’s goals and
capabilities and its changing marketing
opportunities.
Strategic alliances Relationships
between independent parties that agree to
cooperate but still retain separate
identities.
Strategic business units (SBUs) A single
business or collection of related businesses
that can be planned separately from the
rest of the company.
SWOT analysis Evaluates the company’s
overall strengths (S), weaknesses (W),
opportunities (O), and threats (T)



























 marketing
marketing business
business








