Similar presentations:
Collections
1.
COLLECTIONS2.
SoftServe ConfidentialAGENDA
• Arrays in Java
• Collections in Java
• List
• Set
• Map
3.
Arrays4.
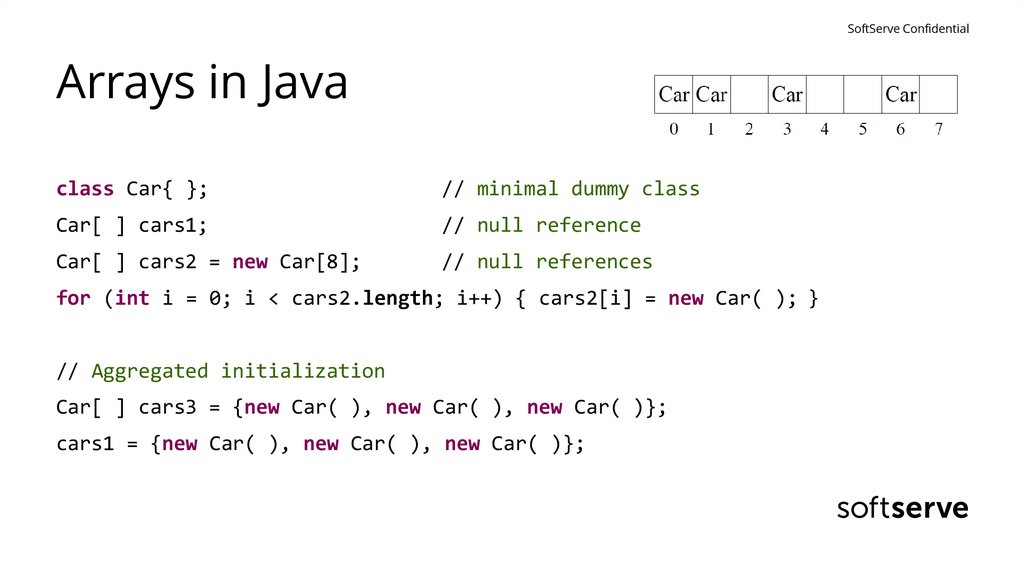
SoftServe ConfidentialArrays in Java
class Car{ };
// minimal dummy class
Car[ ] cars1;
// null reference
Car[ ] cars2 = new Car[8];
// null references
for (int i = 0; i < cars2.length; i++) { cars2[i] = new Car( ); }
// Aggregated initialization
Car[ ] cars3 = {new Car( ), new Car( ), new Car( )};
cars1 = {new Car( ), new Car( ), new Car( )};
5.
SoftServe ConfidentialArrays in Java
Most efficient way to hold references to objects.
Advantages
An array know the type it holds, i.e., compile-time type checking.
An array knows its size, i.e., ask for the length.
An array can hold primitive types directly.
Disadvantages
An array can only hold one type of objects (including primitives).
Arrays are fixed size.
How to add element inside?
6.
Collections7.
SoftServe ConfidentialJava Collection Framework
• The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to
store and manipulate the group of objects.
• Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a
data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and
deletion.
• Java Collection means a single unit of objects and its main advantage is
grow as necessary.
8.
SoftServe ConfidentialCollections in Java
Java Collection framework provides many interfaces (Set, List, Queue,
Deque) and classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue,
HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet).
All collections frameworks contain the following:
• interfaces
• implementations
• algorithms (there are the methods such as searching and sorting)
9.
SoftServe ConfidentialBenefits of collections
• reduces programming effort
• increases program speed and quality
• allows interoperability among unrelated APIs
• reduce effort to design new APIs
• helps to reuse the code
10.
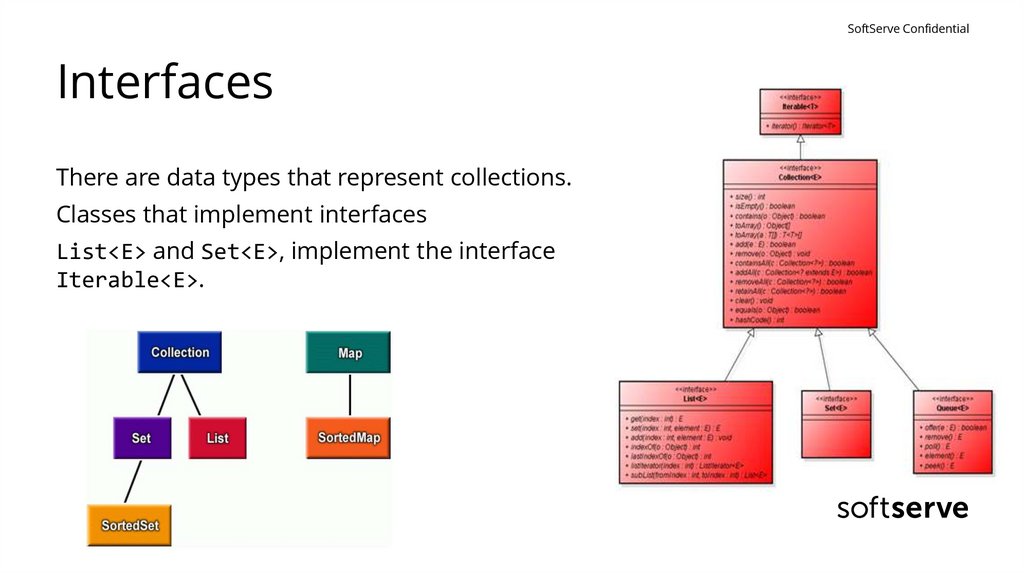
SoftServe ConfidentialInterfaces
There are data types that represent collections.
Classes that implement interfaces
List<E> and Set<E>, implement the interface
Iterable<E>.
11.
SoftServe ConfidentialCollections in Java
• List – a list of objects. Objects can be added to the list (the method add()), replace the
list (method set()), removed from the list (the method remove()), extract (method get()).
There is the ability to pass on the list of organizations with an iterator.
• Set – a set of objects. The same features as that of the List, but the object can be part of
set only once. Double addition of one and the same object in the set is not change the
set.
• Map – a map or associative array. In Map we add pair of objects (key, value).
Accordingly, the search operation is a key value. Adding a couple with an existing key in
the Map leads to the replacement, not to upload it. From Map can be obtain key and a
list of values.
12.
SoftServe ConfidentialCollections in Java
The interface Collection<E> defined methods:
• boolean add(E obj) – adds obj to the collection, it returns true, if the
object is added;
• boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) – adds all the elements;
• void clear() – removes all items from the collection;
• boolean contains(Object obj) – returns true, if the collection contains
an element of obj;
• boolean equals(Object obj) – returns true, if the collections are
equivalent;
13.
SoftServe ConfidentialCollections in Java
• boolean isEmpty() – returns true, if the collection is empty;
• Iterator<E> iterator() – retrieves the iterator;
• boolean remove(Object obj) – removes the object from the
collection;
• int size() – the number of items in the collection;
• Object[] toArray() – copies the collection to an array of objects;
• <T>T[] toArray(T a[]) – copies the elements of the collection to an
array of objects of a particular type.
14.
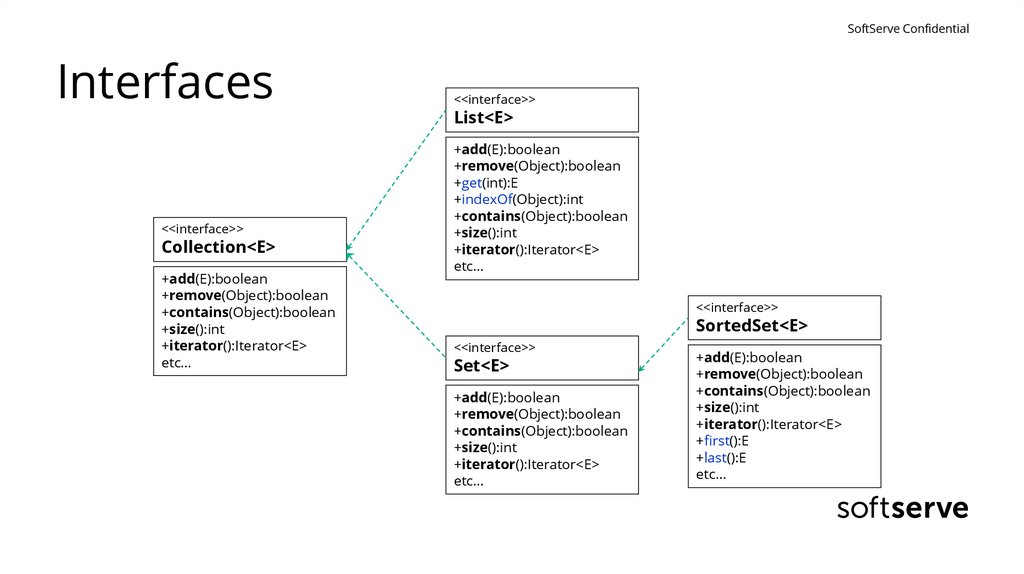
SoftServe ConfidentialInterfaces
<<interface>>
Collection<E>
+add(E):boolean
+remove(Object):boolean
+contains(Object):boolean
+size():int
+iterator():Iterator<E>
etc…
<<interface>>
List<E>
+add(E):boolean
+remove(Object):boolean
+get(int):E
+indexOf(Object):int
+contains(Object):boolean
+size():int
+iterator():Iterator<E>
etc…
<<interface>>
SortedSet<E>
<<interface>>
Set<E>
+add(E):boolean
+remove(Object):boolean
+contains(Object):boolean
+size():int
+iterator():Iterator<E>
etc…
+add(E):boolean
+remove(Object):boolean
+contains(Object):boolean
+size():int
+iterator():Iterator<E>
+first():E
+last():E
etc…
15.
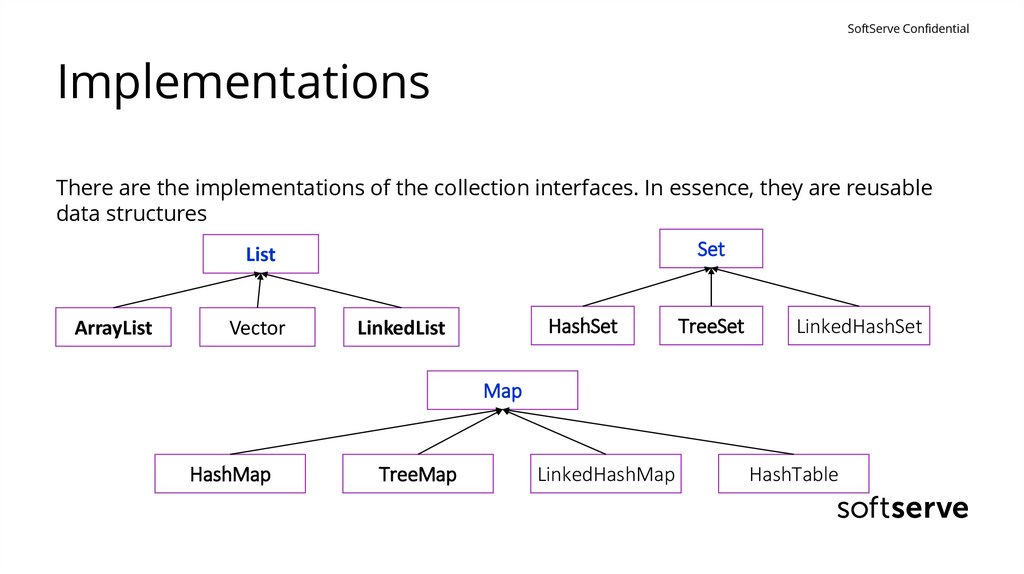
SoftServe ConfidentialImplementations
There are the implementations of the collection interfaces. In essence, they are reusable
data structures
Set
List
ArrayList
Vector
HashSet
LinkedList
TreeSet
LinkedHashSet
Map
HashMap
TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
HashTable
16.
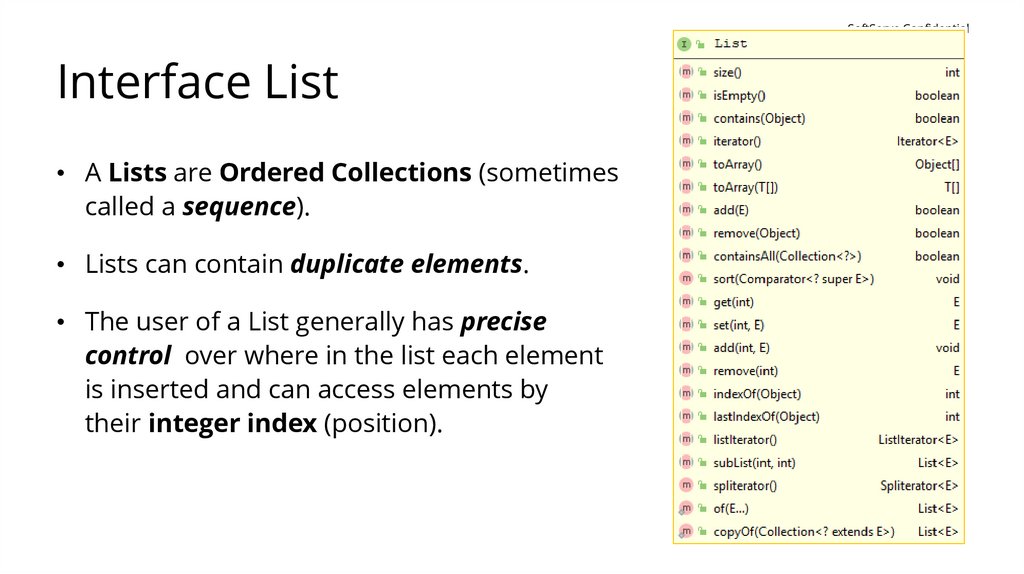
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface List
• A Lists are Ordered Collections (sometimes
called a sequence).
• Lists can contain duplicate elements.
• The user of a List generally has precise
control over where in the list each element
is inserted and can access elements by
their integer index (position).
17.
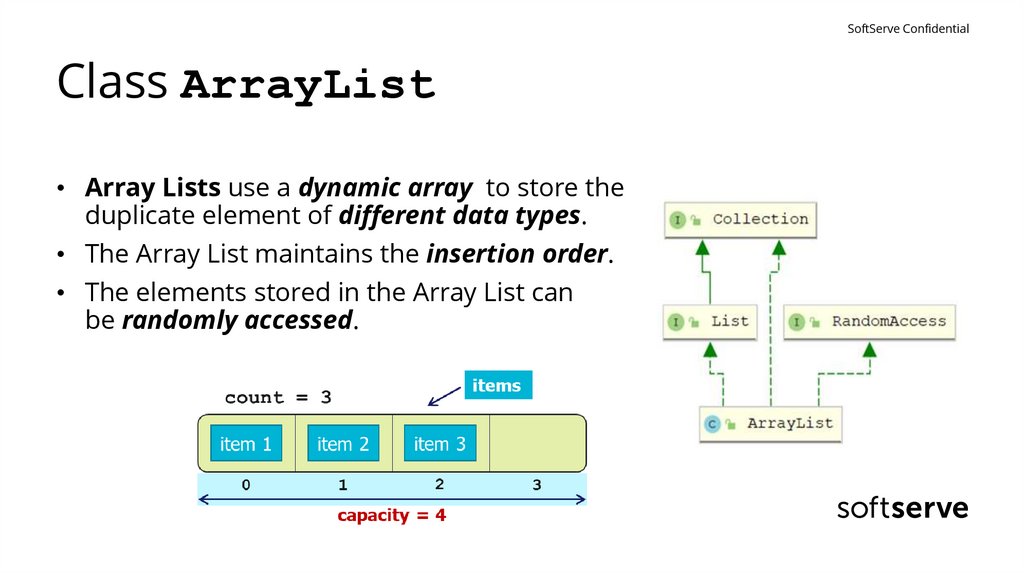
SoftServe ConfidentialClass ArrayList
• Array Lists use a dynamic array to store the
duplicate element of different data types.
• The Array List maintains the insertion order.
• The elements stored in the Array List can
be randomly accessed.
18.
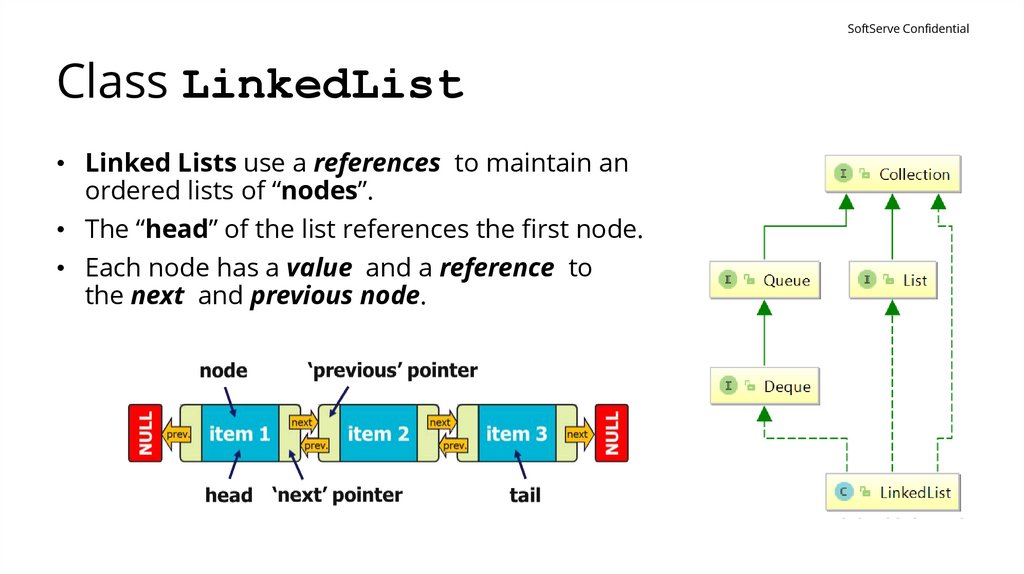
SoftServe ConfidentialClass LinkedList
• Linked Lists use a references to maintain an
ordered lists of “nodes”.
• The “head” of the list references the first node.
• Each node has a value and a reference to
the next and previous node.
19.
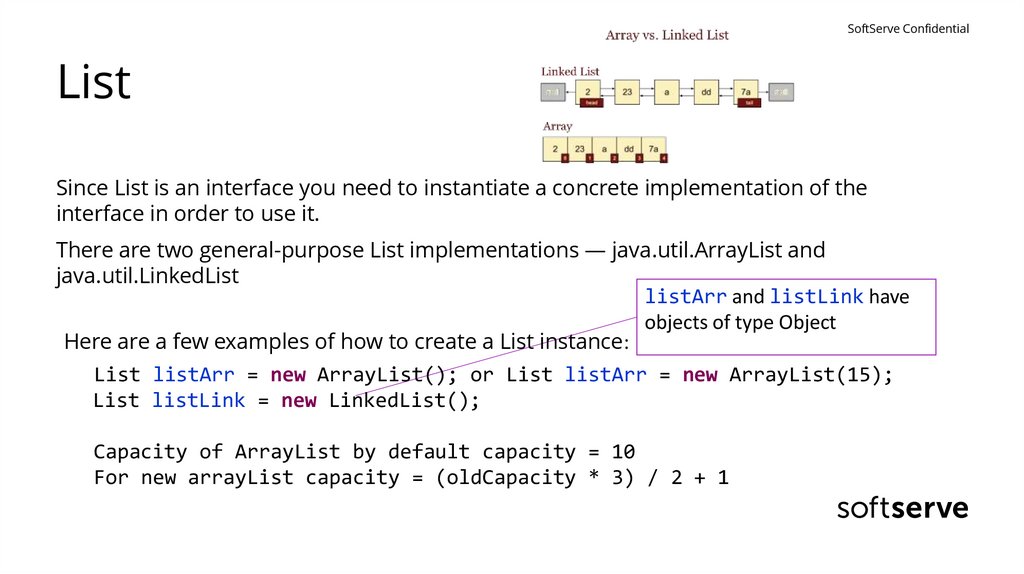
SoftServe ConfidentialList
Since List is an interface you need to instantiate a concrete implementation of the
interface in order to use it.
There are two general-purpose List implementations — java.util.ArrayList and
java.util.LinkedList
listArr and listLink have
objects of type Object
Here are a few examples of how to create a List instance:
List listArr = new ArrayList(); or List listArr = new ArrayList(15);
List listLink = new LinkedList();
Capacity of ArrayList by default capacity = 10
For new arrayList capacity = (oldCapacity * 3) / 2 + 1
20.
SoftServe ConfidentialList
Adding elements
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("First element");
list.add("Second element");
list.add(0, "One more first element");
Access through index
String element2 = list.get(1);
Access through new for-loop
for(Object object : list) {
String element = (String) object;
// do something
}
21.
SoftServe ConfidentialList
Removing Elements
remove(Object element) or remove(int index)
Cleaning a list
list.clear();
List size
int size = list.size();
Generic List
List<MyType> myType = new ArrayList<MyType>( );
myType.add(new MyType( ));
MyType my = myType.get(0);
22.
SoftServe ConfidentialList
LinkedList has the same functionality as the ArrayList.
Different way of implementation and efficiency of operations.
Adding to the LinkedList is faster
Pass through the list is almost as effective as the ArrayList,
Arbitrary removal from the list is slower than ArrayList.
23.
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface Set
• A Sets are Unordered Collection that cannot
contain duplicate elements.
• This interface models the mathematical set
abstraction and is used to represent sets, such
as the cards comprising a poker hand, the
courses making up a student's schedule, or
the processes running on a machine.
24.
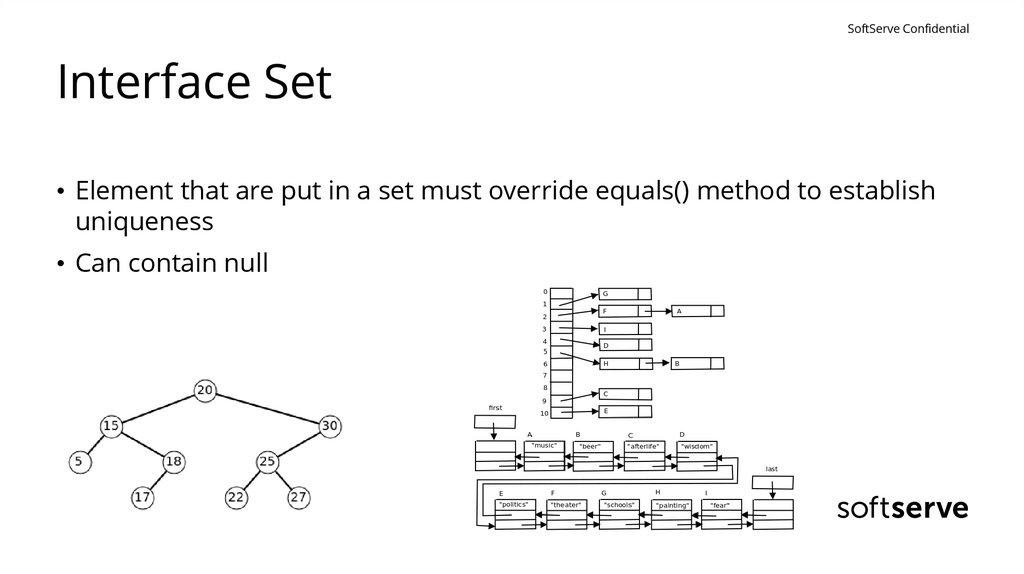
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface Set
• Element that are put in a set must override equals() method to establish
uniqueness
• Can contain null
25.
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface Set
• The HashSet class
• Uses Hash Tables to speed up finding, adding, and removing
elements.
• The TreeSet class
• Uses a Binary Tree to speed up finding, adding, and removing
elements.
• The LinkedHashSet class
• Uses Hash Tables to storing elements and provides the order of
insertion.
26.
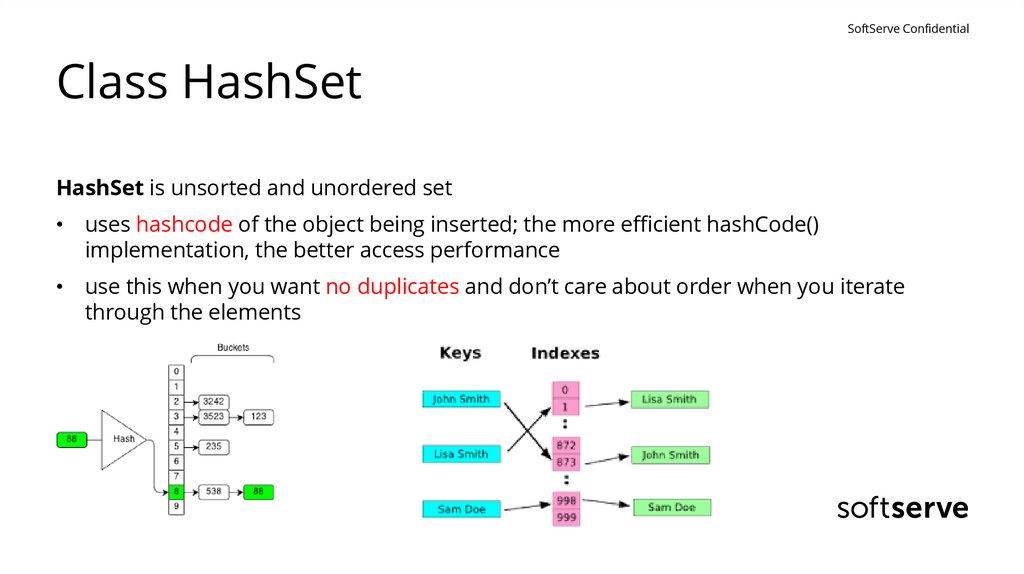
SoftServe ConfidentialClass HashSet
HashSet is unsorted and unordered set
• uses hashcode of the object being inserted; the more efficient hashCode()
implementation, the better access performance
• use this when you want no duplicates and don’t care about order when you iterate
through the elements
27.
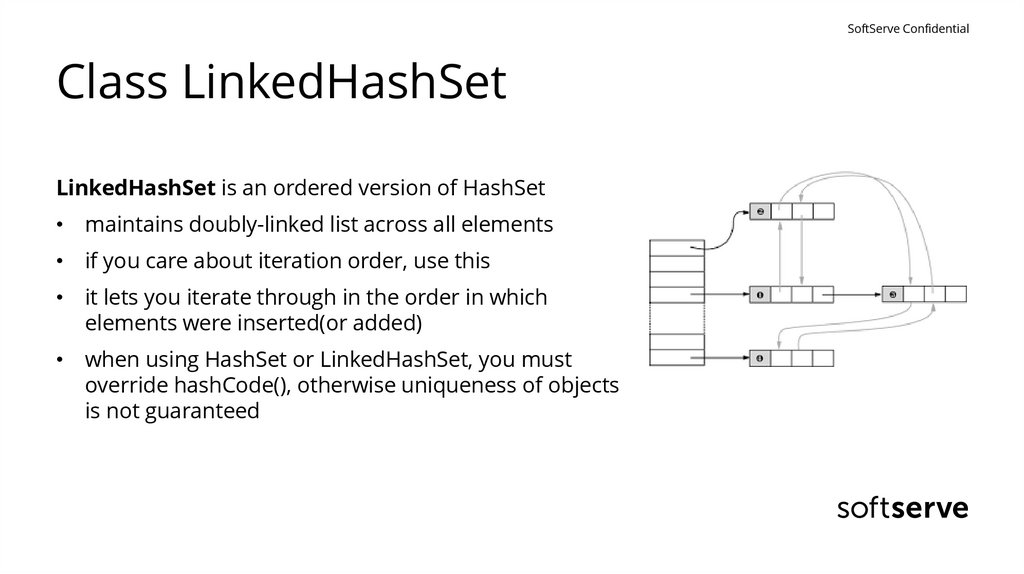
SoftServe ConfidentialClass LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet is an ordered version of HashSet
• maintains doubly-linked list across all elements
• if you care about iteration order, use this
• it lets you iterate through in the order in which
elements were inserted(or added)
• when using HashSet or LinkedHashSet, you must
override hashCode(), otherwise uniqueness of objects
is not guaranteed
28.
SoftServe ConfidentialClass TreeSet
TreeSet is one of the two sorted collections (the other being
TreeMap)
• uses Red-Black tree structure (special binary search tree
with minimum possible height)
• guarantees that the elements will be in ascending order
according to natural order
• lets you specify your own ordering rules by using
Comparable or Comparator as of java 6, TreeSet also
implements NavigableSet
29.
SoftServe ConfidentialExample
import java.util.*;
public class FindDups {
public static void main(String args[ ]){
Set s = new HashSet( );
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
if (!s.add(args[i]))
System.out.println("Duplicate detected: " + args[i]);
}
System.out.println(s.size( ) + " distinct words detected: " + s);
}
}
30.
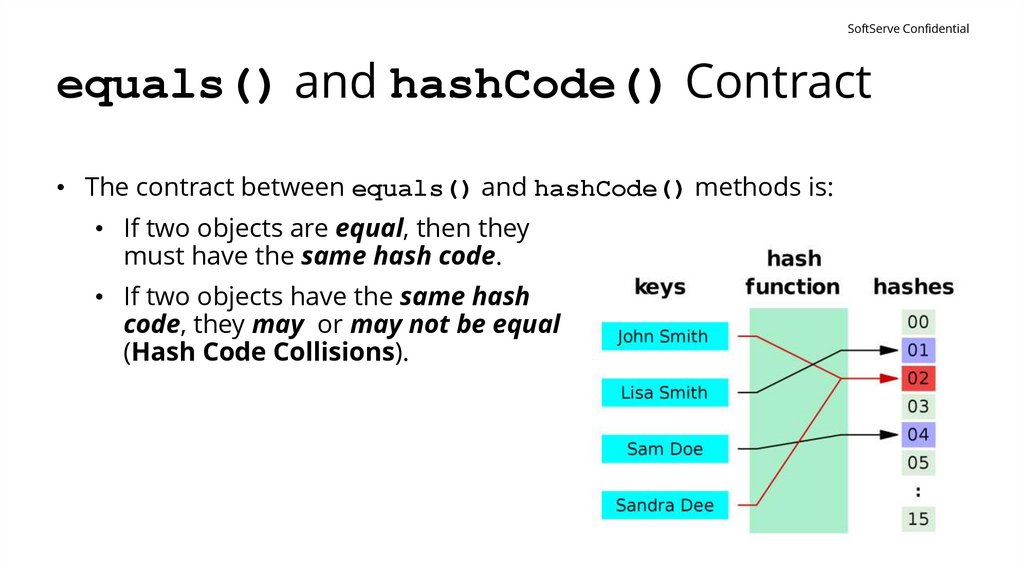
SoftServe Confidentialequals() and hashCode() Contract
• The contract between equals() and hashCode() methods is:
• If two objects are equal, then they
must have the same hash code.
• If two objects have the same hash
code, they may or may not be equal
(Hash Code Collisions).
31.
SoftServe ConfidentialIterator
Iterator – a helper object. Used to iterate over collection of objects.
Iterators are based on the interface
• boolean hasNext() – checks whether there are elements in the collection
• Object next() – shows the next item in the collection
• void remove() – removes the last selected item from the collection
Collection interface has a method Iterator iterator();
32.
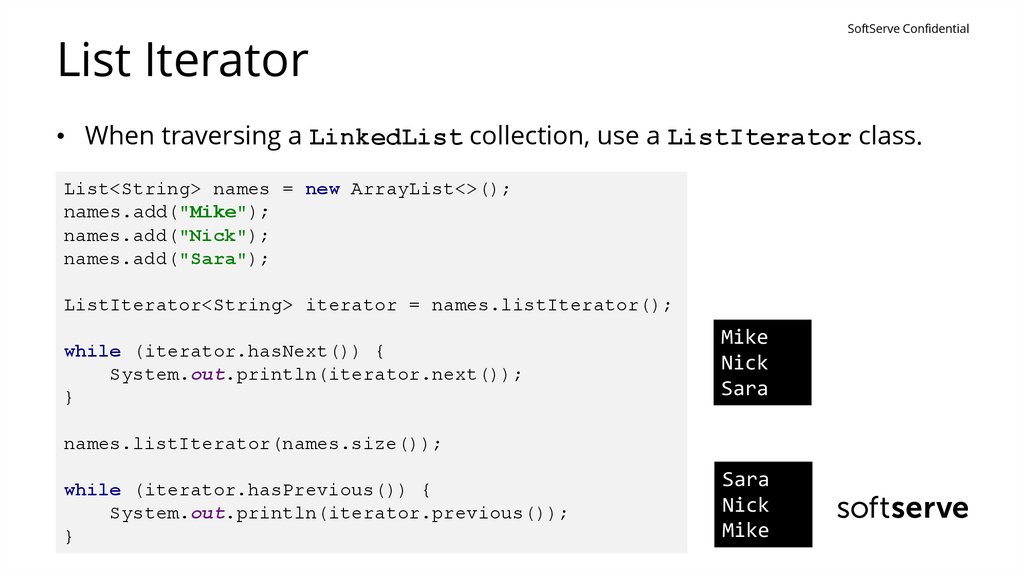
SoftServe ConfidentialList Iterator
• When traversing a LinkedList collection, use a ListIterator class.
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("Mike");
names.add("Nick");
names.add("Sara");
ListIterator<String> iterator = names.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Mike
Nick
Sara
names.listIterator(names.size());
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.println(iterator.previous());
}
Sara
Nick
Mike
33.
SoftServe ConfidentialSet Iterator
• Iterators are also used when processing sets, but sets don’t support
ListIterator class.
• Instead, for sets you must use Iterator class.
Set<String> names = new HashSet<>();
names.add("Mike");
names.add("Nick");
names.add("Sara");
Iterator<String> iterator = names.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Mike
Nick
Sara
34.
SoftServe ConfidentialIterator and Loop
• Iterators are often used in while and “for-each” loops.
• hasNext() method returns true if there is a next element.
• next() method returns a reference to the value of the next element.
Set<String> names = new HashSet<>();
names.add("Mike");
names.add("Nick");
names.add("Sara");
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
Mike
Nick
Sara
• Where is the iterator in the “for-next” loop?
It is used “behind the scenes”.
35.
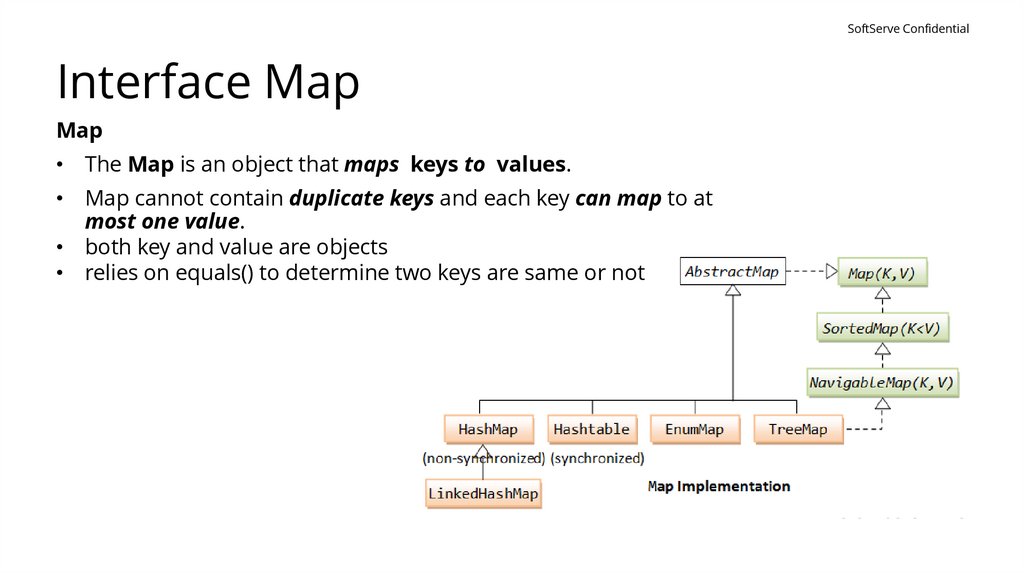
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface Map
Map
• The Map is an object that maps keys to values.
• Map cannot contain duplicate keys and each key can map to at
most one value.
• both key and value are objects
• relies on equals() to determine two keys are same or not
36.
SoftServe ConfidentialInterface Map
• A Map stores keys, values, and the
associations between them.
• Keys - provides an easy way to
represent an object.
• Values - the actual object that is
associated with the key.
37.
SoftServe ConfidentialMap
The most commonly used Map implementations are HashMap and TreeMap.
Map mapA = new HashMap();
Map mapB = new TreeMap();
Adding elements
mapA.put("key1", "one");
mapA.put("key2", "two");
mapA.put(1,3);
mapA.put(student1, room1);
String value2 = (String) mapA.get("key2");
Removing element
mapA.remove(Object key);
38.
SoftServe ConfidentialClasses HashMap and TreeMap
• A Map allows you to associate elements from a key set with elements
from a value collection.
• The HashMap and TreeMap classes both implement the Map interface.
Book book = new Book();
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
Map<String, Book> books = new HashMap<>();
books.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), book);
books.put(uuid.toString(), new Book());
books.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), book);
book = books.get(uuid);
39.
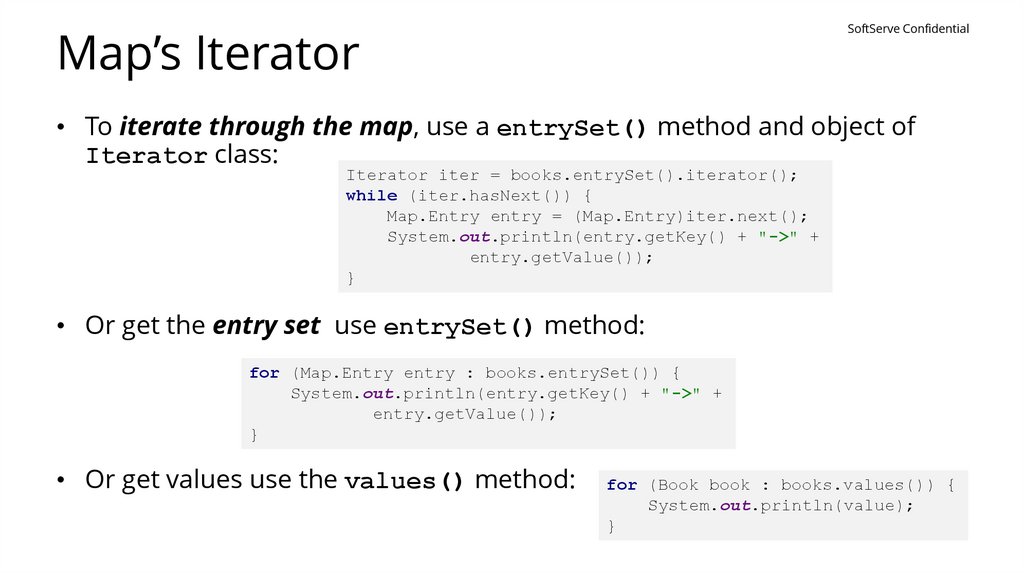
Map’s IteratorSoftServe Confidential
• To iterate through the map, use a entrySet() method and object of
Iterator class:
Iterator iter = books.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "->" +
entry.getValue());
}
• Or get the entry set use entrySet() method:
for (Map.Entry entry : books.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "->" +
entry.getValue());
}
• Or get values use the values() method:
for (Book book : books.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
40.
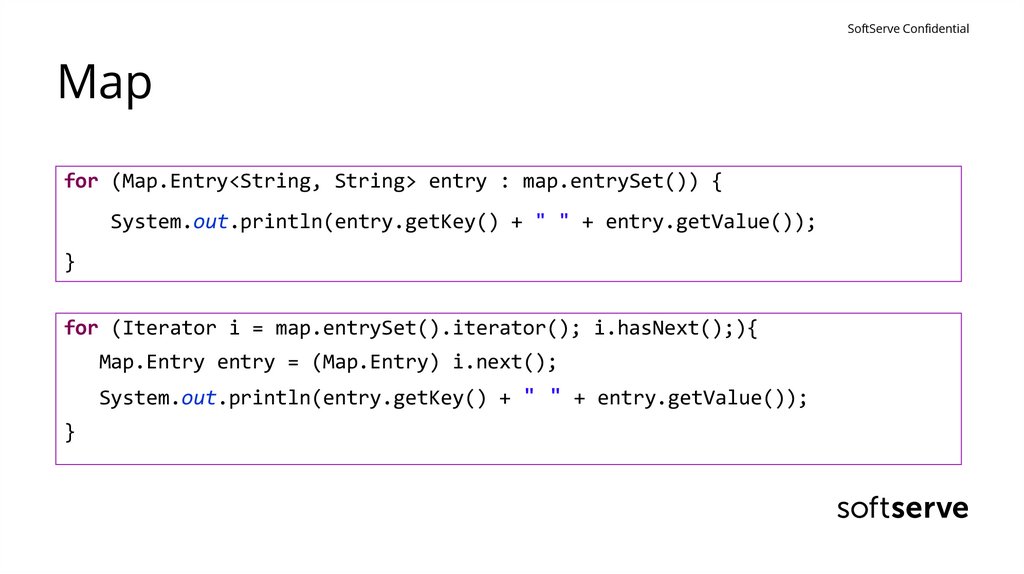
SoftServe ConfidentialMap
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
for (Iterator i = map.entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext();){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) i.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " " + entry.getValue());
}
41.
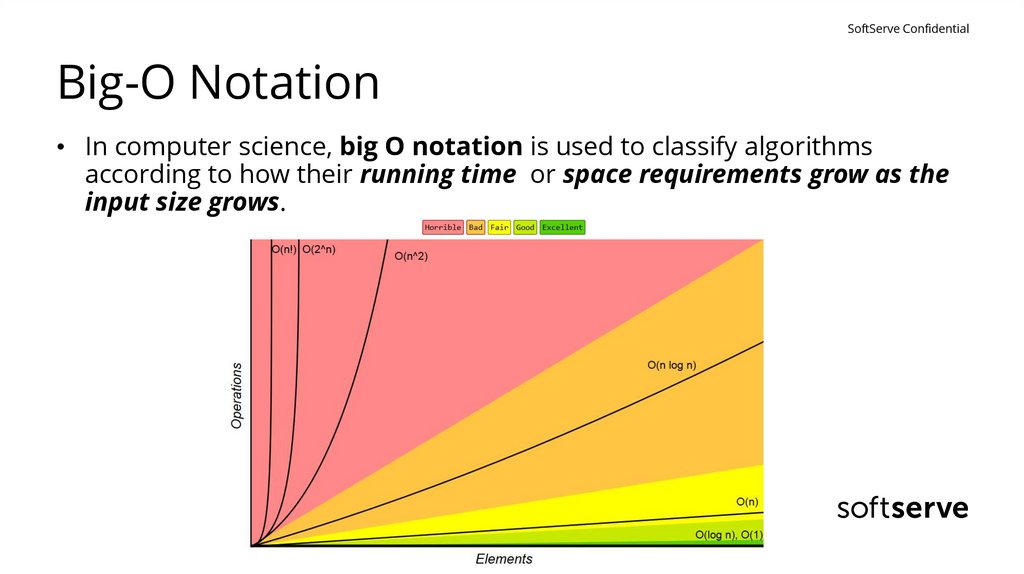
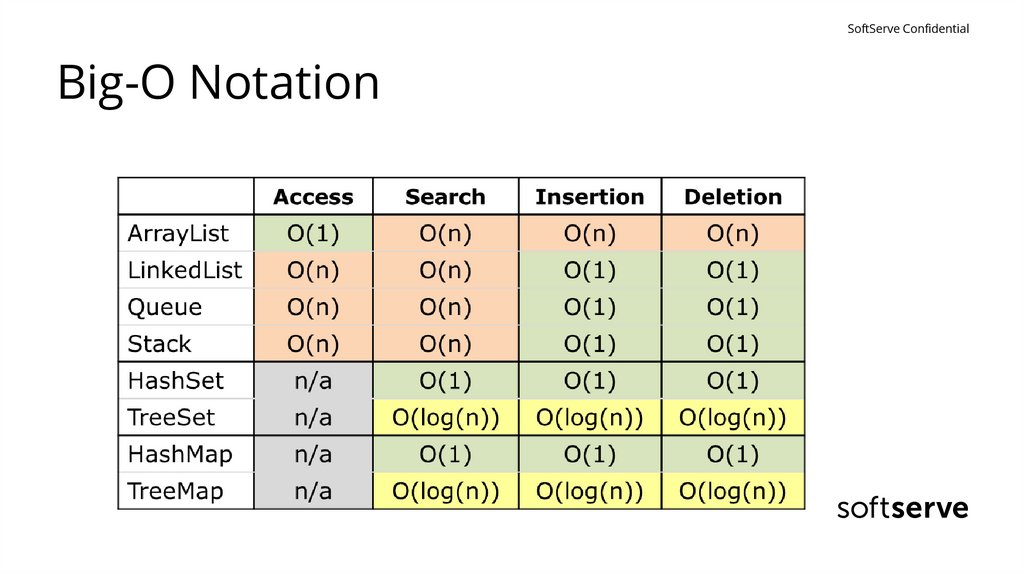
SoftServe ConfidentialBig-O Notation
• In computer science, big O notation is used to classify algorithms
according to how their running time or space requirements grow as the
input size grows.
42.
SoftServe ConfidentialBig-O Notation
43.
SoftServe ConfidentialPractical task 1
Declare collection myCollection of 10 integers and fill it (from the console or random).
• Find and save in list newCollection all positions of element more than 5 in the
collection. Print newCollection
• Remove from collection myCollection elements, which are greater then 20. Print
result
• Insert elements 1, -3, -4 in positions 2, 8, 5. Print result in the format: “position – xxx,
value of element – xxx”
• Sort and print collection
Use one or more of the next Collections: List, ArrayList, LinkedList
44.
SoftServe ConfidentialPractical task 2
In the main() method declare map employeeMap of pairs <Integer, String>.
• Add to employeeMap seven pairs (ID, name) of some persons. Display the map on the
screen.
• Ask user to enter ID, then find and write corresponding name from your map. If you can't
find this ID - say about it to user (use function containsKey()).
• Ask user to enter name, verify than you have name in your map and write corresponding
ID. If you can't find this name - say about it to user (use function containsValue()).
45.
SoftServe ConfidentialHomework
1. Write parameterized methods union(Set set1, Set set2) and intersect(Set set1, Set set2),
realizing the operations of union and intersection of two sets. Test the operation of
these techniques on two pre-filled sets.
2. Create map personMap and add to it ten persons of type <String, String> (lastName,
firstName).
Output the entities of the map on the screen.
There are at less two persons with the same firstName among these 10 people?
Remove from the map person whose firstName is ”Orest” (or other). Print result.
46.
SoftServe ConfidentialHomework
3. Write class Student that provides information about the name of the student and his
course. Class Student should consist of
a) properties for access to these fields
b) constructor with parameters
c) method printStudents (List students, Integer course), which receives a list of students
and the course number and prints to the console the names of the students from
the list, which are taught in this course (use an iterator)
d) methods to compare students by name and by course
e) In the main() method
• declare List students and add to the list five different students
• display the list of students ordered by name
• display the list of students ordered by course.





























 programming
programming








